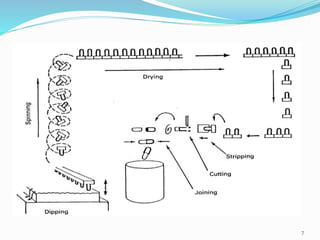
The document provides a comprehensive overview of gelatin capsules, including their design, manufacturing process, advantages, and disadvantages. It distinguishes between hard and soft gelatin capsules, detailing their content, suitability for certain drugs, and production techniques. Additionally, it discusses quality evaluation methods, packing, and special applications such as enteric coating and sustained release formulations.