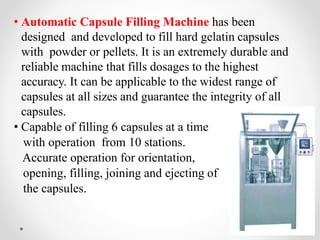
The document provides a comprehensive overview of capsules, including types, advantages, and disadvantages of hard and soft gelatin capsules. It details the manufacturing processes, filling methods, and evaluation tests for capsules, along with their constituents and packaging requirements. The information is aimed at understanding capsule formulations and their applications in pharmaceuticals.