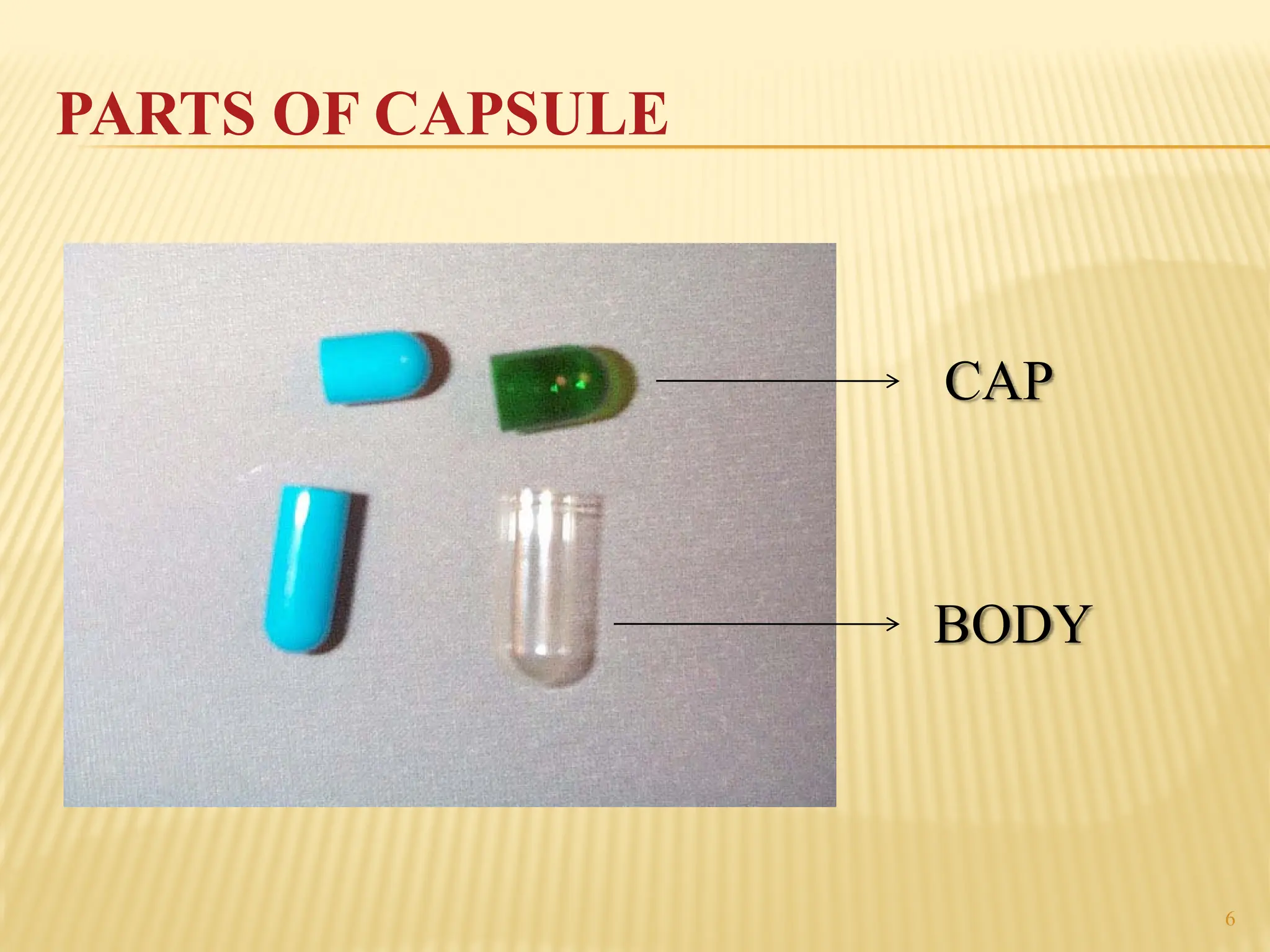
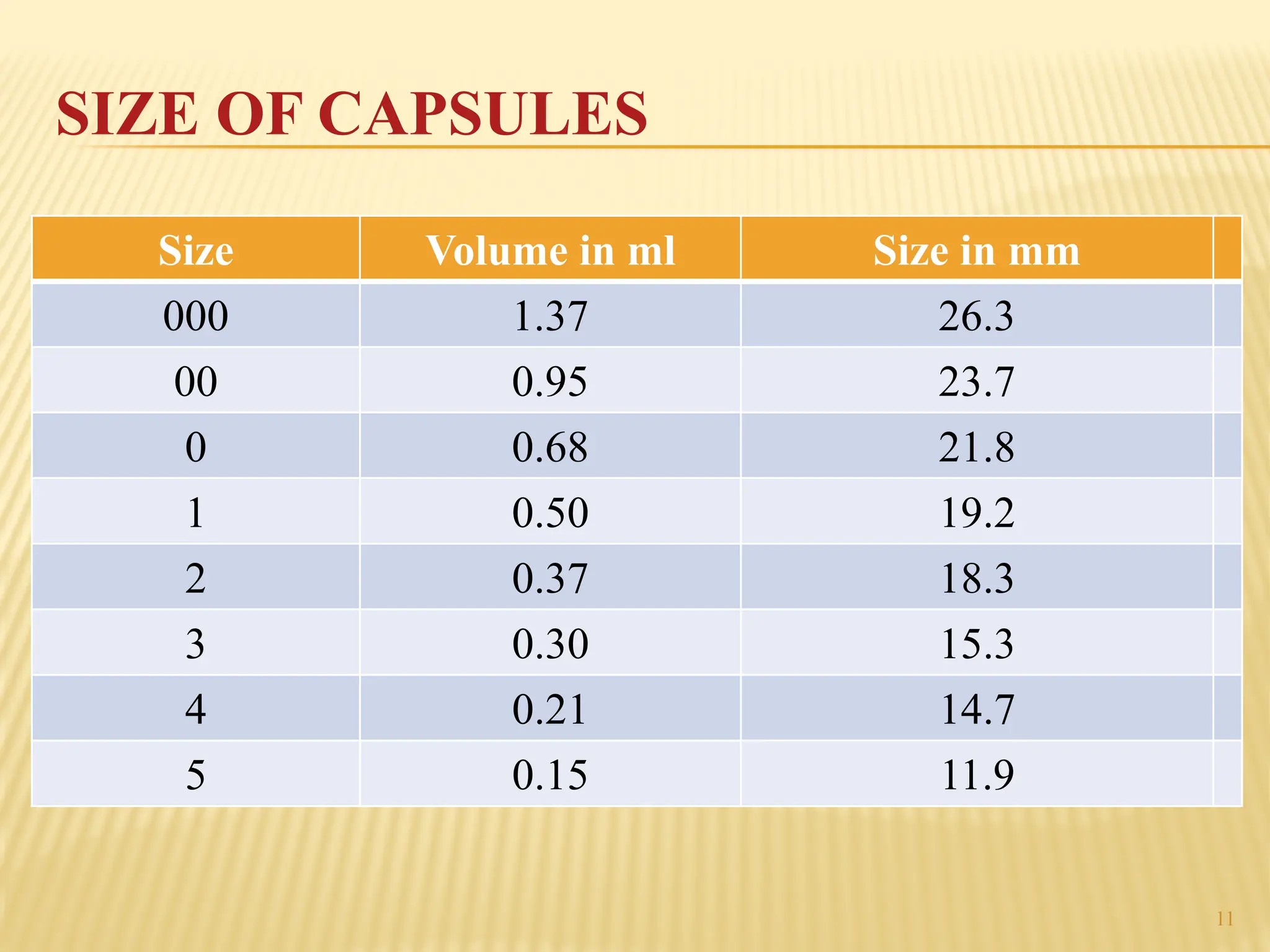
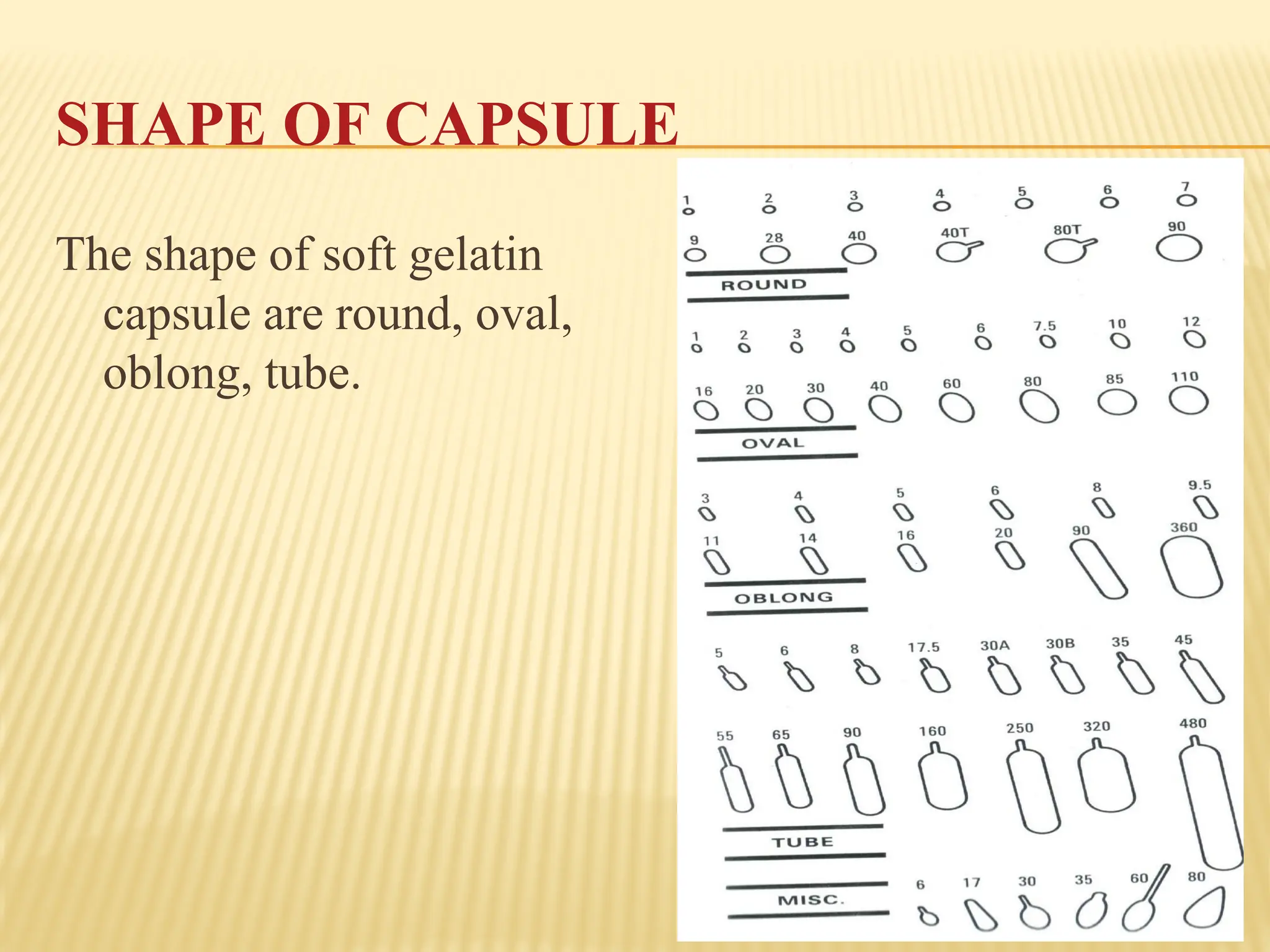
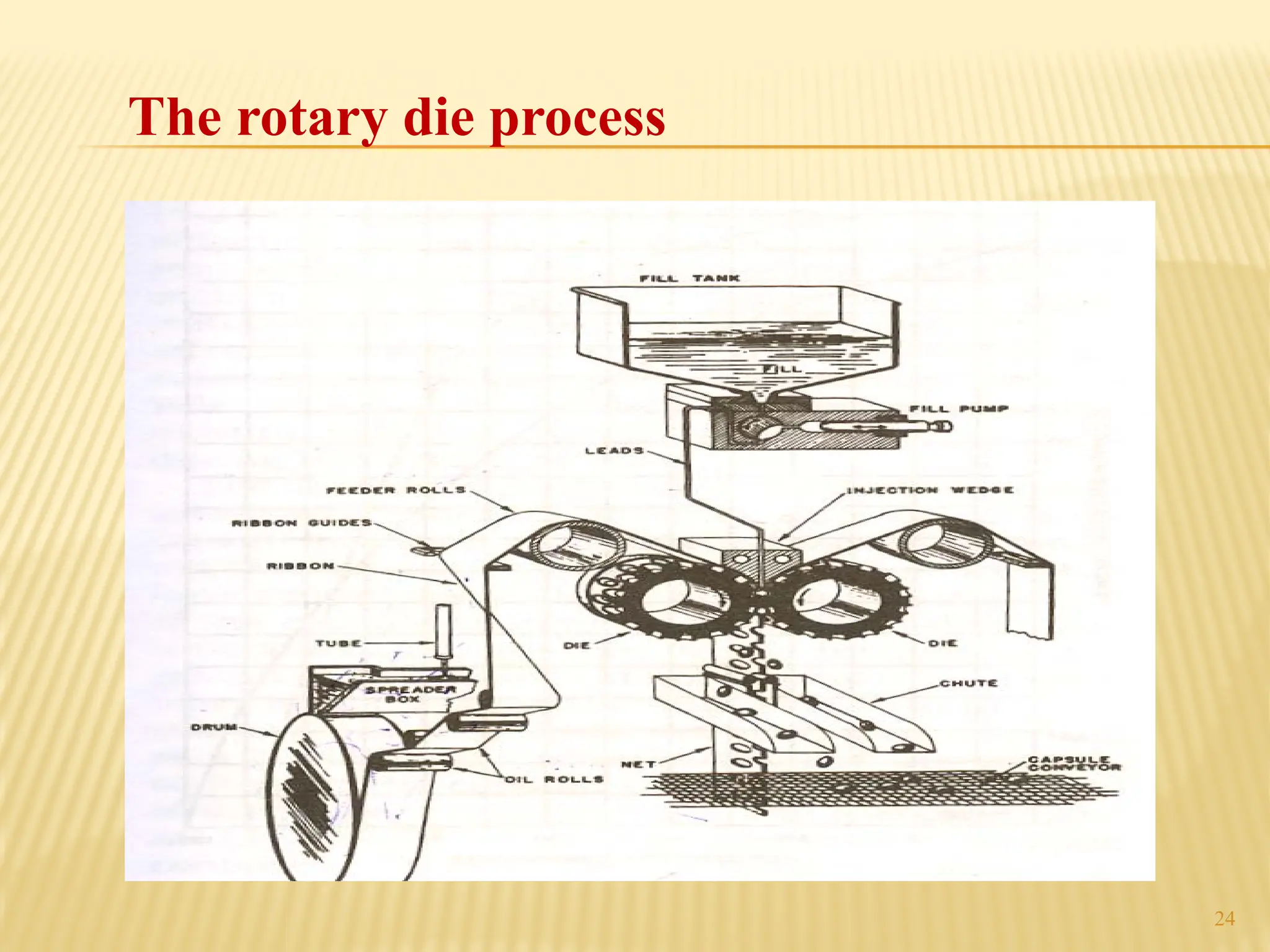
The document provides a detailed overview of gelatin capsules, including their types, manufacturing processes, and specifications. It covers hard and soft gelatin capsules, detailing materials used, shapes, filling machines, and methods of production. Additionally, it discusses important specifications such as bloom strength, viscosity, and evaluation tests for quality assurance.