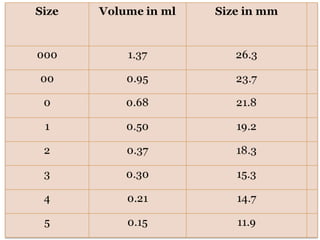
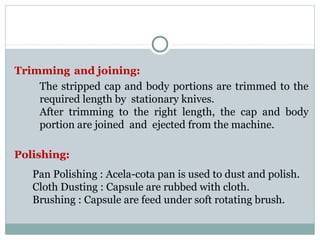
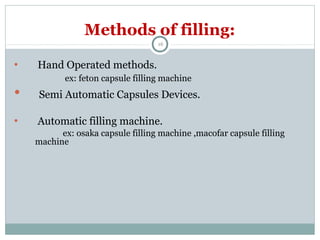
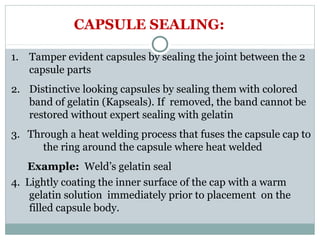
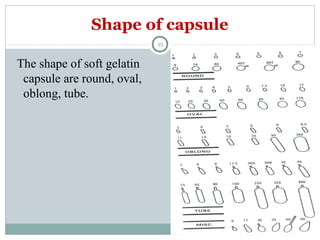
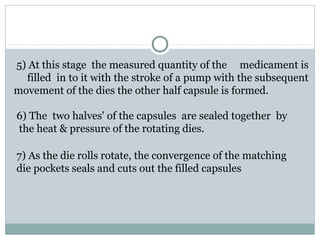
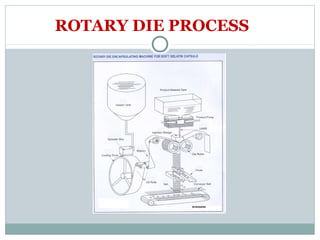
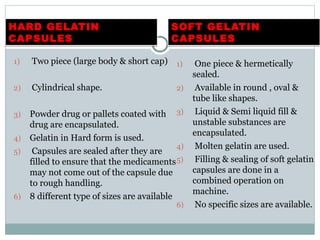
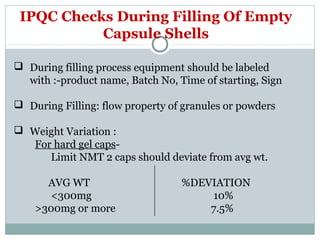
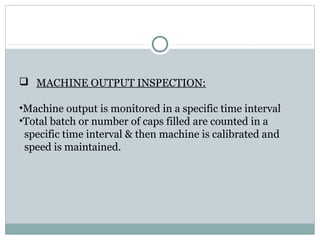
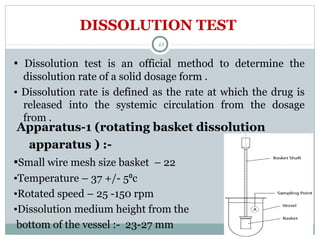
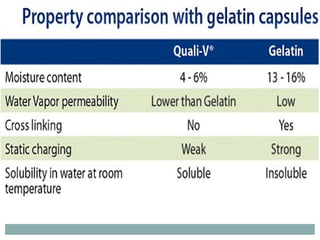
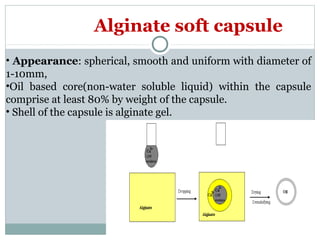
Hard and soft gelatin capsules are commonly used solid oral dosage forms. Recent advancements include non-gelatin capsules made from HPMC or starch which provide alternatives for people with gelatin allergies. The manufacturing process for hard gelatin capsules involves dipping pins in gelatin solution to form shells, drying the shells, stripping them from the pins, trimming, joining, and polishing. Soft gelatin capsules are manufactured using various processes like plate, rotary die, or reciprocating die methods. Quality control checks are performed during manufacturing and evaluation includes testing for stability, content uniformity, disintegration, and dissolution.