Embed presentation
Download to read offline


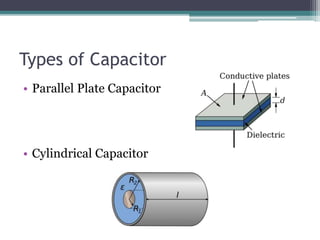

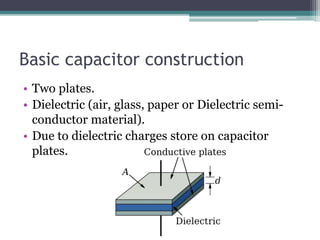


A capacitor is a device that stores electric charge between two conductive plates separated by an insulator. It consists of two parallel plates with a non-conductive material, such as glass or air, in between. Capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store charge, and it is directly proportional to the charge stored and inversely proportional to the voltage. Capacitors come in different shapes and sizes and are used in a variety of electronic applications such as audio systems, sensing devices, and separating alternating and direct current.







