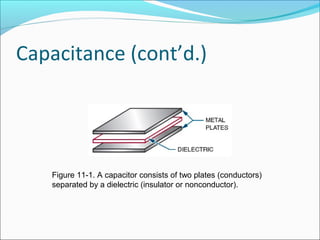
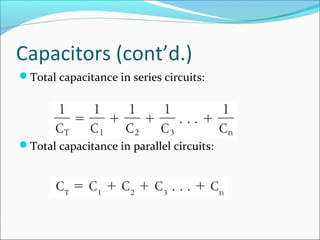
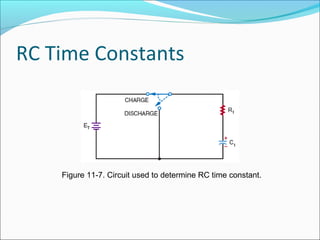
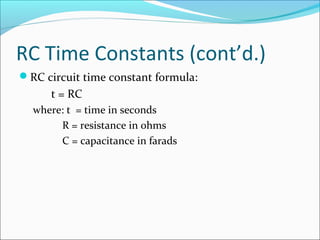
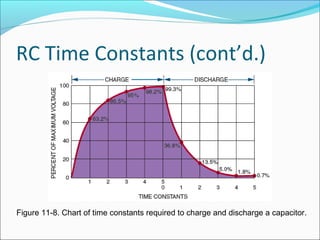
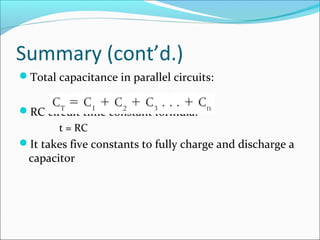
Capacitance refers to the ability of a capacitor to store electrical energy in an electrostatic field. A capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. The factors that affect capacitance include the area and distance between plates and the dielectric material. There are different types of capacitors including electrolytic, paper, plastic, ceramic, and variable capacitors. RC circuits have a time constant, t, equal to the product of the resistance, R, and capacitance, C, that describes the time required for a capacitor to charge or discharge in the circuit.