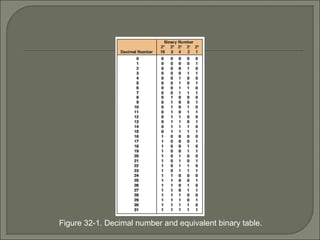
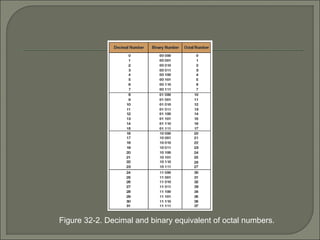
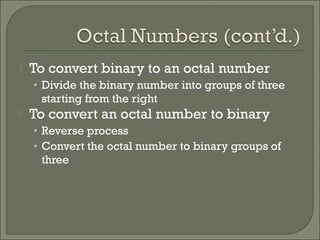
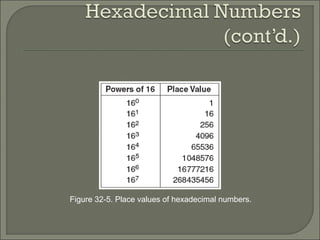
The document discusses the binary number system and how to convert between binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal numbers. It also covers binary-coded decimal (BCD). The binary system uses only two digits, 0 and 1. To convert a decimal number to binary, you divide the decimal by 2 and write down the remainders in reverse order. Octal and hexadecimal break binary down into groups of 3 and 4 digits respectively to make large binary numbers easier to read and enter. BCD represents each decimal digit with a 4-bit code to allow easy conversion between decimal and binary.