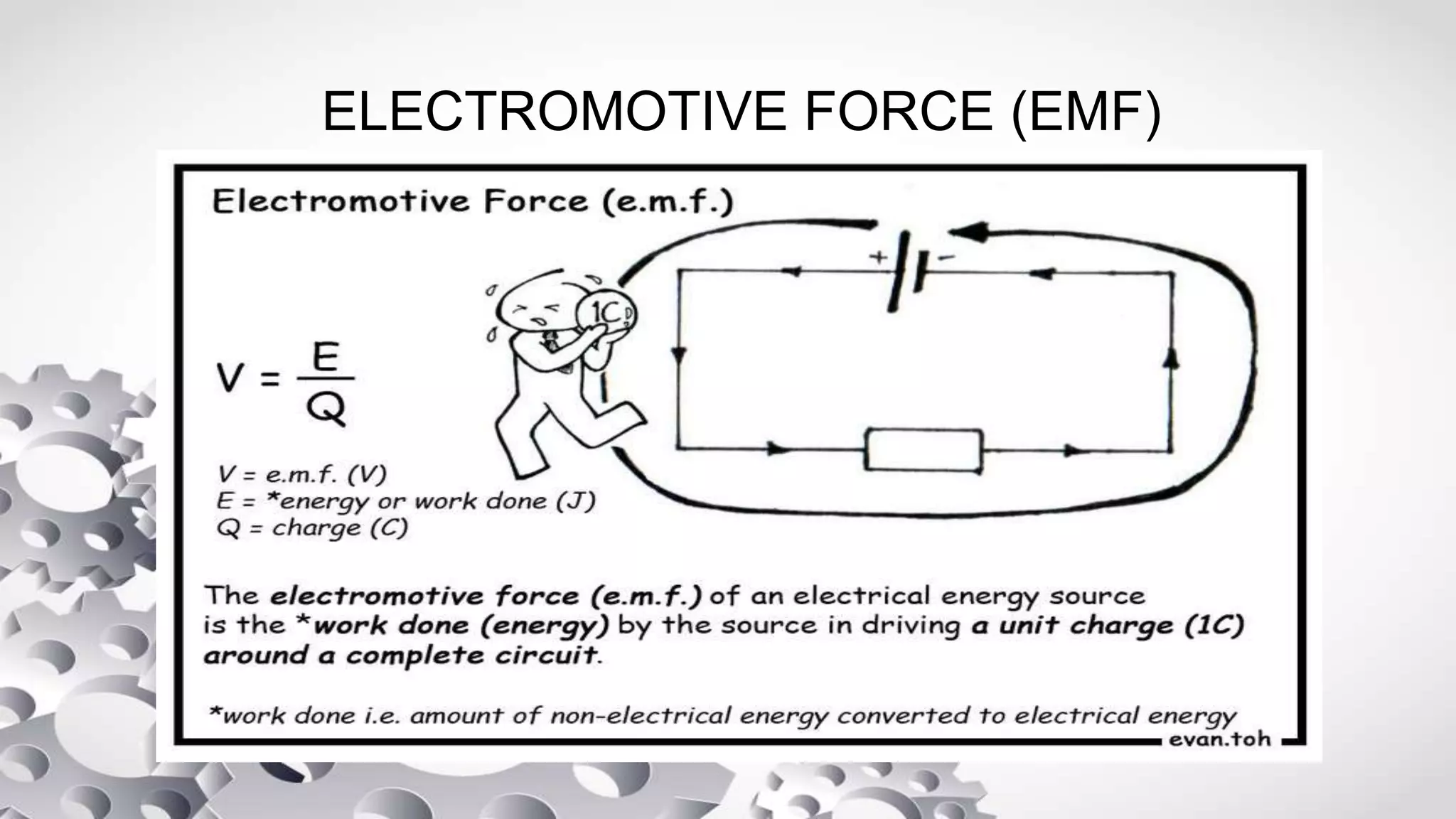
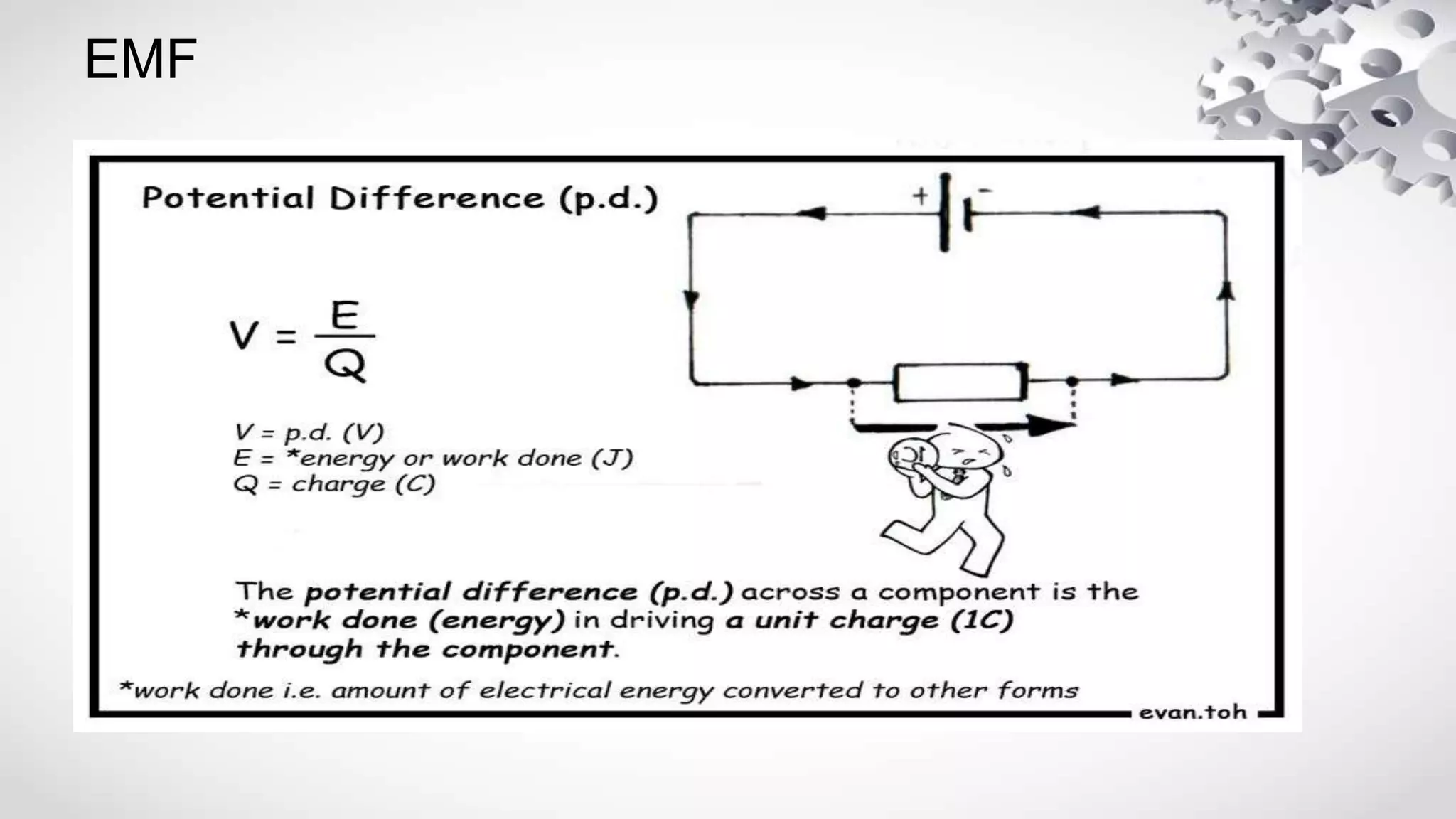
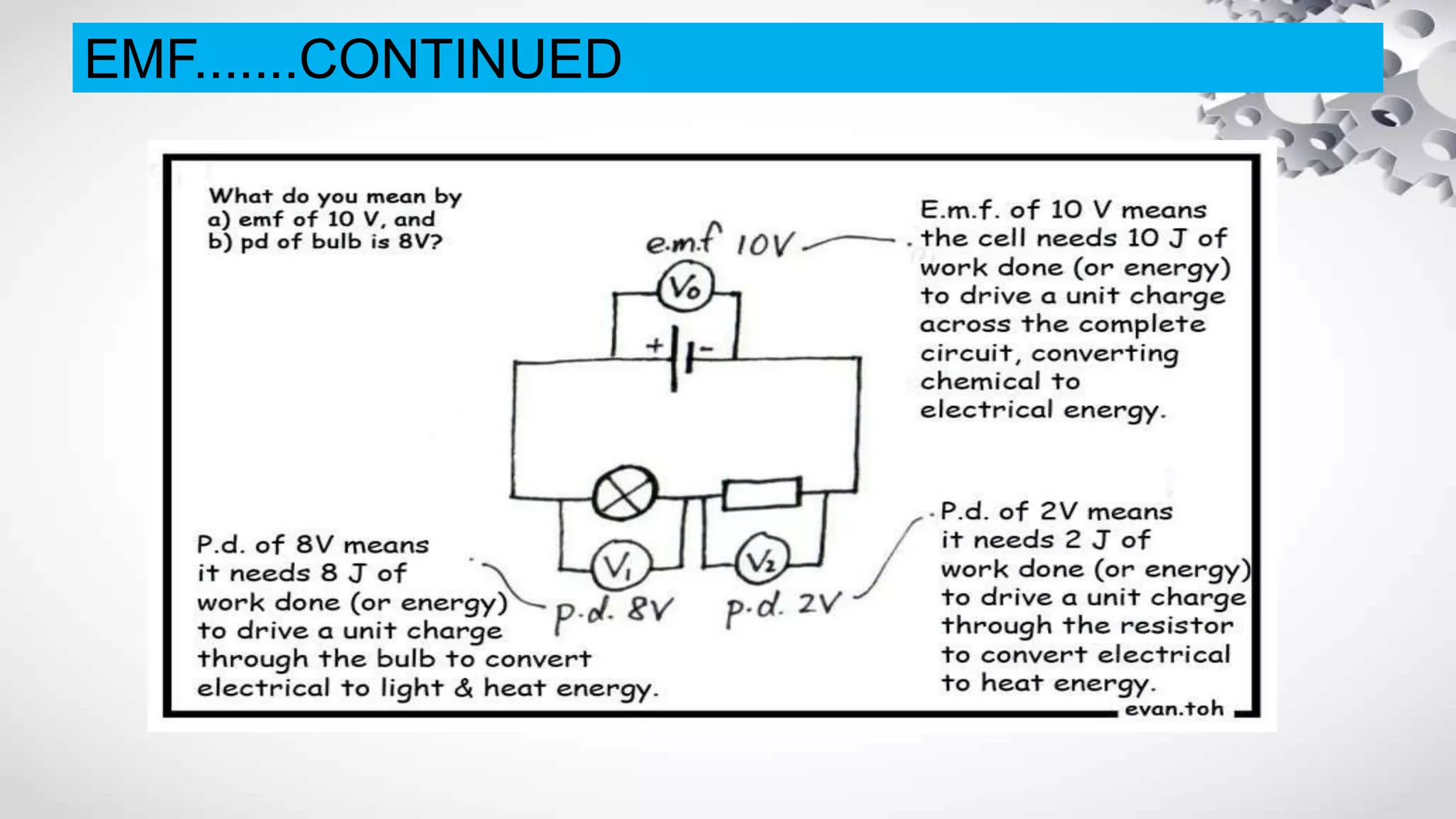
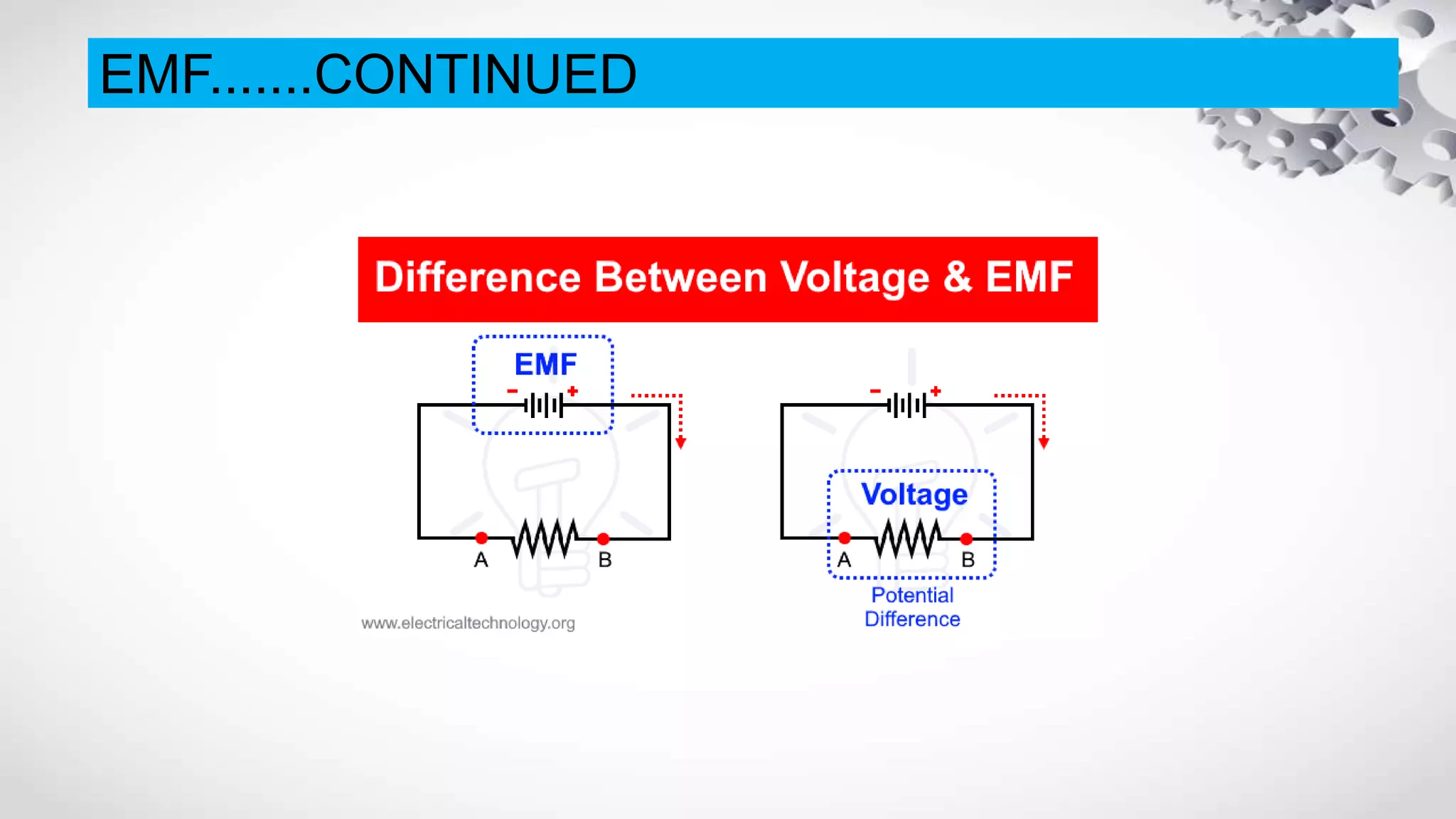
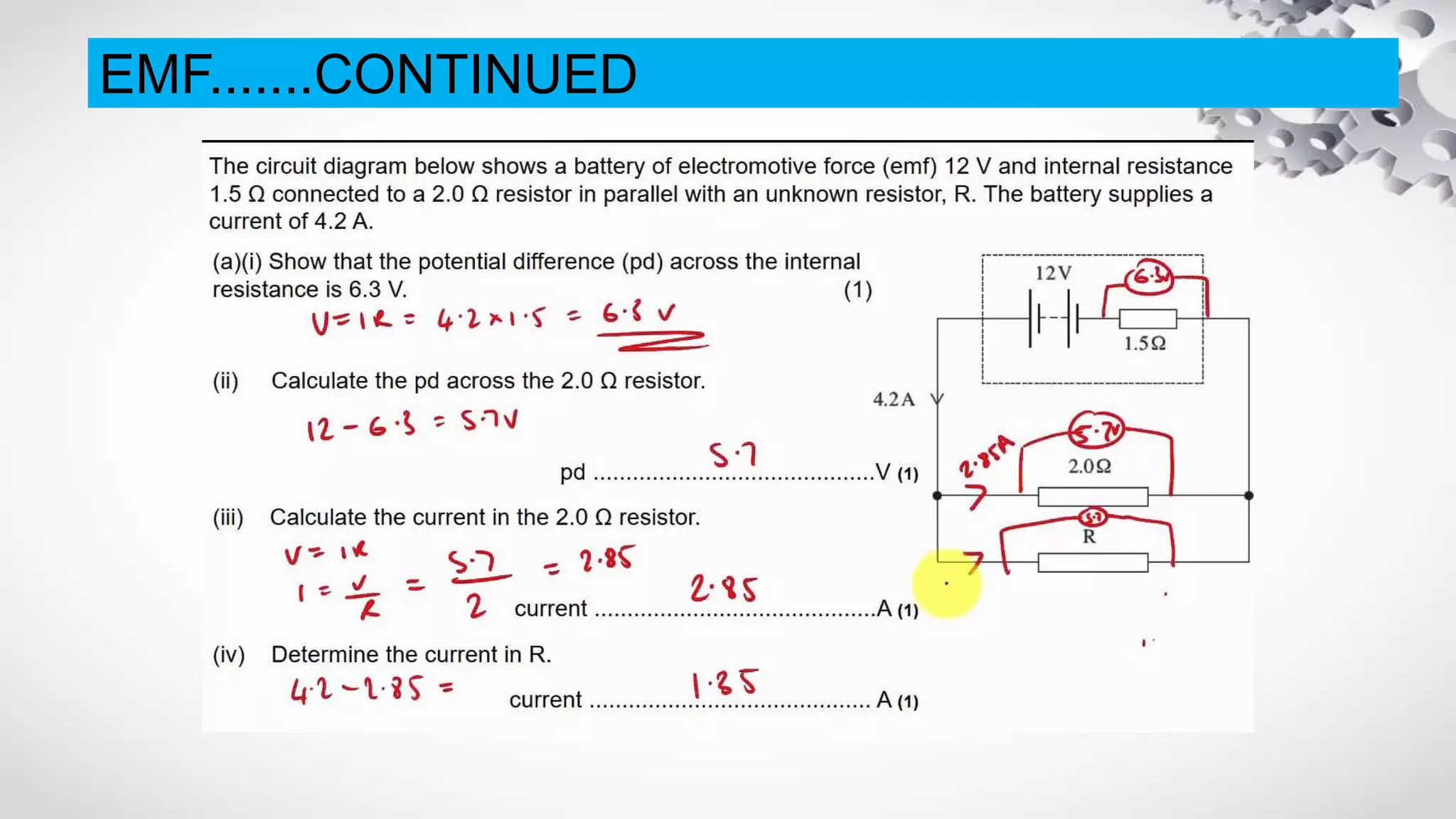
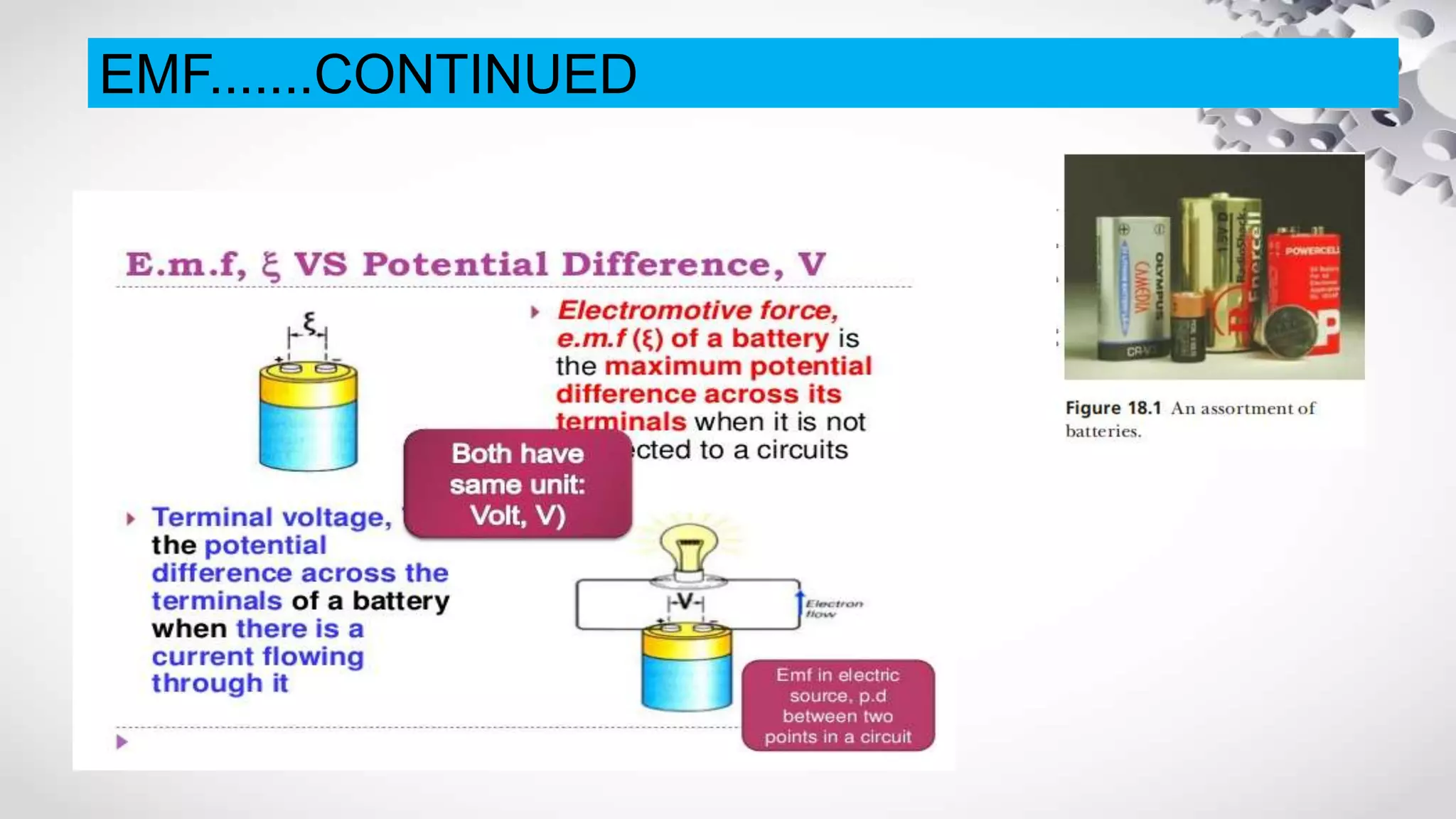
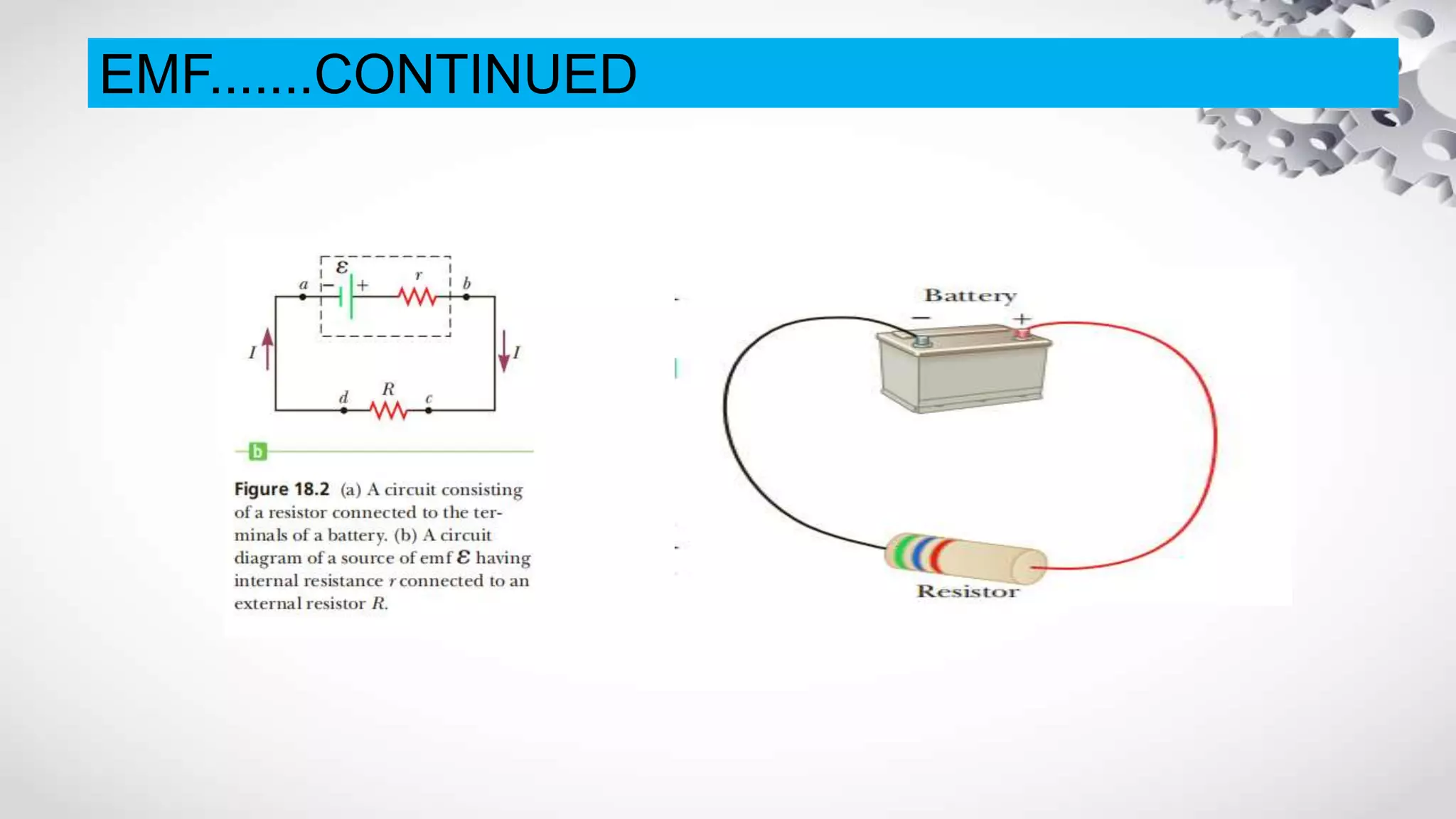
The document discusses electromotive force (EMF) and how it relates to voltage, work, and current flow in a circuit. It explains that a battery or generator produces a voltage difference across its terminals by converting chemical or mechanical energy into electrical energy. When a resistor is connected across the battery terminals, charge carriers flow through the circuit as current. The ability of the battery to move these charge carriers is measured by its voltage and represents the work done per unit charge by the EMF source. Voltage is distributed among and dropped across the different components in a circuit based on the amount of current and resistance.