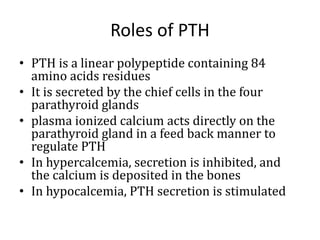
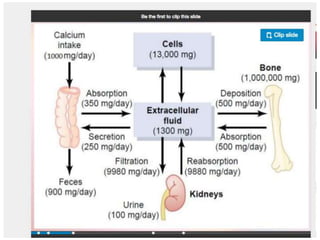
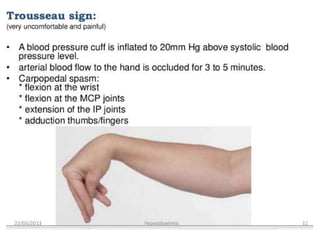
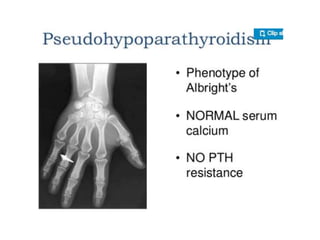
This document discusses calcium imbalance and hypocalcemia. It defines hypocalcemia and describes its various causes including prematurity, birth asphyxia, infants of diabetic mothers, vitamin D deficiency, hypoparathyroidism, and renal failure. The roles of parathyroid hormone, vitamin D, and calcitonin in regulating calcium levels are explained. Symptoms of hypocalcemia include neuromuscular irritability, cardiac involvement, and dermatological manifestations. The pathophysiology and various factors affecting calcium absorption and homeostasis are also summarized.