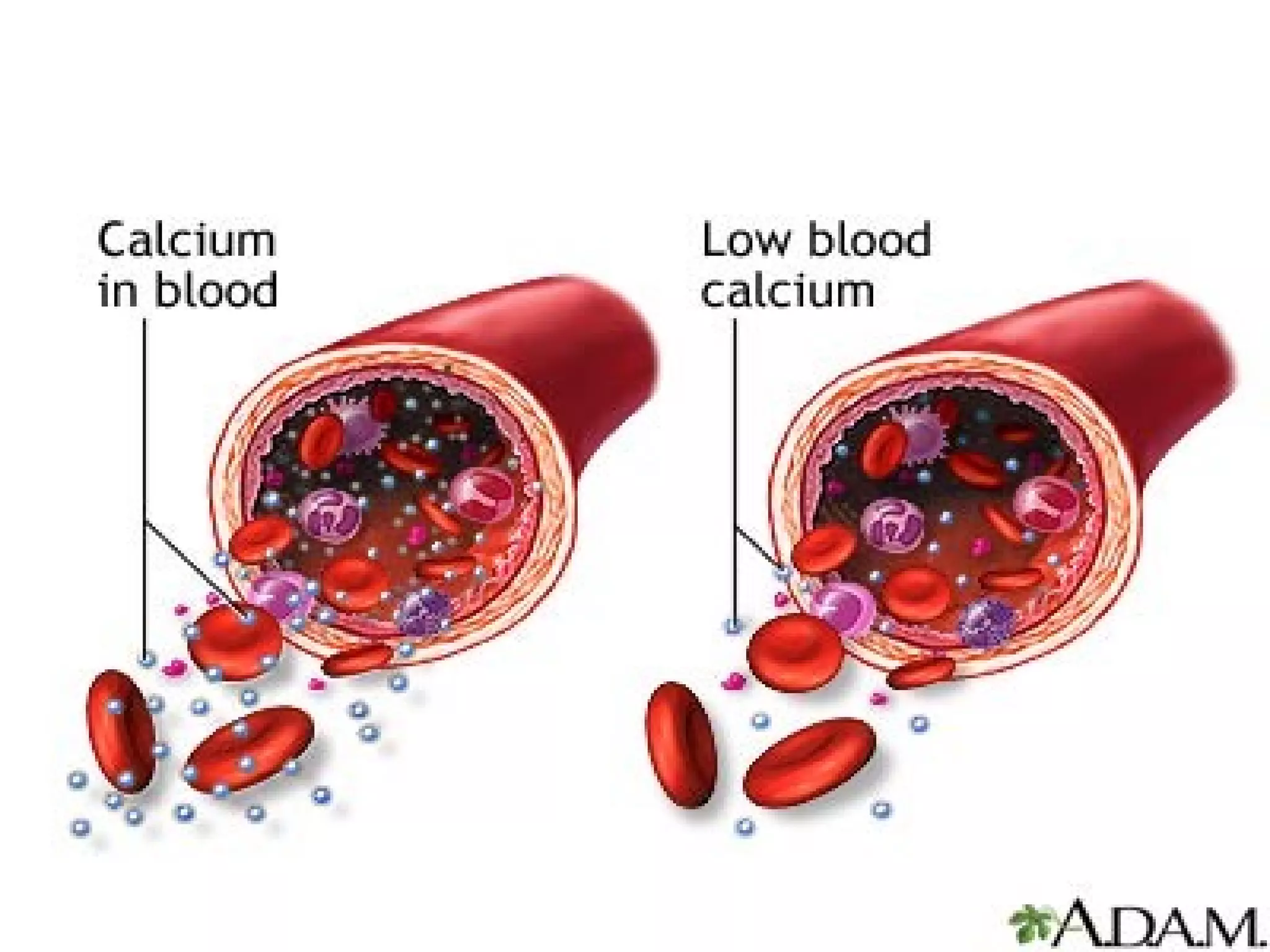
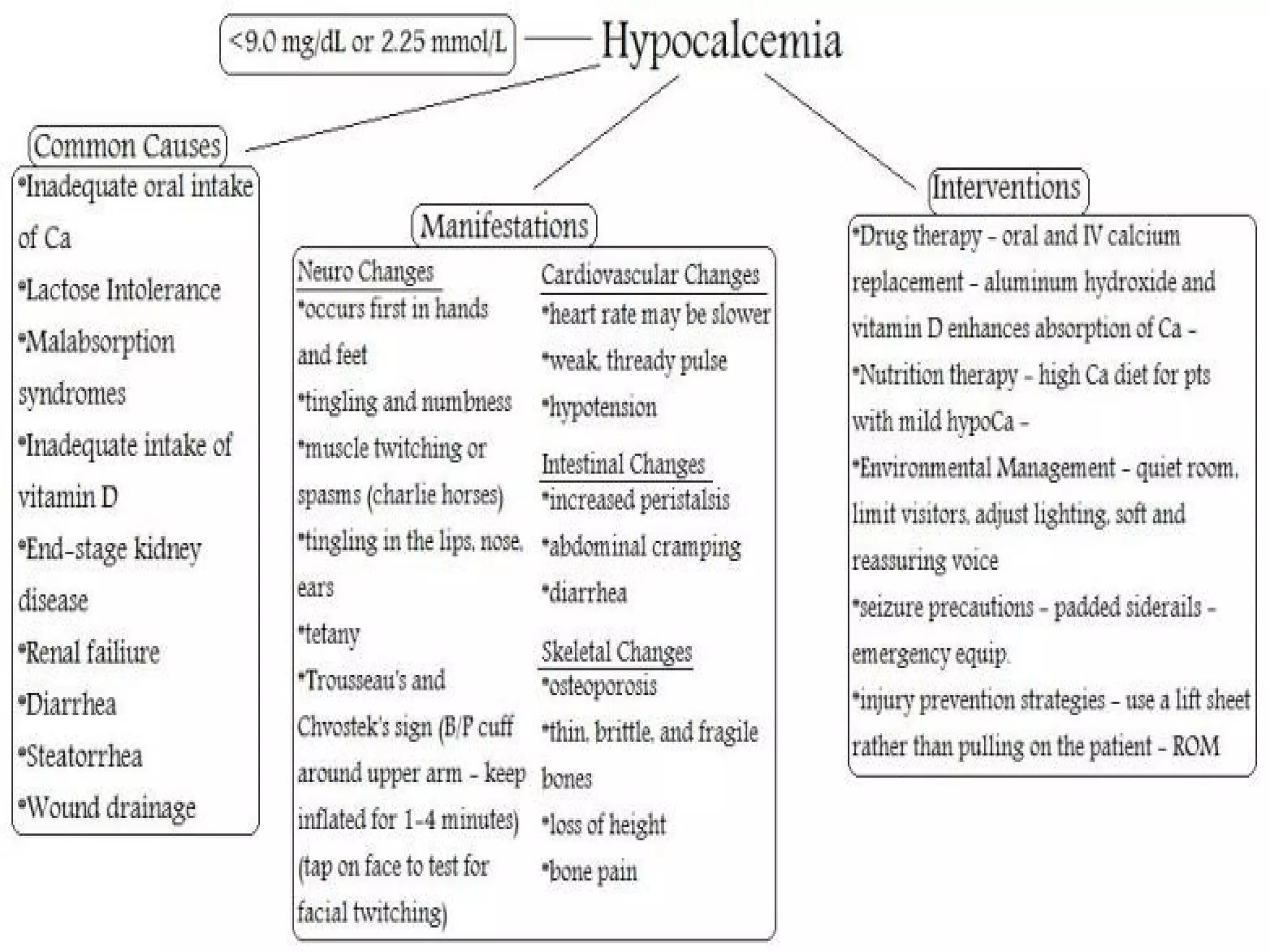
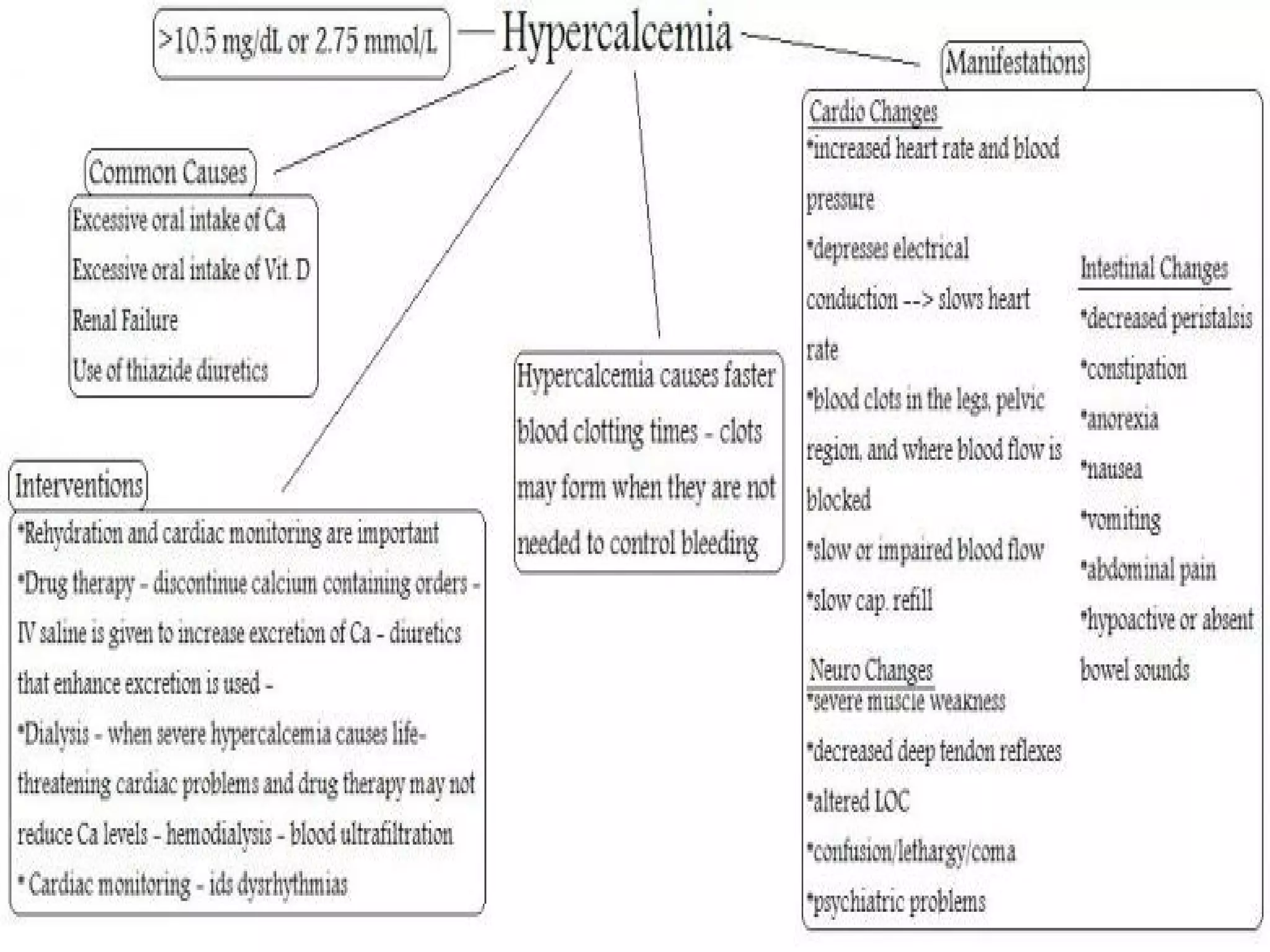
This document discusses calcium imbalances, specifically hypocalcemia and hypercalcemia. Hypocalcemia is defined as a calcium level below 8.5 mg/dl and can result from low calcium stores or extracellular levels. Symptoms include neuromuscular excitability leading to tetany and seizures. Hypercalcemia is a calcium level over 10 mg/dl and usually stems from increased bone absorption. Symptoms include decreased muscle function, gastrointestinal issues, and cardiac dysrhythmias. Both conditions require monitoring calcium levels and addressing the underlying cause through diet, medications, and IV calcium supplementation as needed.