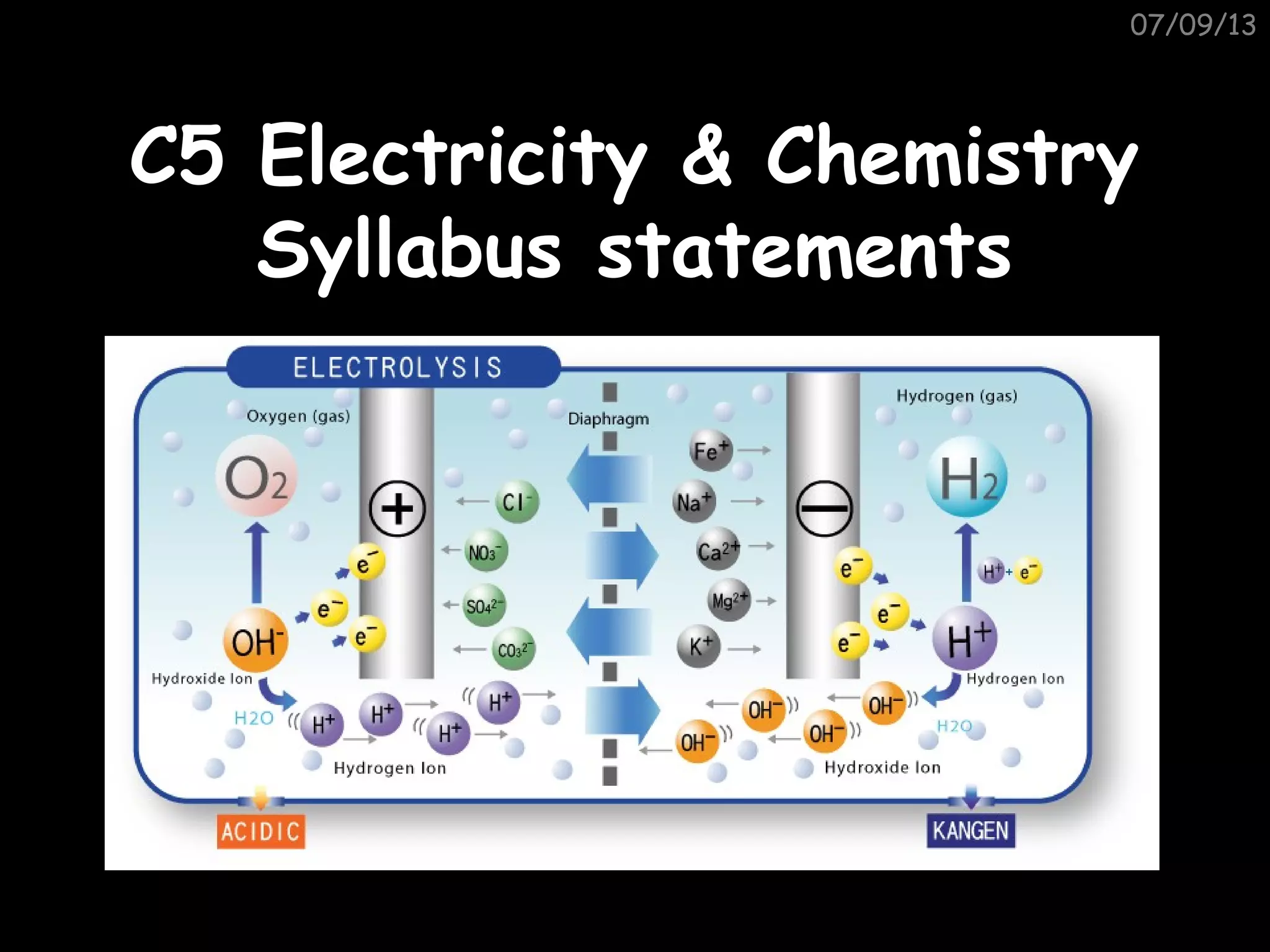
This document outlines the key topics and concepts covered in a syllabus for a C5 Electricity & Chemistry course. It includes 9 points that describe electrolysis processes, products, and principles. Specifically, it covers how electrolysis breaks ionic compounds into simpler substances through the chemical effects of electricity. It also describes the use of electrodes, electrolytes, anodes and cathodes and how they relate to the reactions and products in different electrolysis examples, including molten salts, aqueous solutions, and metal refining. Finally, it mentions electroplating of metals and the industrial production of aluminum, chlorine, hydrogen and sodium hydroxide.