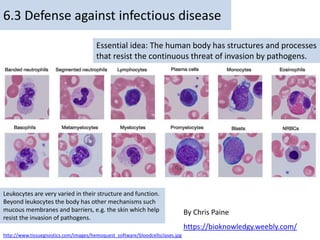
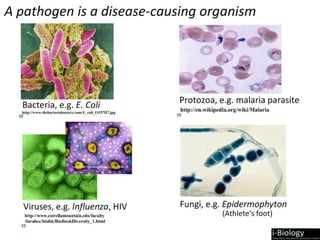
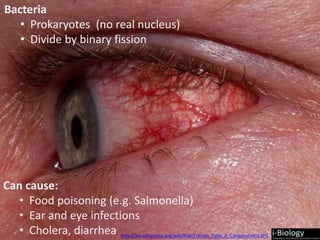
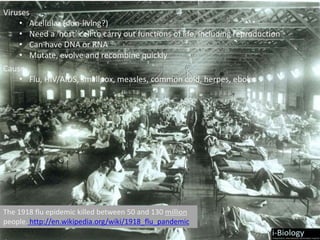
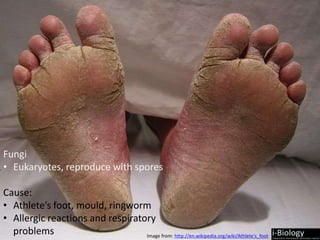
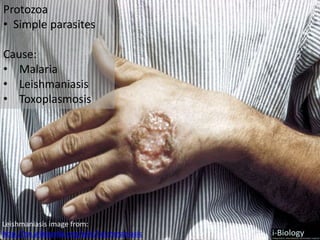
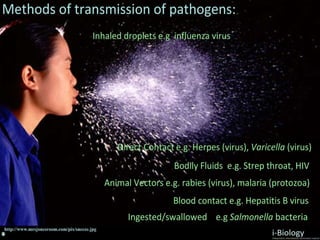
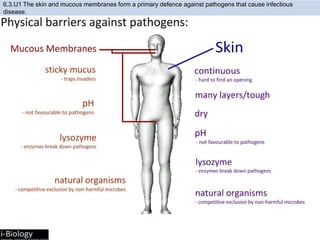
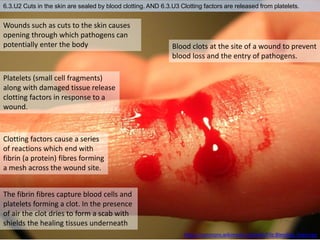
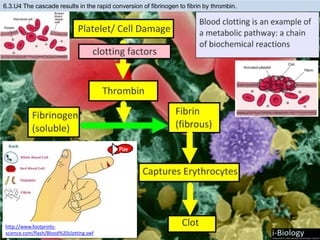
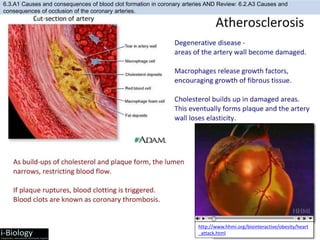
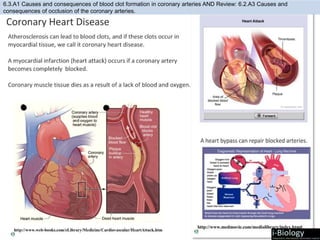
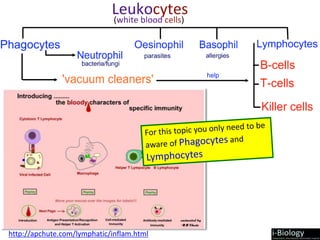
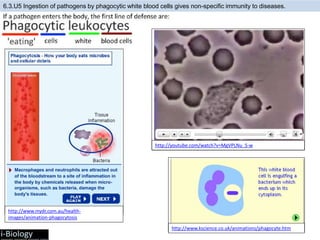
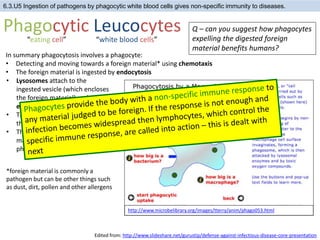
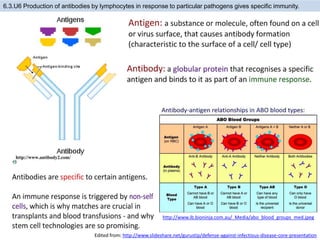
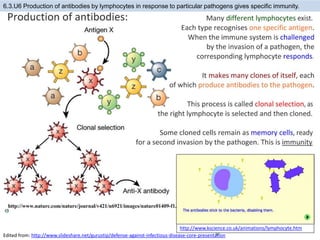
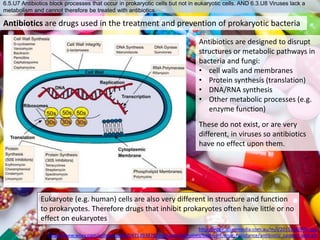
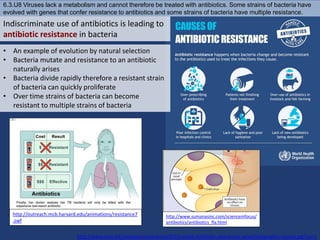
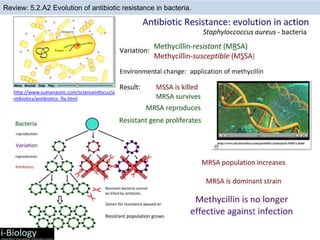
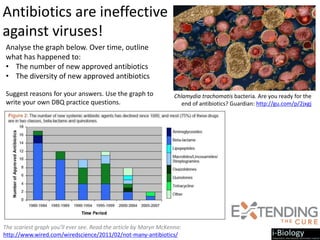
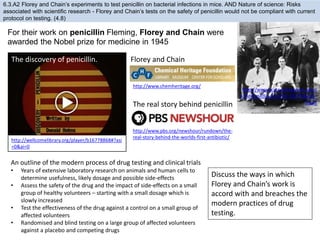
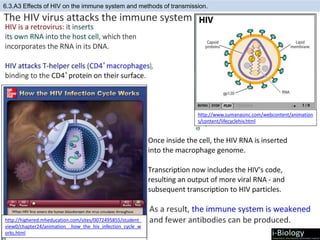
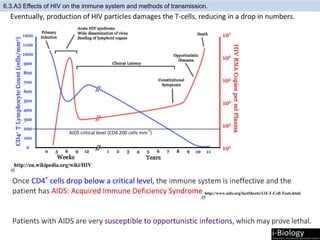
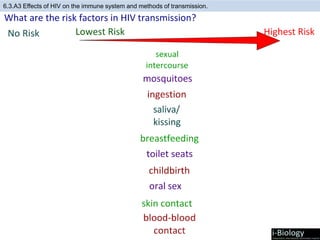
The human body has structures and processes that resist the continuous threat of invasion by pathogens. These include leukocytes that ingest and destroy pathogens, as well as physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes. The body also has mechanisms for blood clotting to prevent the entry of pathogens through cuts in the skin. Lymphocytes produce antibodies that provide specific immunity against particular pathogens. While antibiotics can treat bacterial infections by blocking bacterial processes, they are ineffective against viruses which lack metabolism and cannot be treated in the same way.