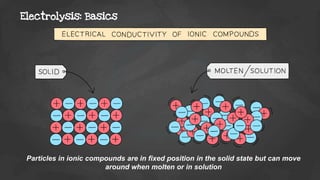
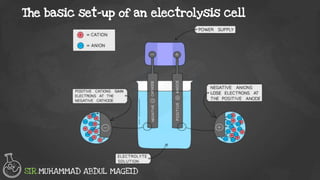
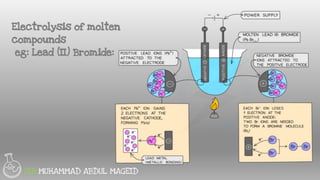
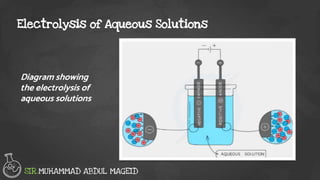
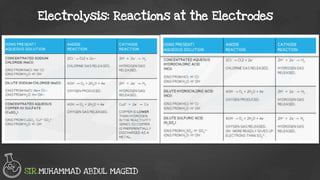
Electrolysis is the process of using an electric current to drive nonspontaneous chemical reactions. During electrolysis, ions move towards the electrodes and undergo changes. At the anode, ions lose electrons and form gases. At the cathode, ions gain electrons and form elements or hydrogen gas. The products of electrolysis depend on factors like the electrolyte, its concentration, and the reactivities of the ions. Electrolysis has many industrial applications like electroplating and producing reactive elements.