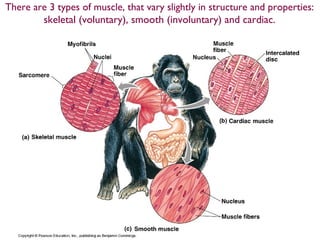
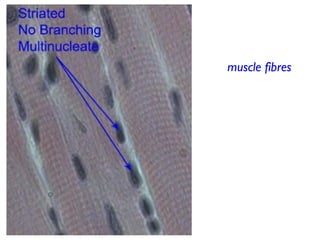
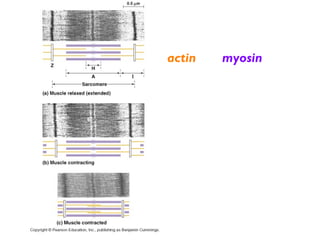
There are three main types of muscle tissue - skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Muscle fibers are multinucleate cells formed from the fusion of individual embryonic muscle cells. Within each fiber are many parallel myofibrils composed of repeating sarcomere units. A sarcomere contains overlapping actin and myosin filaments. When an action potential reaches the neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine is released causing calcium ions to enter the fiber and allow the myosin heads to bind to actin, pulling the filaments together and contracting the muscle fiber. ATP provides energy to break the binding and reset the filaments for the next contraction.