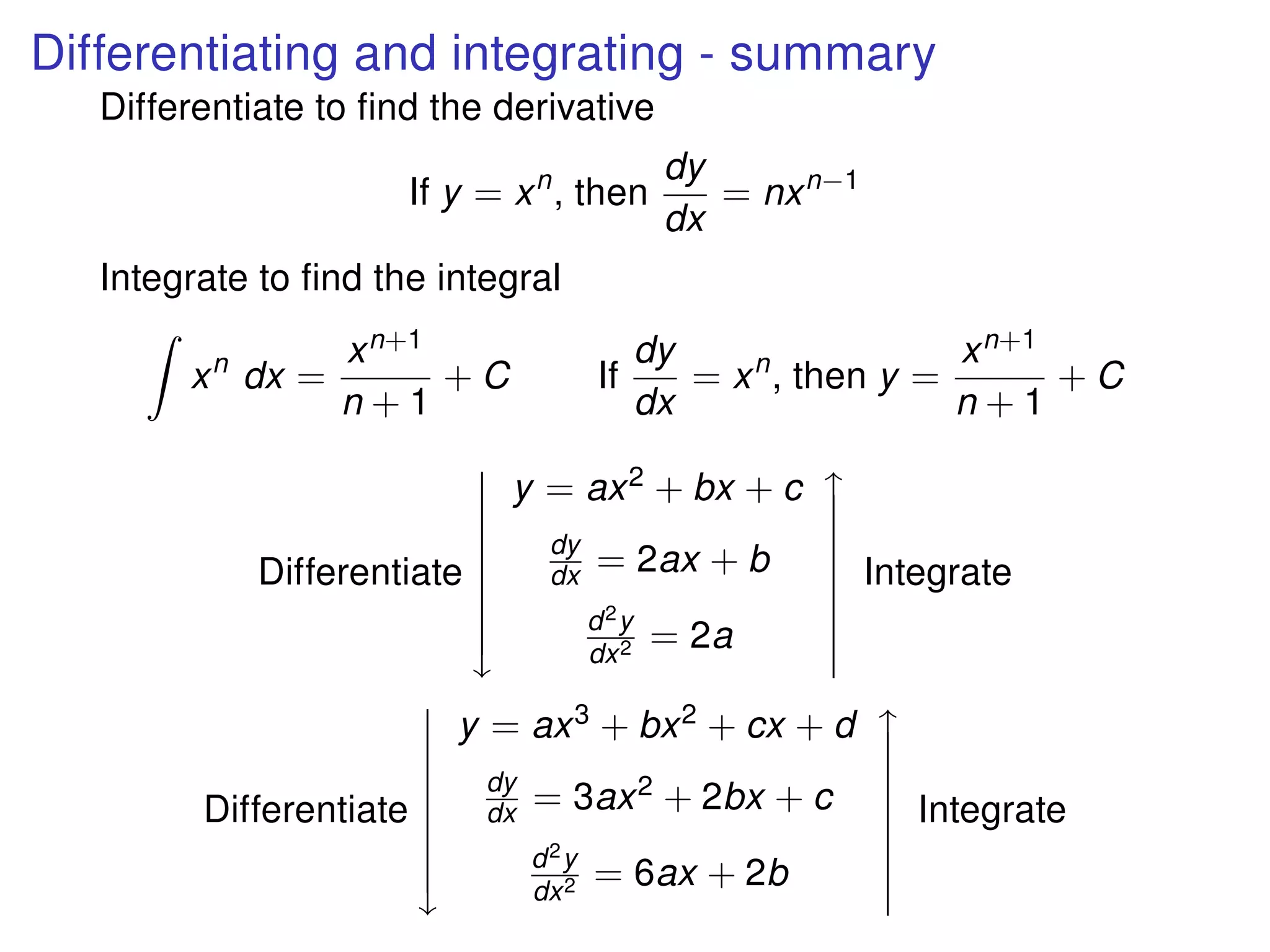
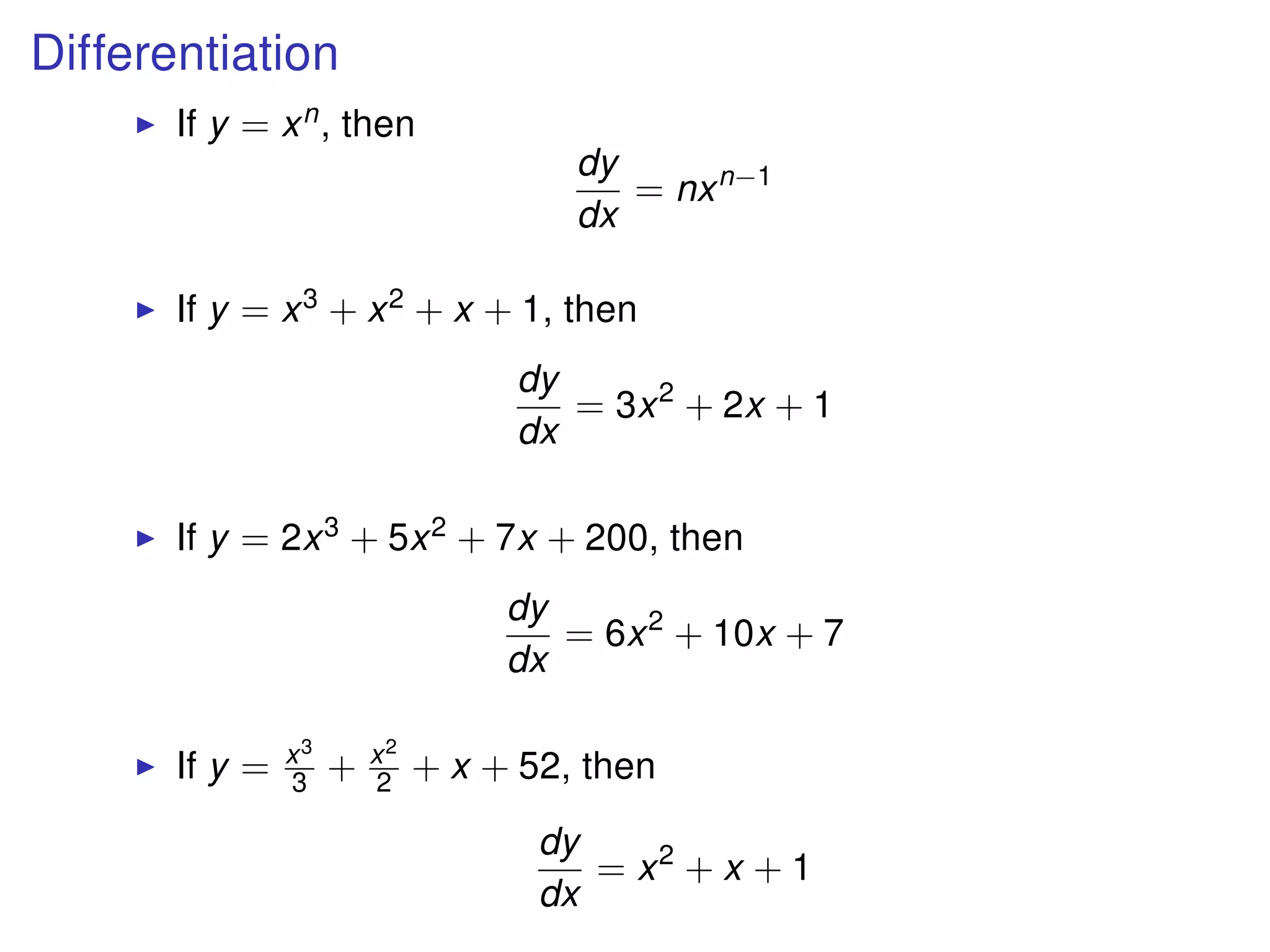
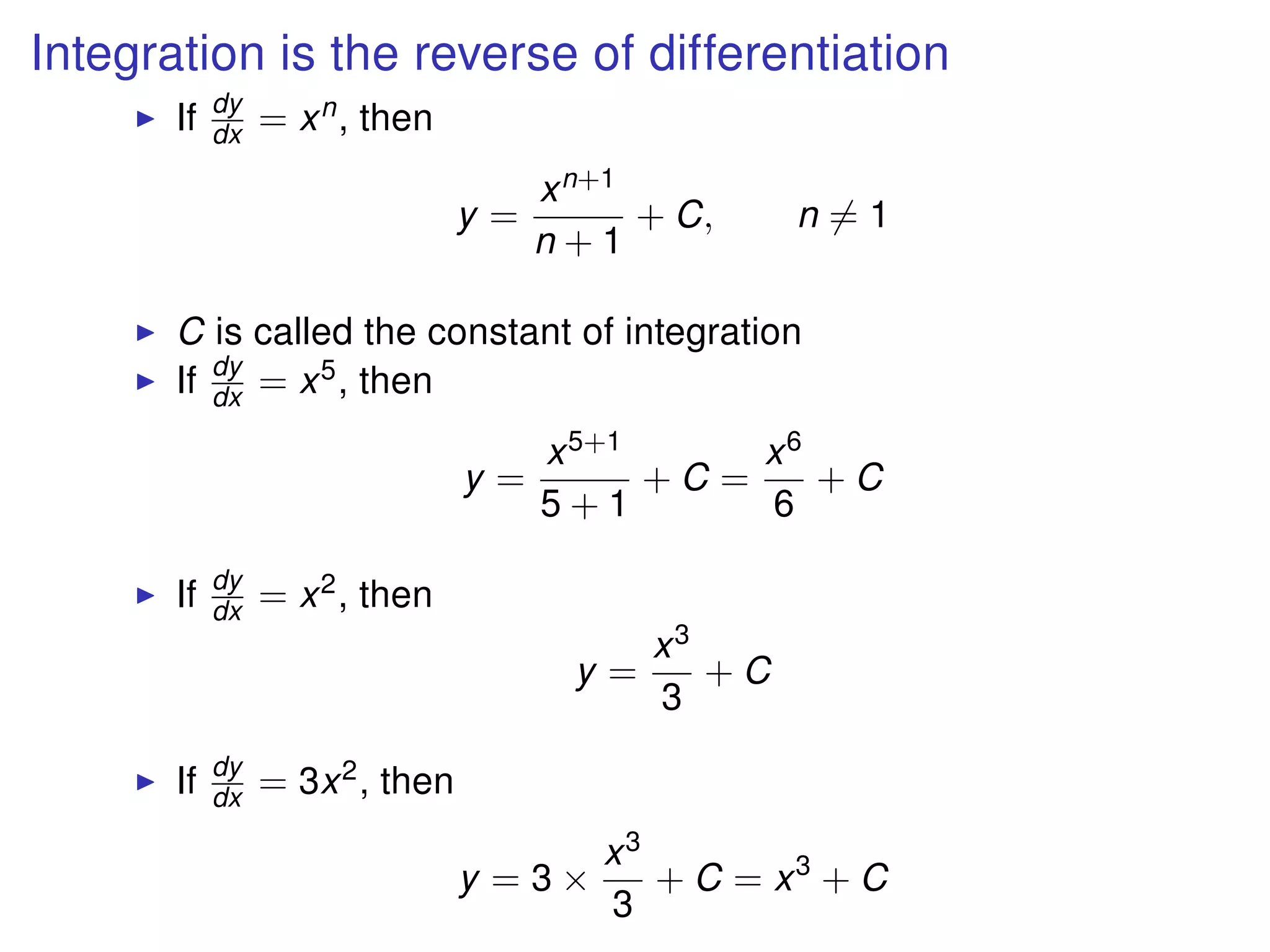
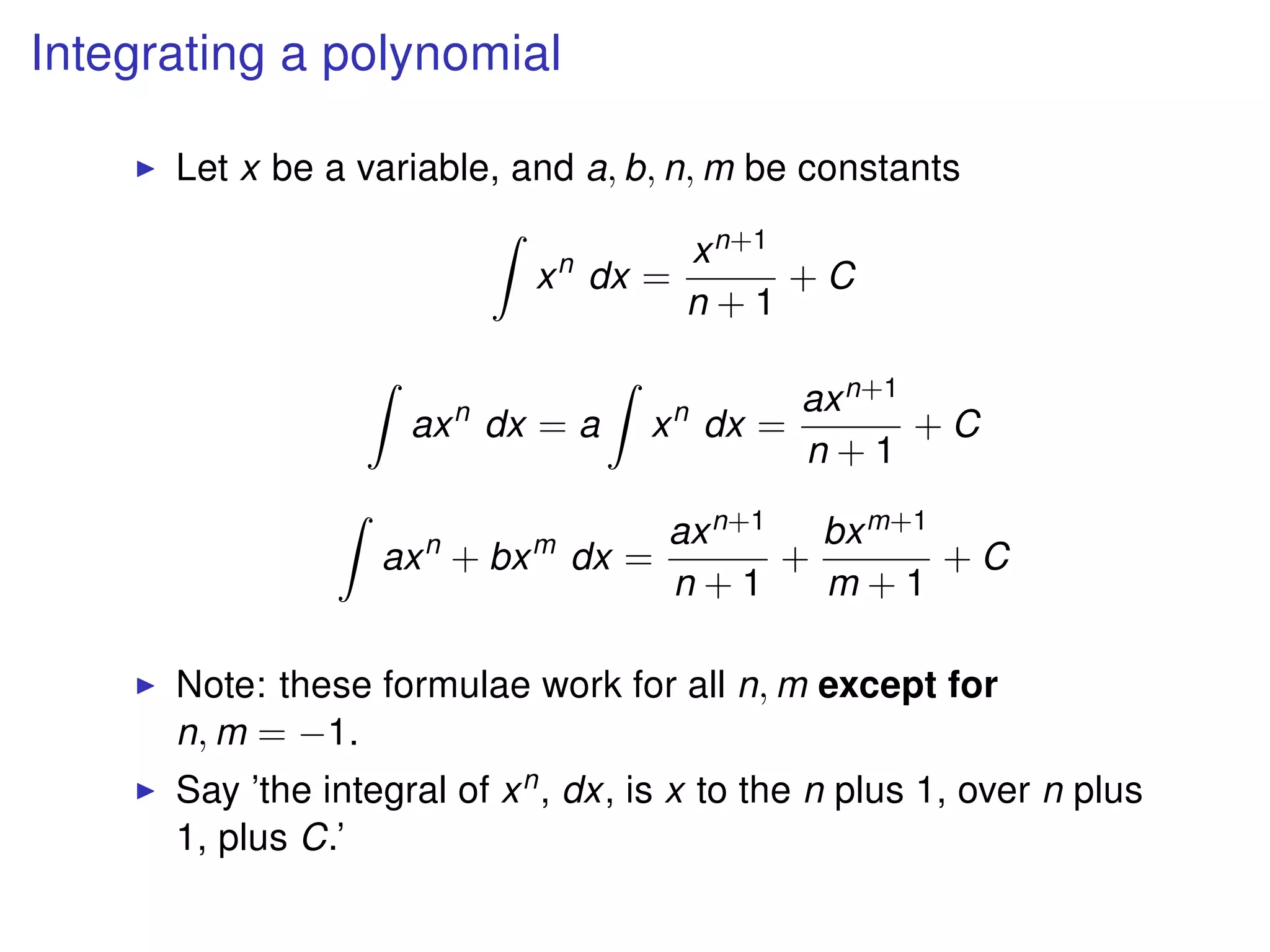
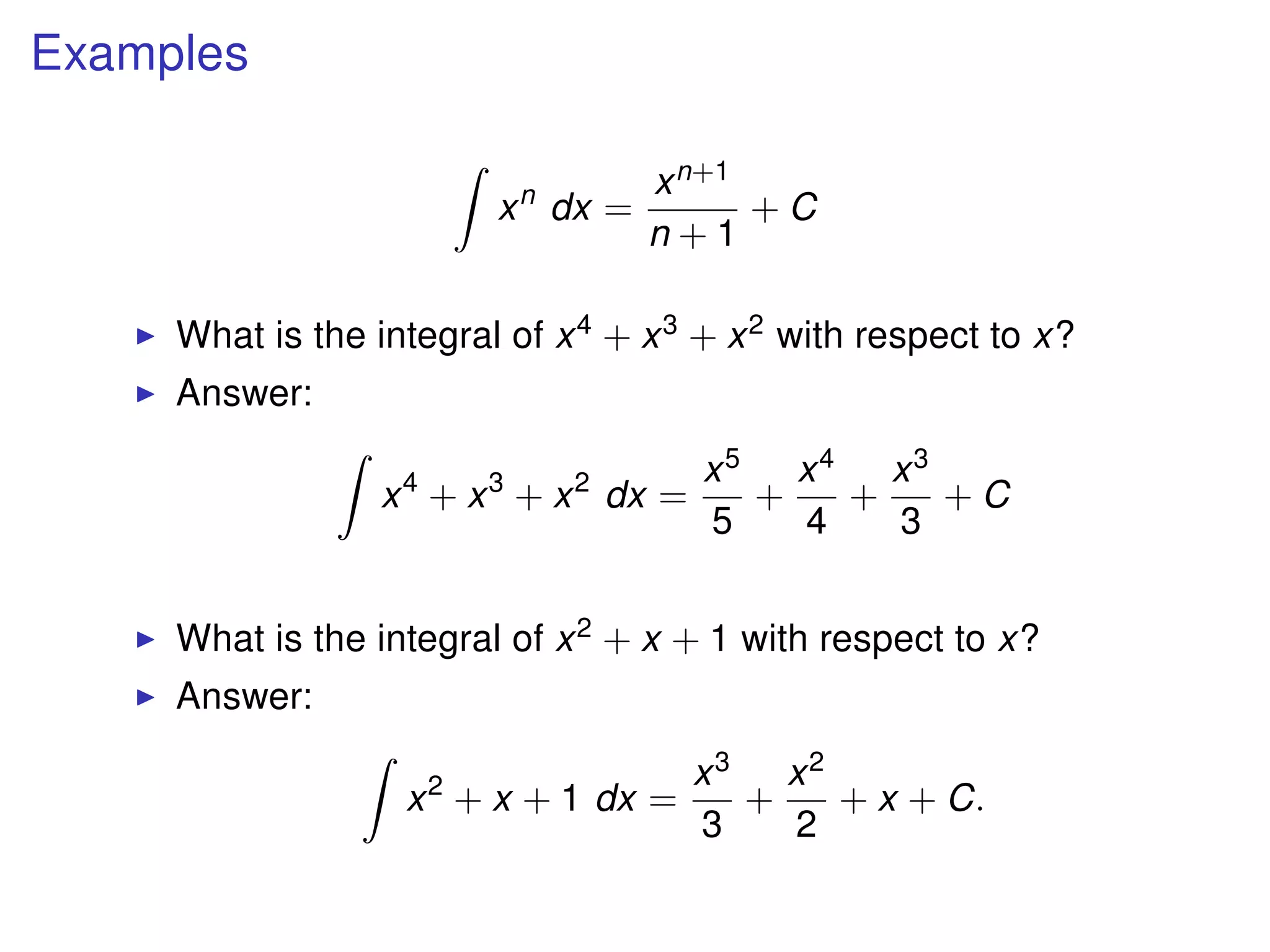
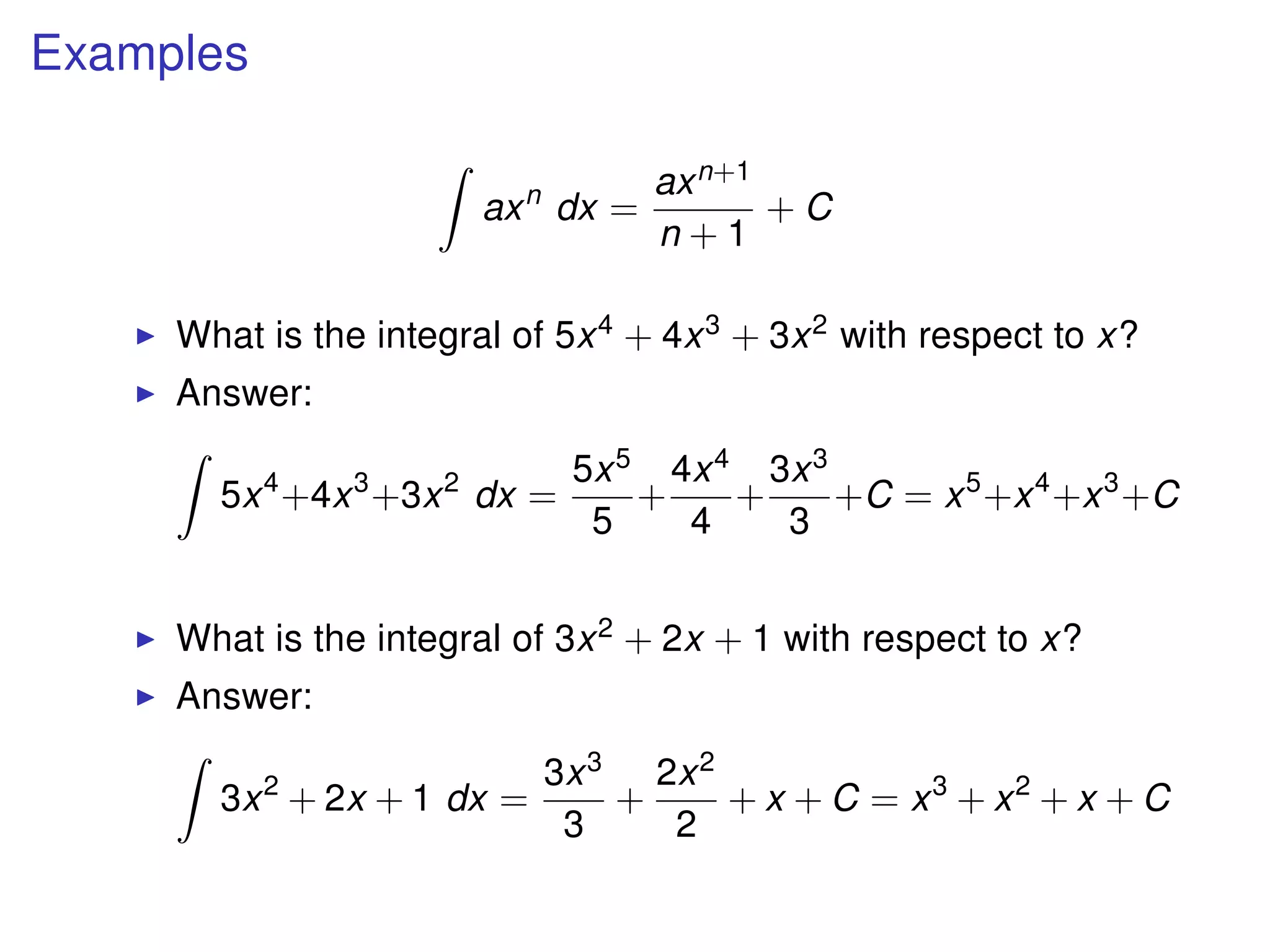
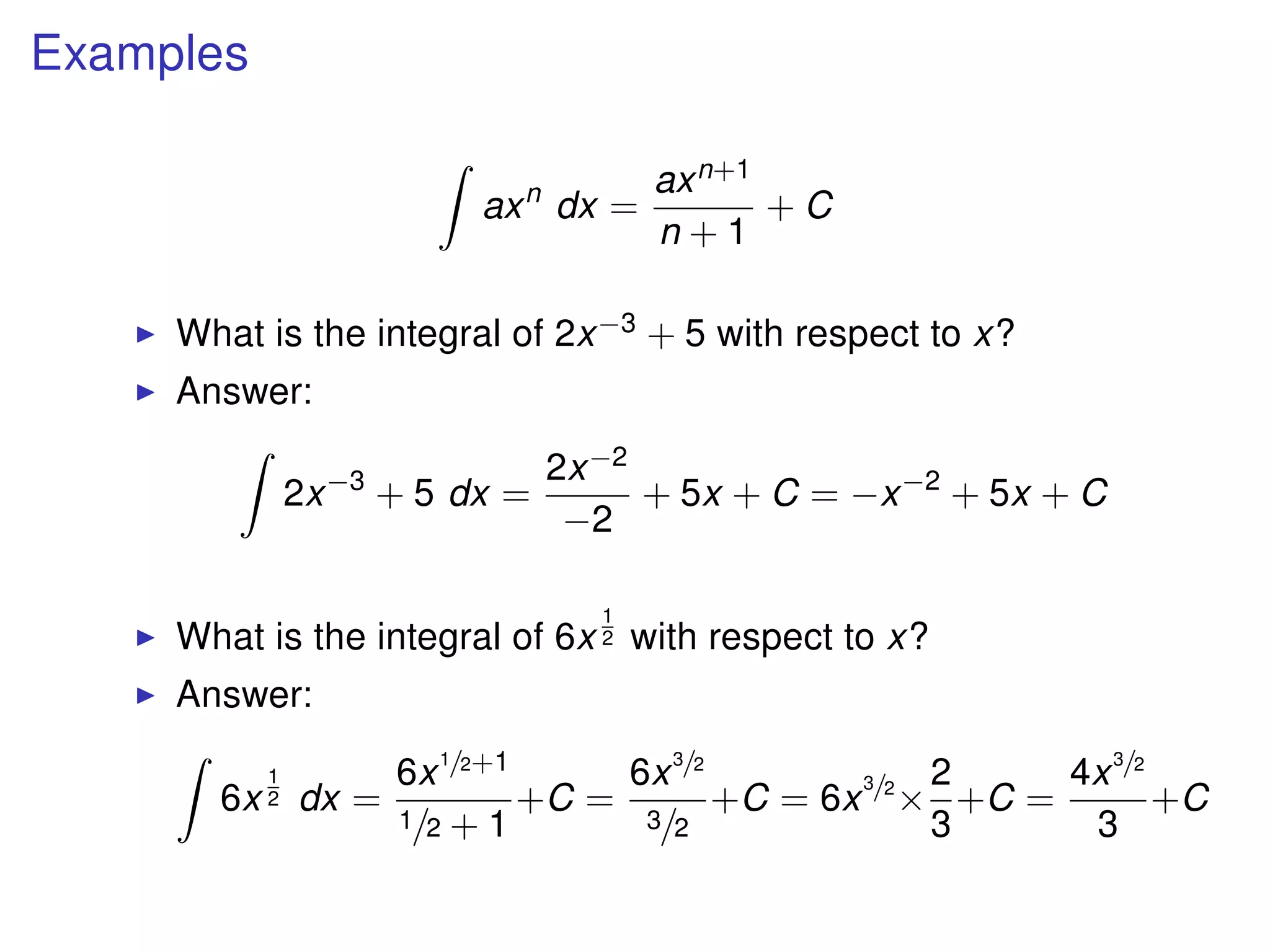
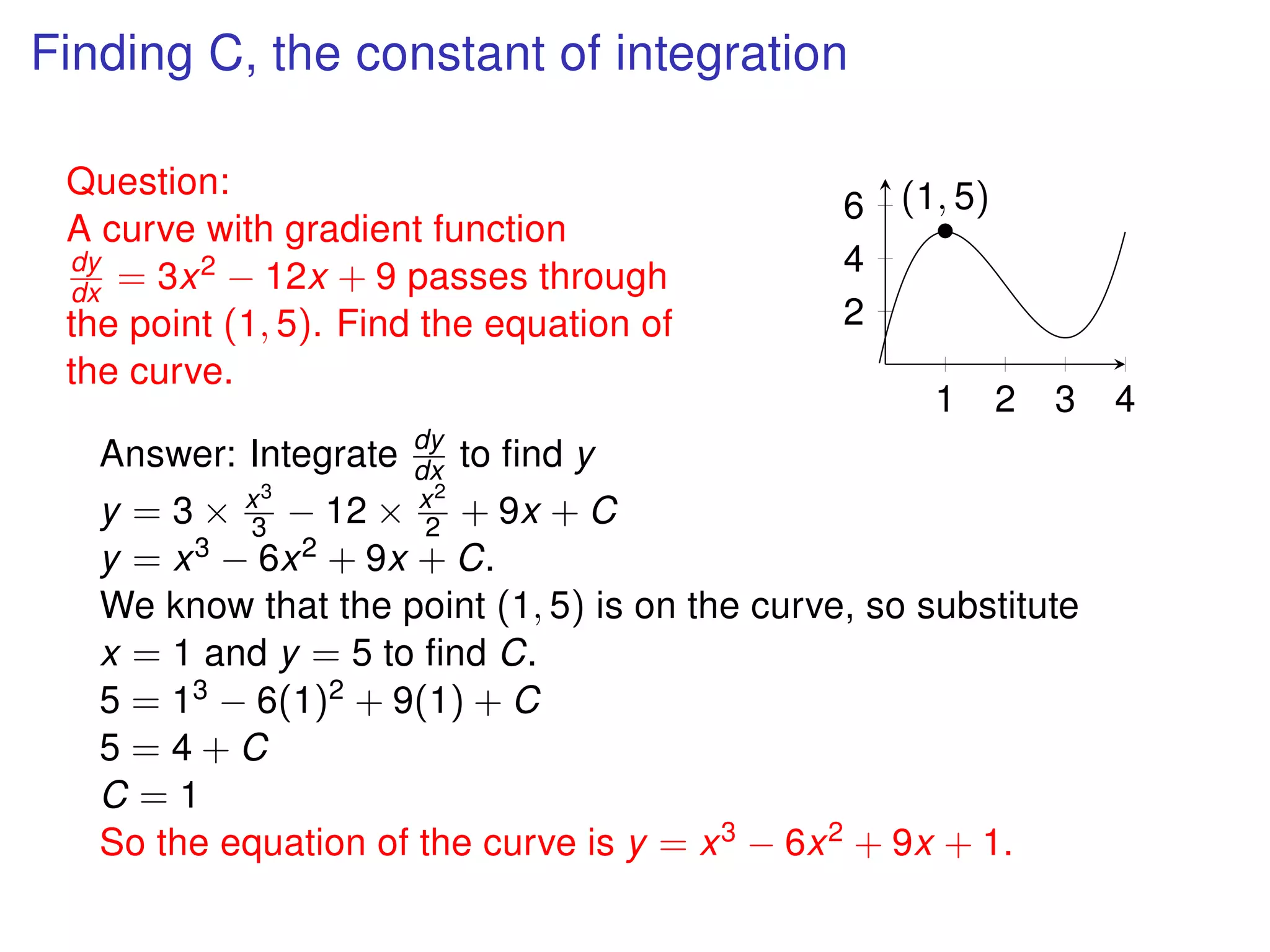
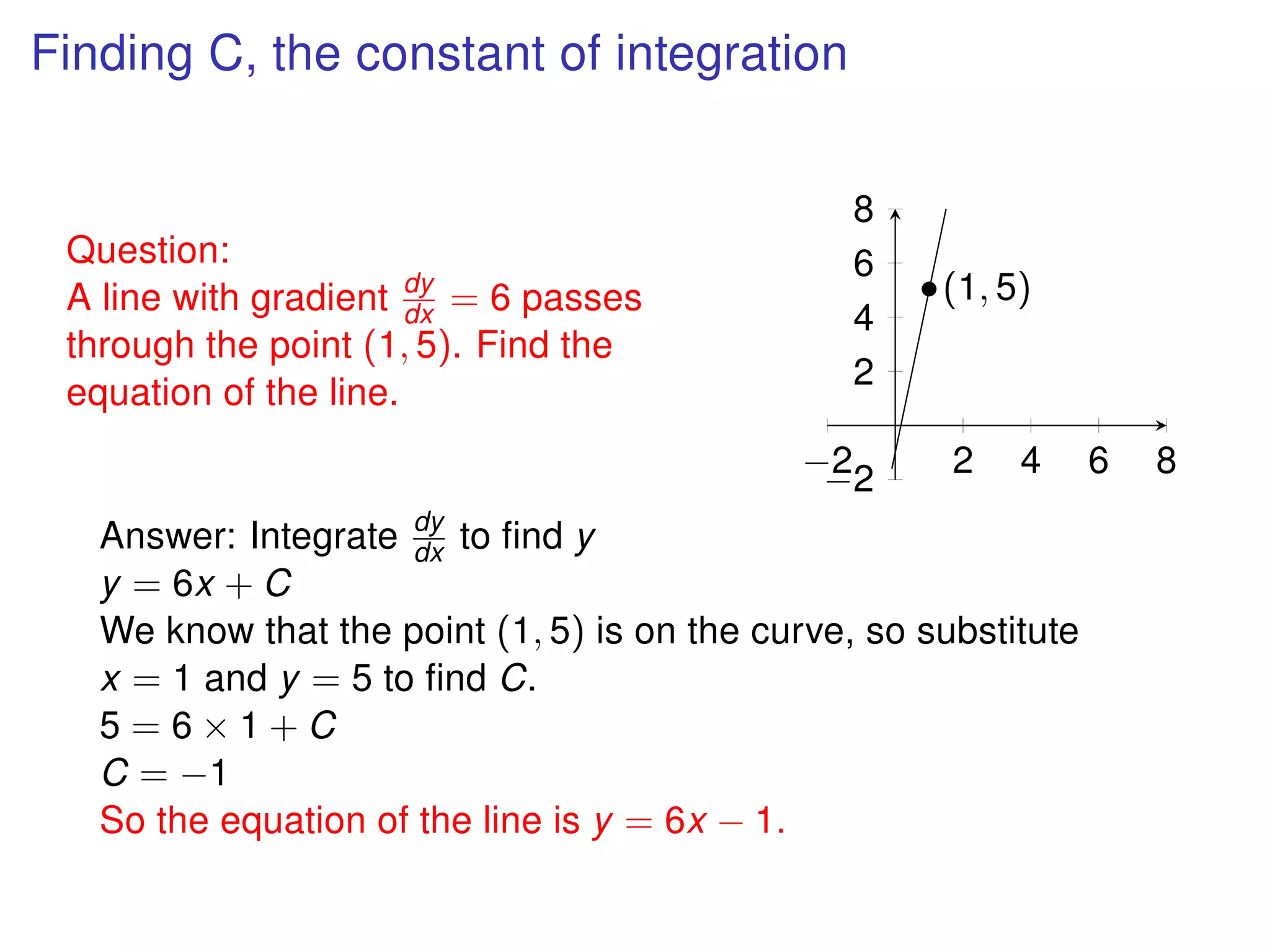
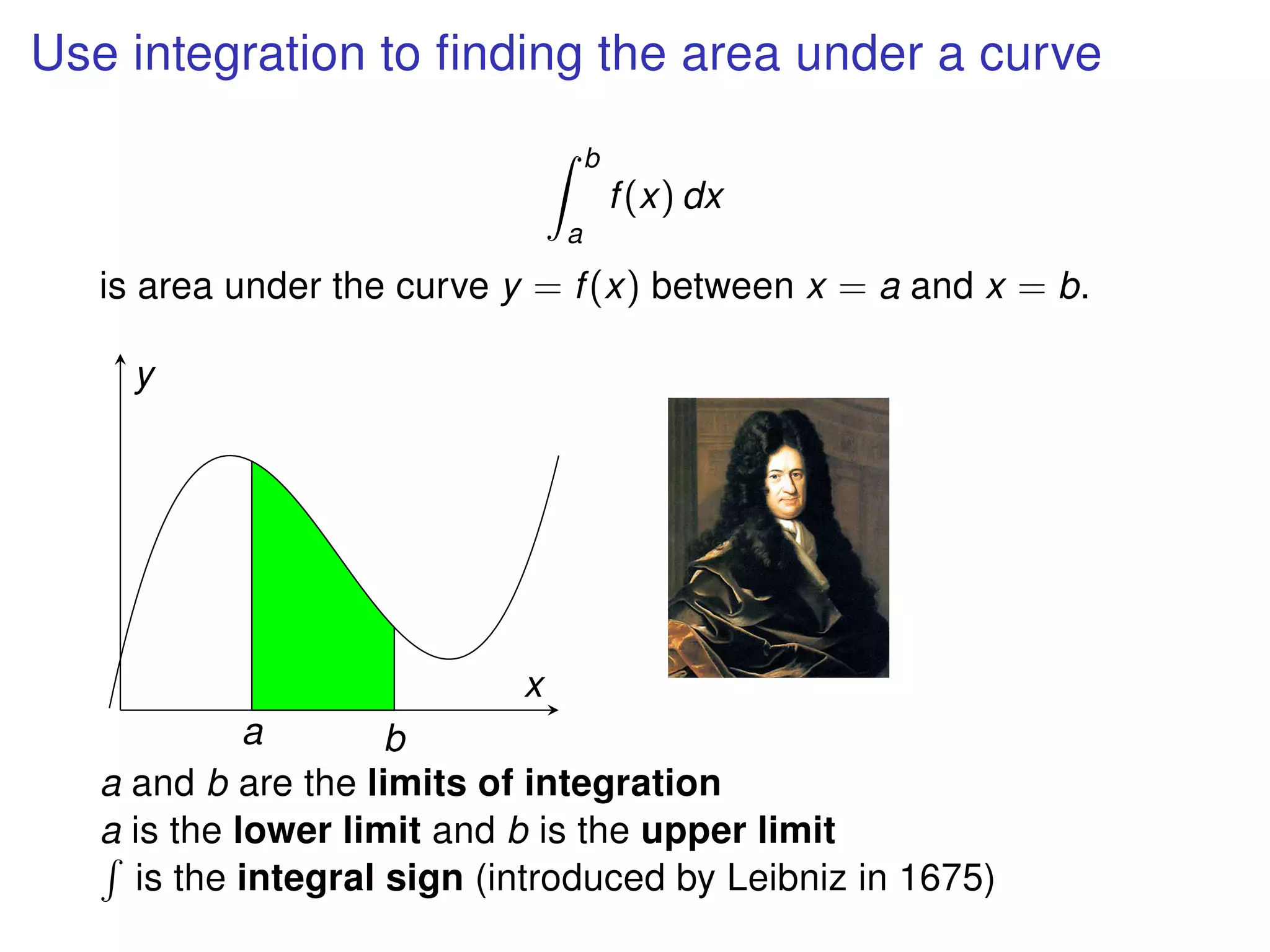
The document discusses integration, which is the reverse process of differentiation. It provides formulas for integrating polynomial expressions like xn and axn and explains how to find the constant of integration C. Examples are given for integrating expressions and finding the area under a curve by integrating between limits of integration.





![The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part II
If f(x) dx = F(x), then
b
a
f(x) dx = [F(x)]b
a = [F(b)] − [F(a)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c2stlecture6handout-140603105319-phpapp01/75/C2-st-lecture-6-handout-15-2048.jpg)
![Example
Question:
What is the area under the
curve y = 3x3 + 2 between
x = 0 and x = 2?
−1 1 2
10
20
30
Answer:
2
0 3x3 + 2 dx = [3x4
4 + 2x]2
0
= [3×(2)4
4 + 2 × 2] − [3×04
4 + 2 × 0]
= [12 + 4] − [0 + 0]
= [16] − [0] = 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c2stlecture6handout-140603105319-phpapp01/75/C2-st-lecture-6-handout-16-2048.jpg)
![Example 2
Question:
What is the area under the
curve y = 6x2 + 2x−3 between
x = −2 and x = −1?
−2 −1
10
20
Answer:
−1
−2 6x2 + 2x−3 dx = [2x3 − x−2]−1
−2
= [2(−1)3 − (−1)−2] − [2(−2)3 − (−2)−2]
= [−2 − 1] − [−16 − 1
4 ]
= [−3] − [−64−1
4 ]
= 53
4 = 131
4 = 13.25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c2stlecture6handout-140603105319-phpapp01/75/C2-st-lecture-6-handout-17-2048.jpg)