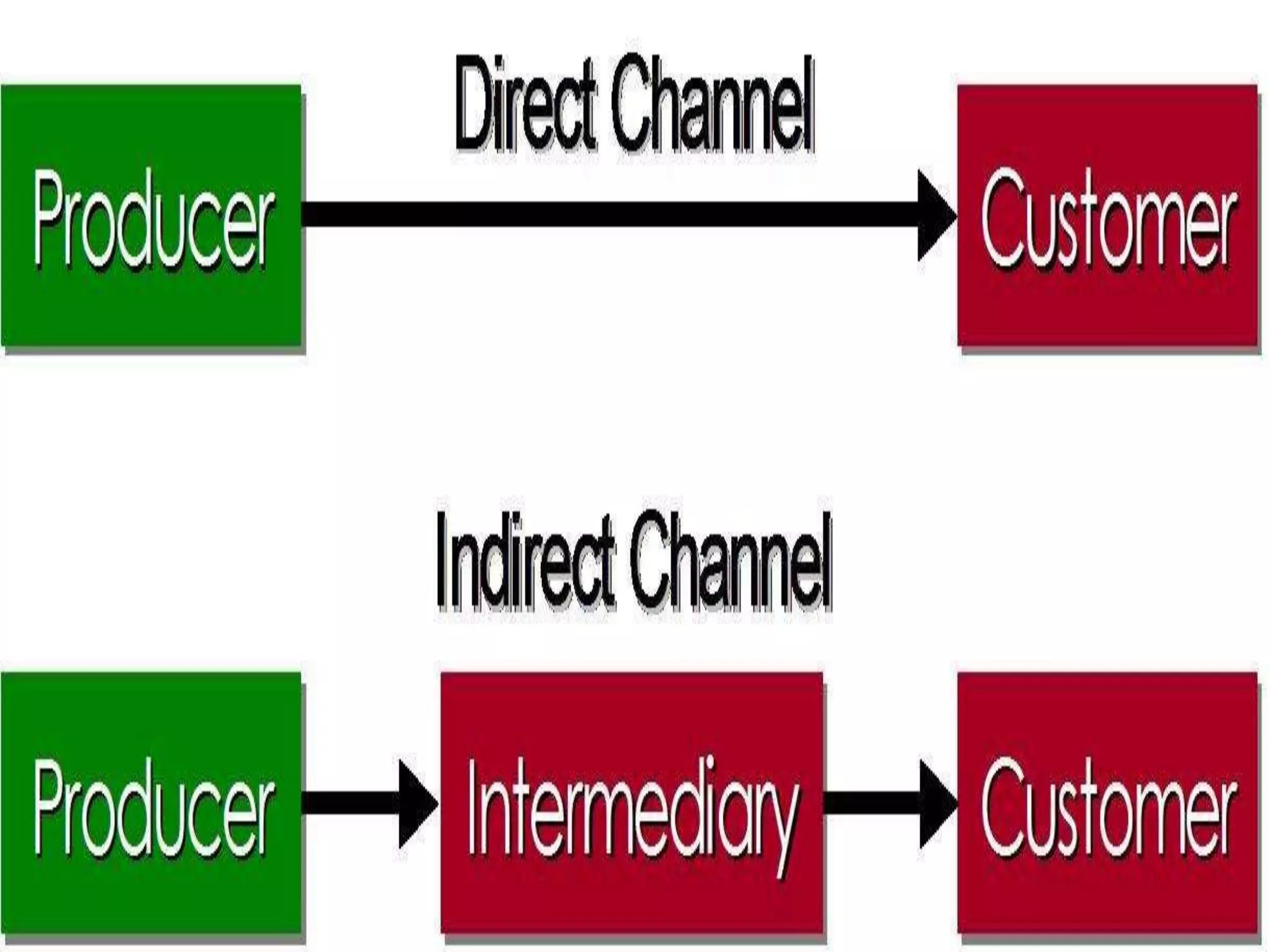
This document discusses distribution channels and classification of industrial and consumer goods. It defines distribution channels as the route by which products move from producer to consumer, whether direct or indirect. Direct channels involve no middlemen, while indirect channels may involve retailers, wholesalers, or agents. Consumer goods are purchased for personal use and are classified as convenience goods, shopping goods, or specialty goods. Industrial goods are used to produce other goods and include raw materials, semi-finished goods, parts, and machinery.