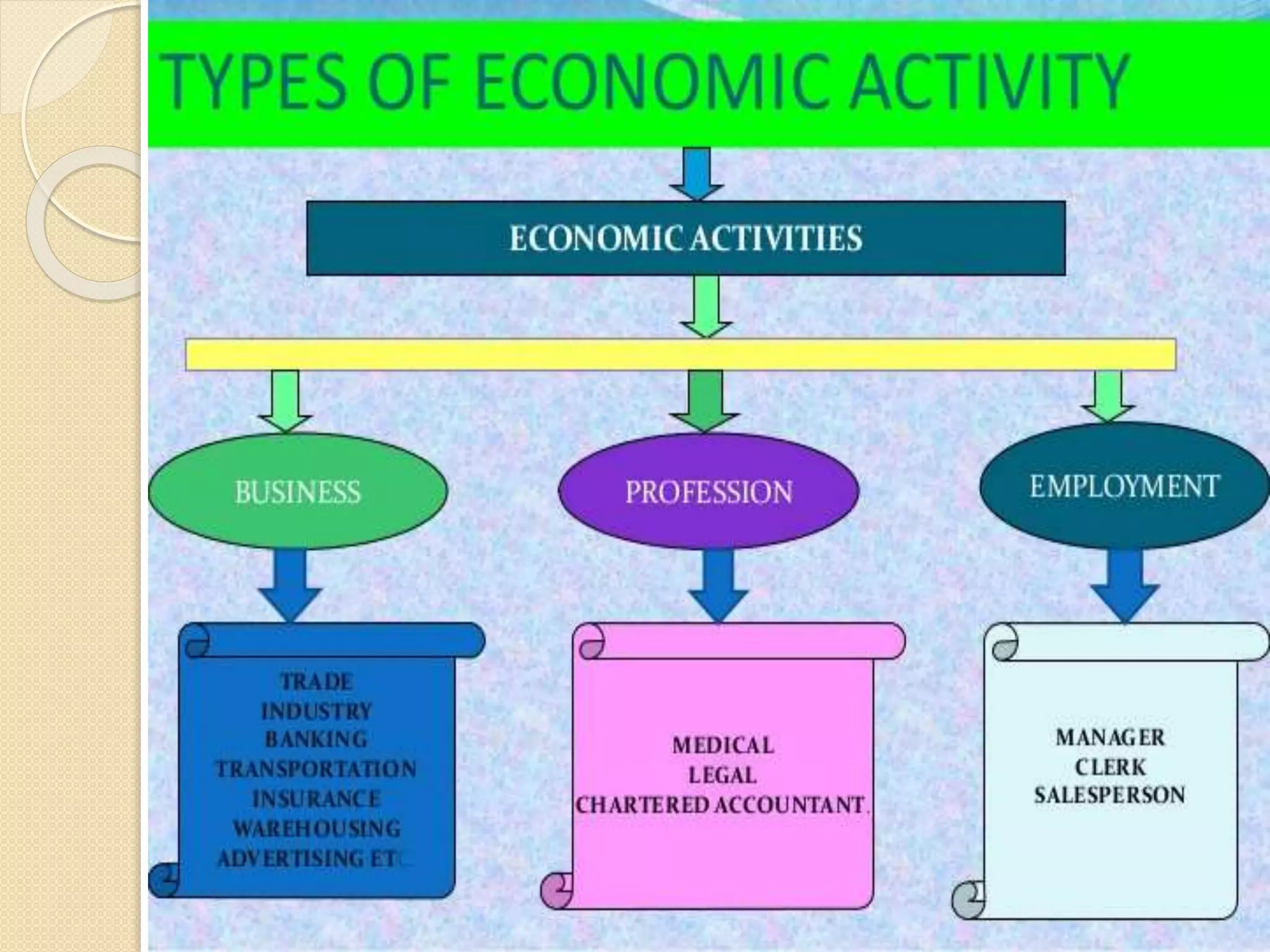
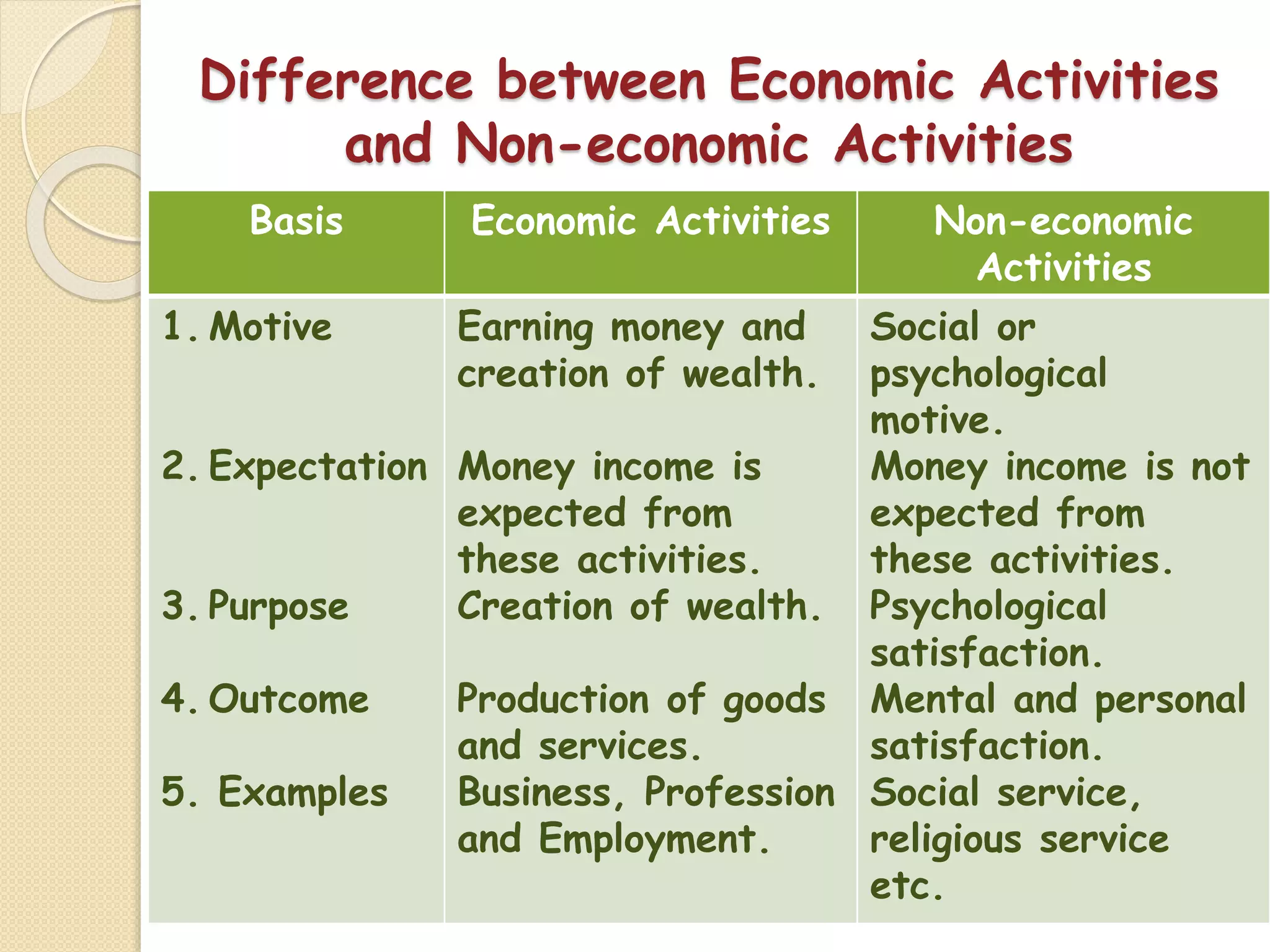
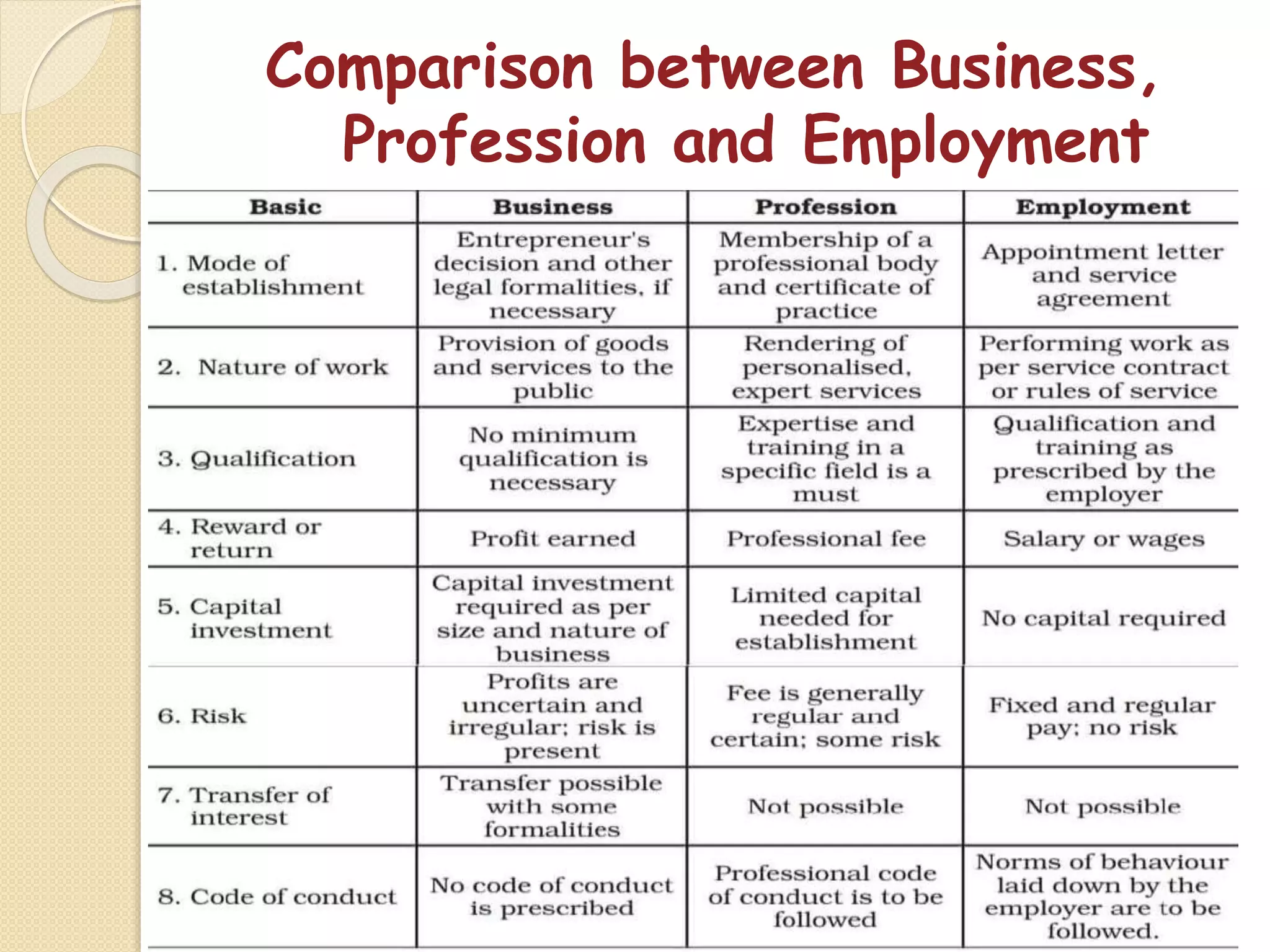
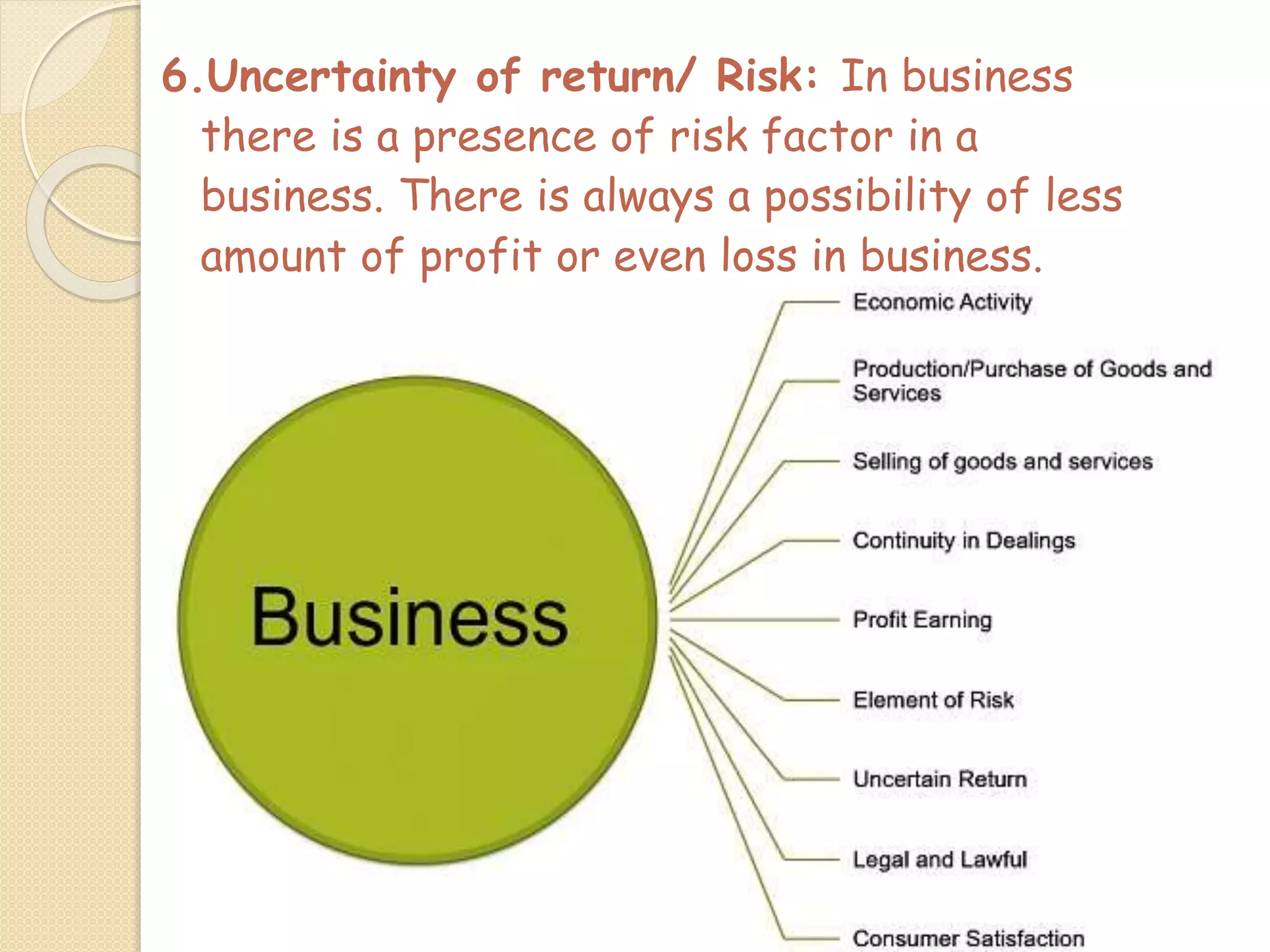
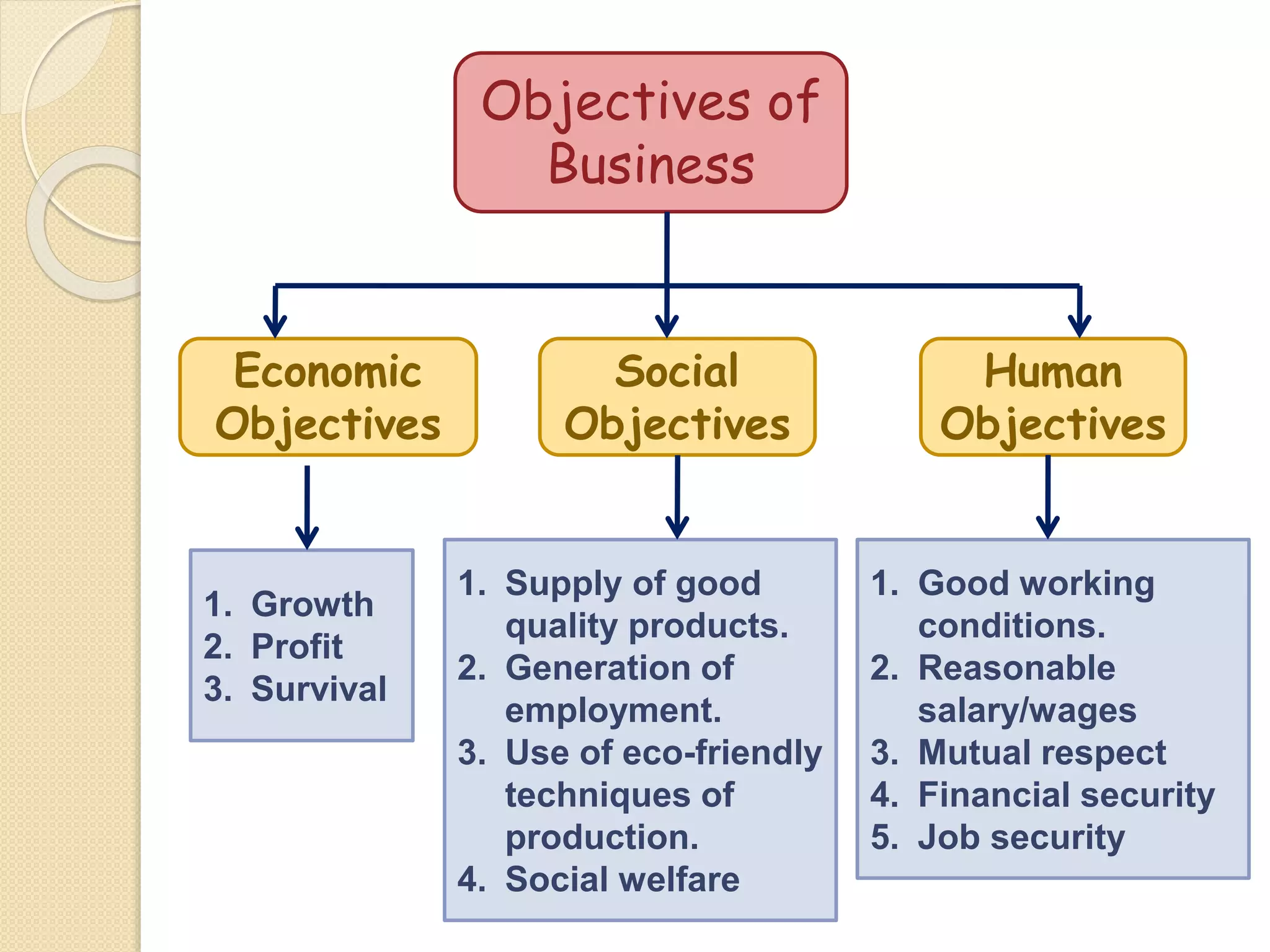
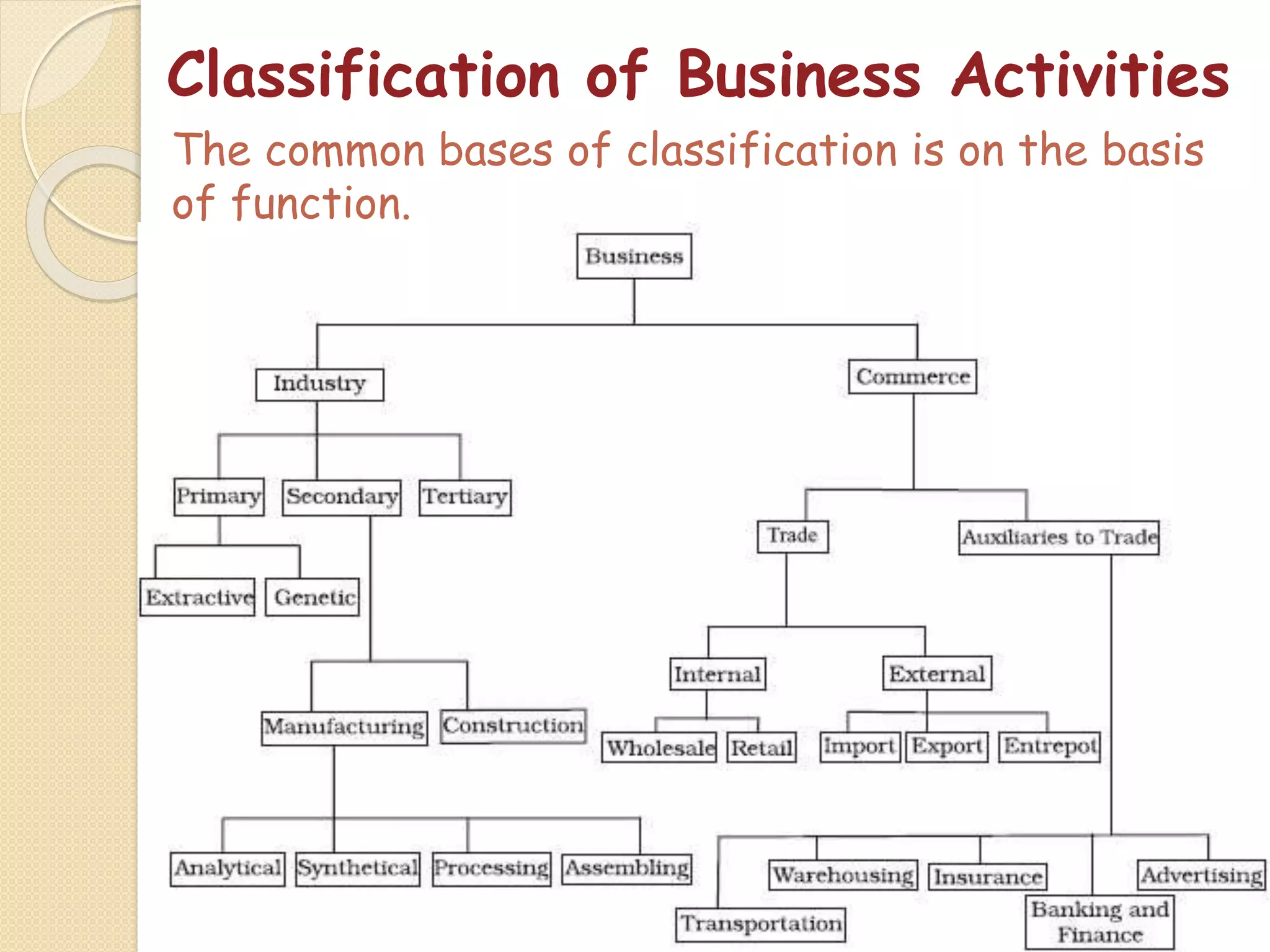
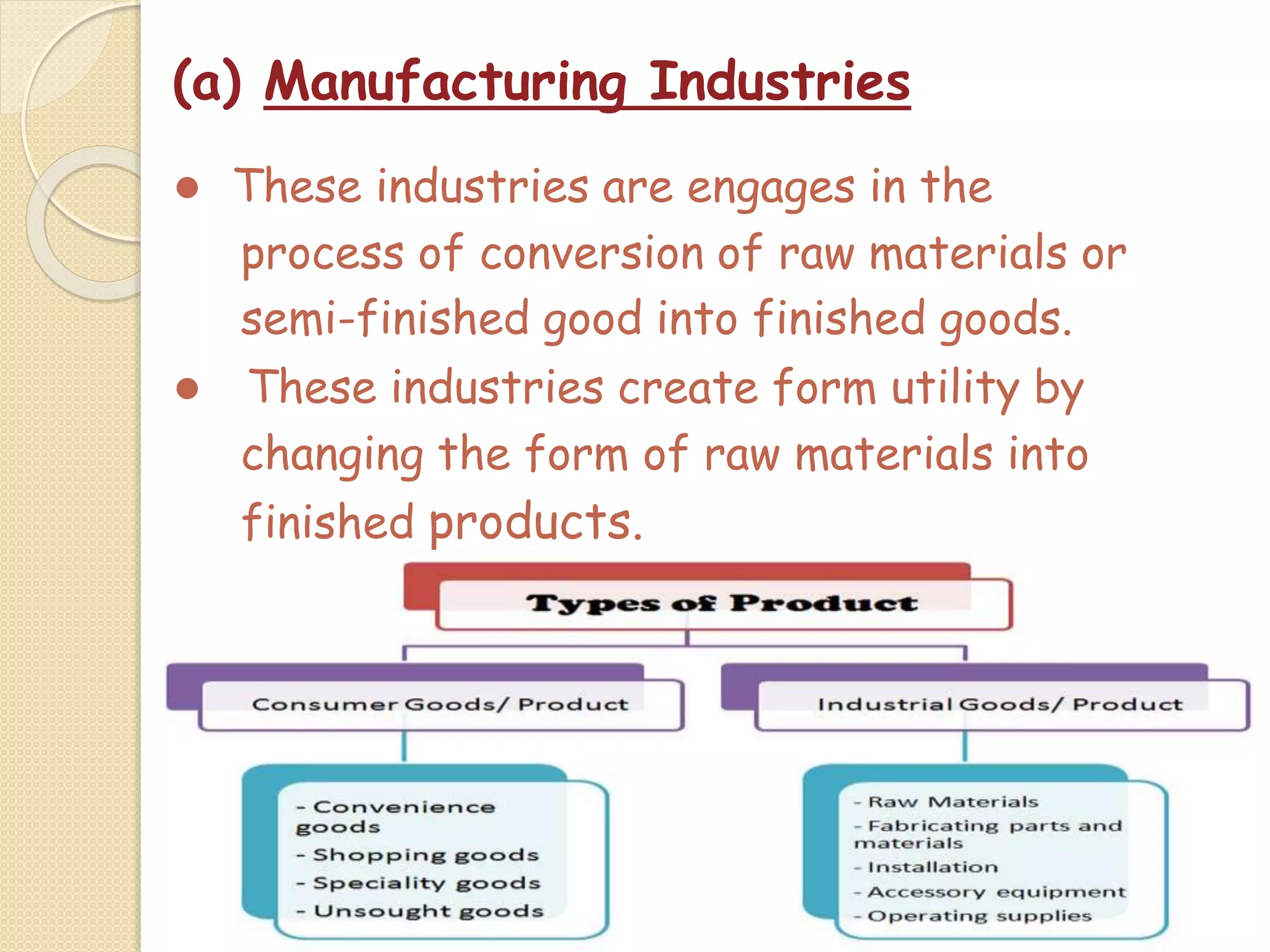
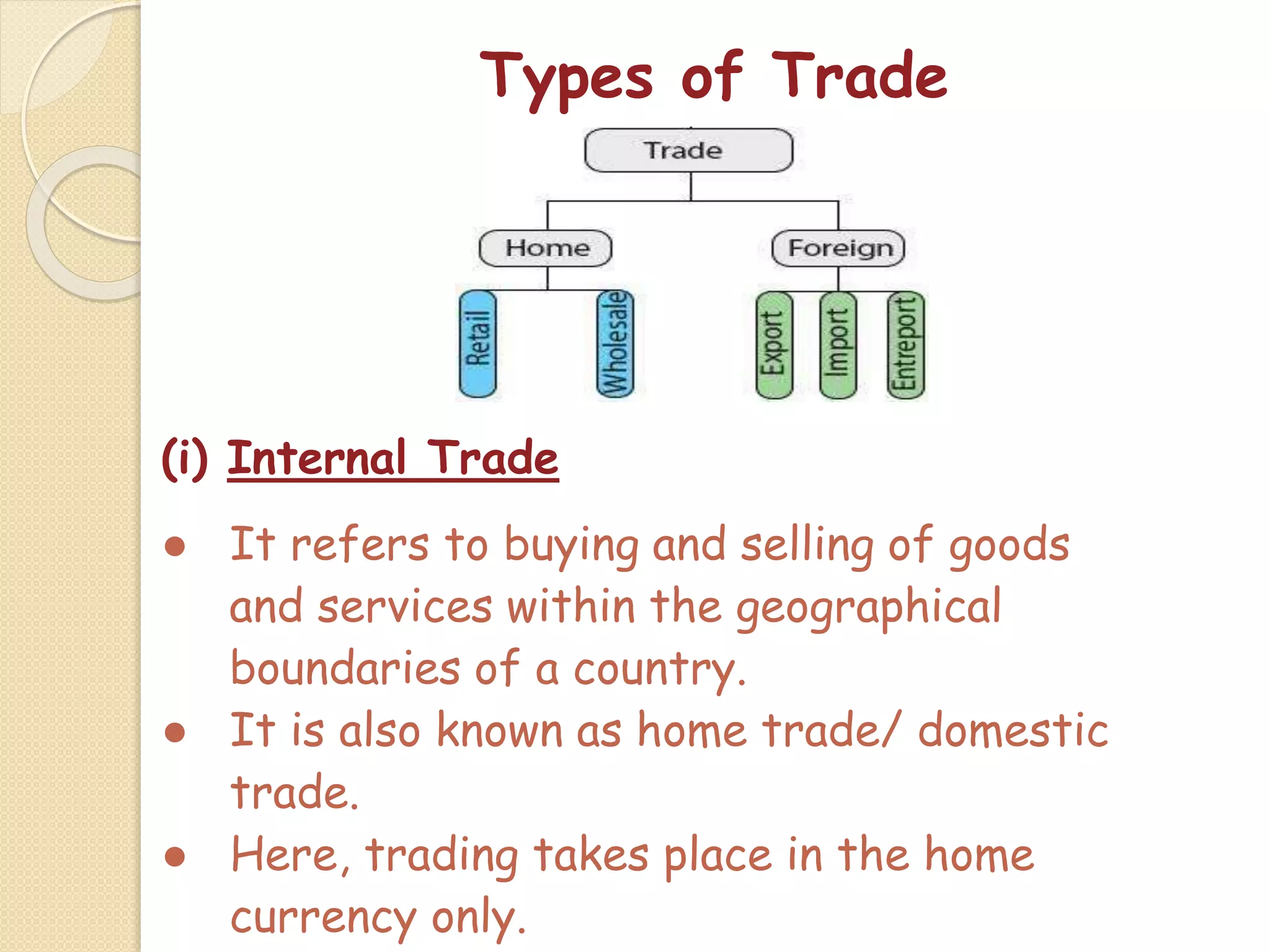
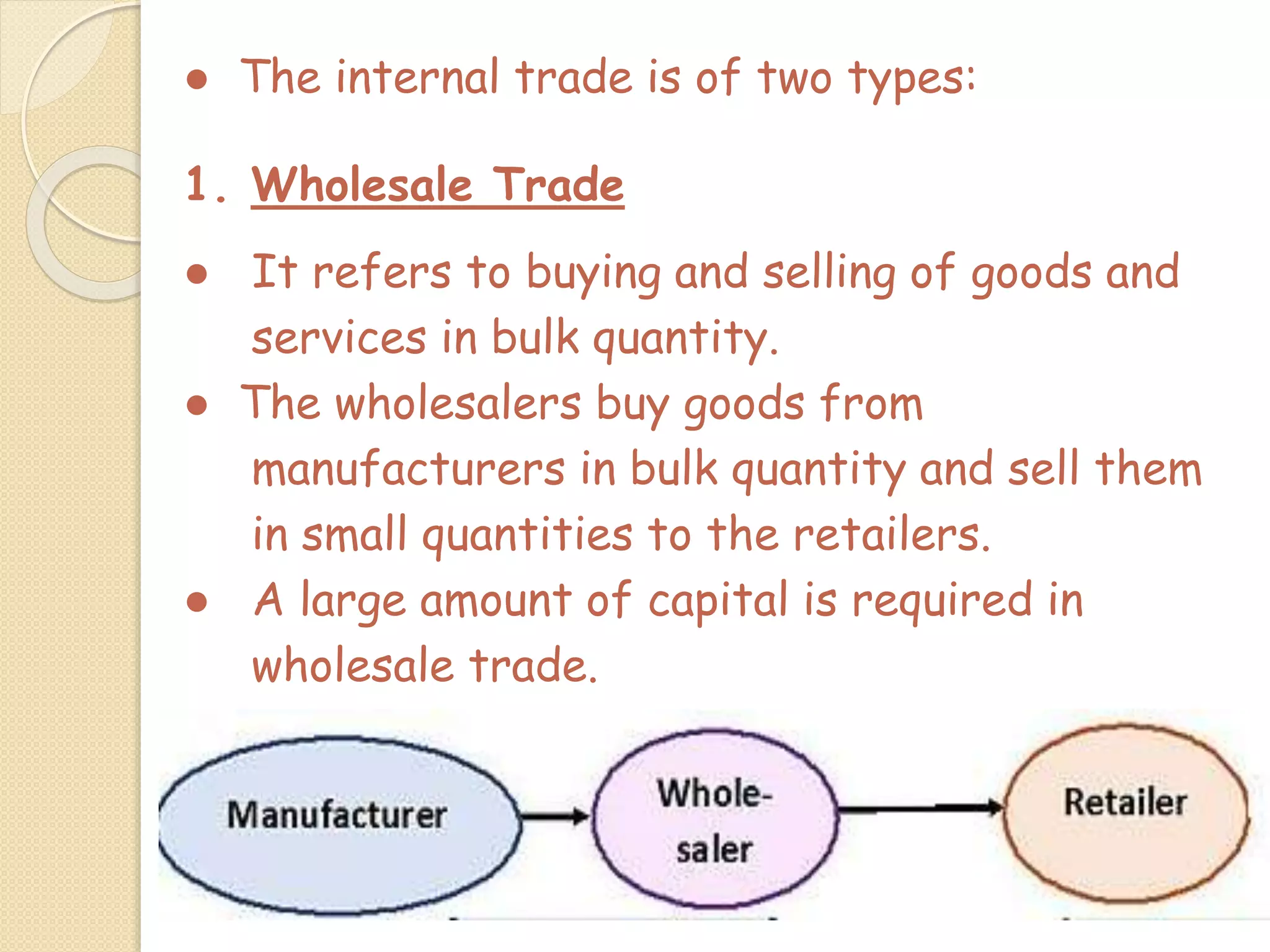
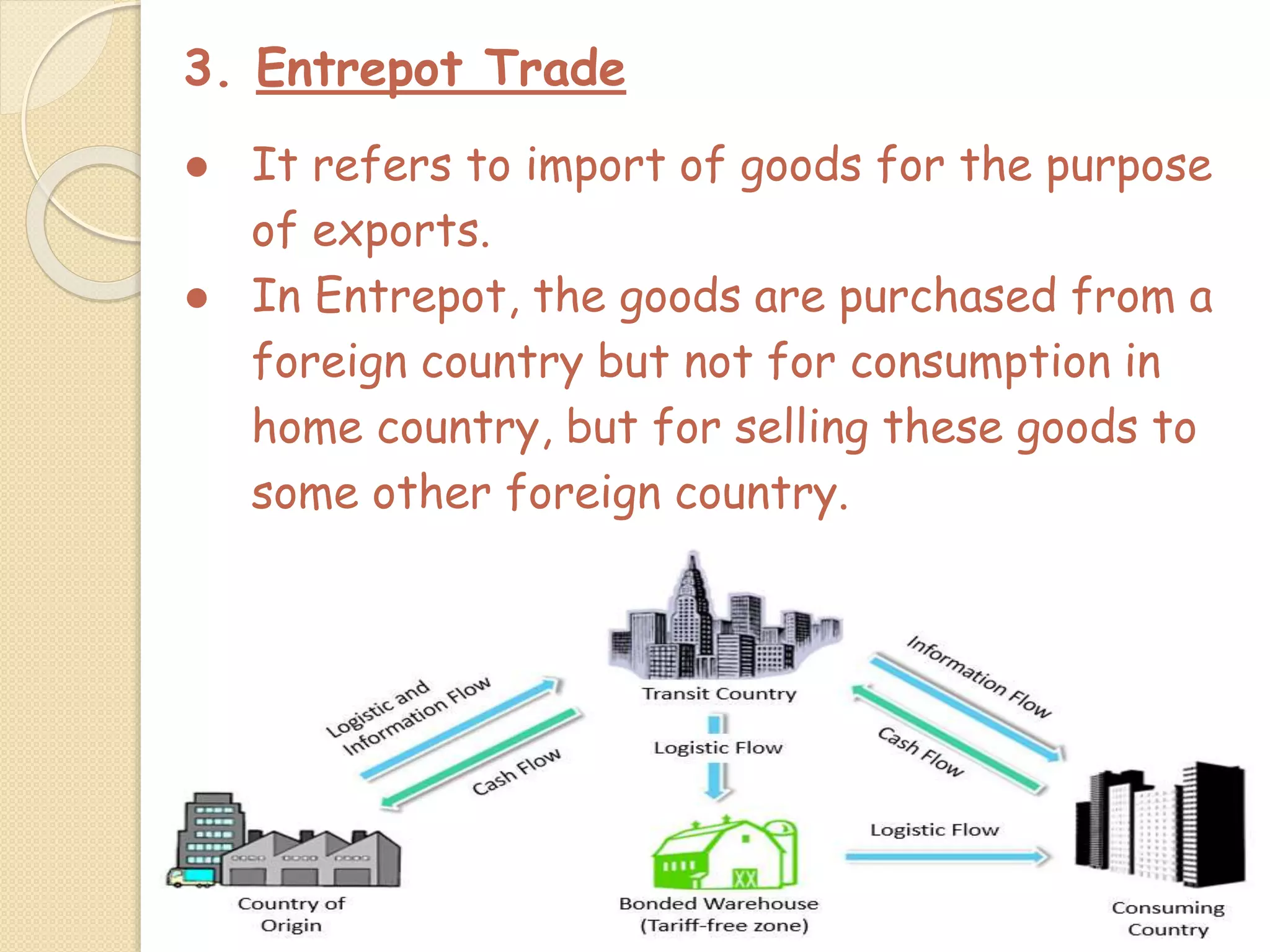
The document outlines the nature and purpose of business, distinguishing between economic activities aimed at earning profit and non-economic activities focused on personal satisfaction. It elaborates on various types of economic activities, including business, profession, and employment, while discussing the multiple objectives of business, such as economic growth, social responsibility, and employee welfare. Additionally, it classifies business activities into industries and commerce, emphasizing the role of trade and auxiliary services in facilitating business operations.