This document provides an overview of business and related concepts. It defines business as the sum of all economic activities from production to consumption of goods and services. Key points made include:
- Human activities are classified as either economic, which aim to earn money, or non-economic. Business falls under economic activities.
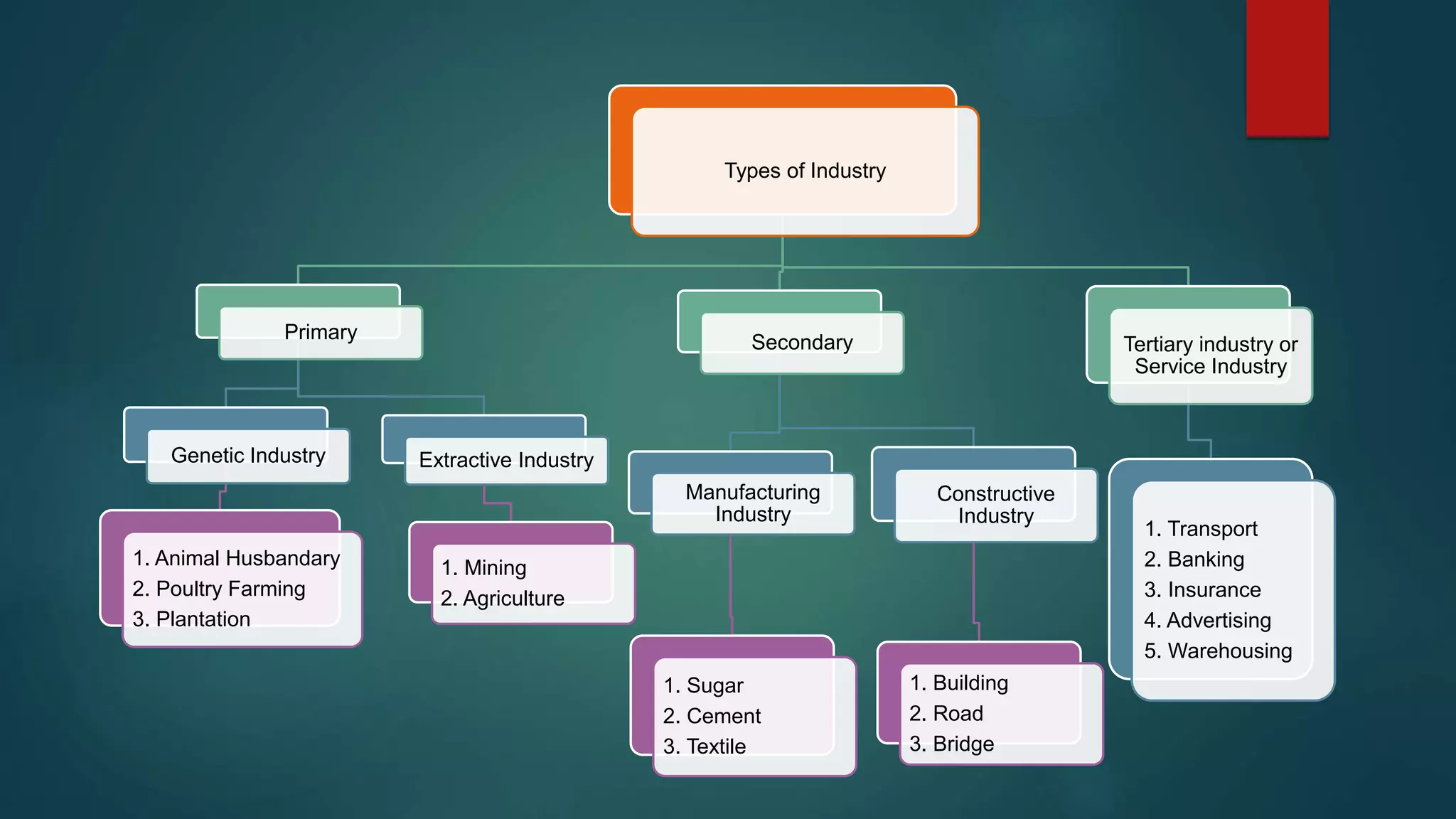
- Business encompasses industry, which is production, and commerce, which is the transportation of goods to consumers.
- Industry is further divided into primary, secondary and tertiary. Commerce involves trade and aids to trade like transportation and warehousing to overcome barriers.
- Characteristics of business are that it is an economic activity, involves exchange, has regular dealings, profit motive, risk, and
![Chapter-1
Business: An Introduction
BY: ISHA KALRA
ASSISTANT PROFESSOR [BBA AND MBA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganisationchapter-1-170814055048/75/Business-organisation-chapter-1-1-2048.jpg)