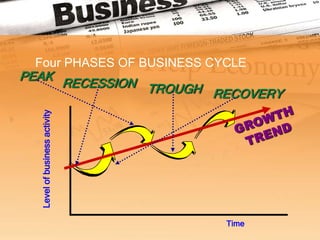
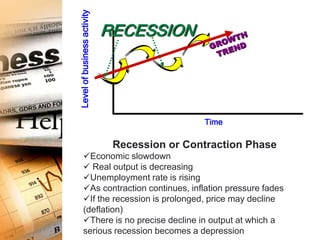
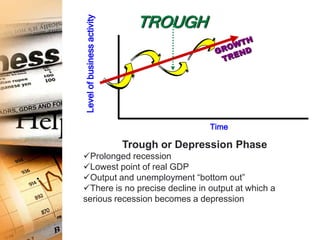
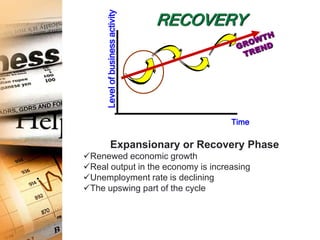
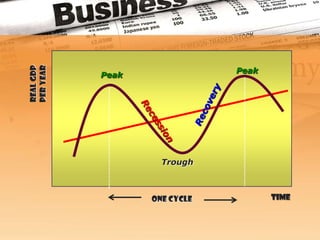
The business cycle refers to recurring periods of economic growth (expansion or prosperity phase) and contraction (recession phase) that occur over several years. There are four phases in the business cycle: peak, recession, trough, and recovery. During the peak phase, economic growth and activity are at their highest levels. The recession phase is a period of declining economic activity and rising unemployment. The trough marks the lowest point after which a recovery or expansion phase begins with renewed economic growth. Economists use indicators like unemployment claims and new orders to track and predict where the economy is in the business cycle.