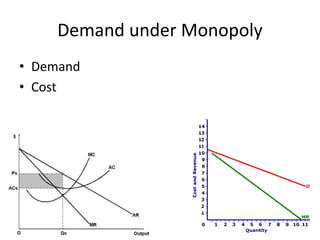
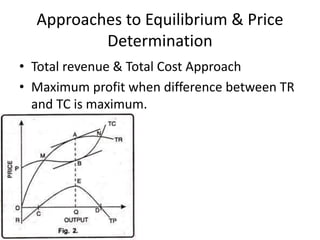
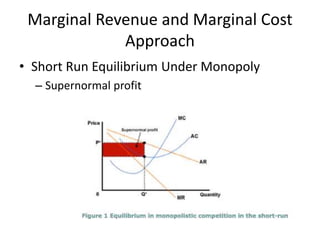
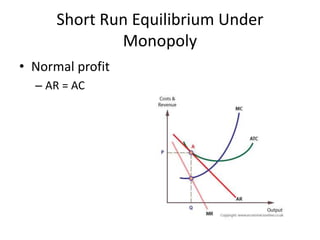
The document discusses the features and types of monopoly, emphasizing that a monopoly is characterized by a single seller with no close substitutes and barriers to entry. It explains price determination in monopolistic markets, detailing approaches to achieving equilibrium through marginal revenue and cost analysis, along with the short and long run scenarios. Additionally, the text addresses misconceptions about monopoly pricing compared to free competition and discusses the implications of demand elasticity on pricing strategies.