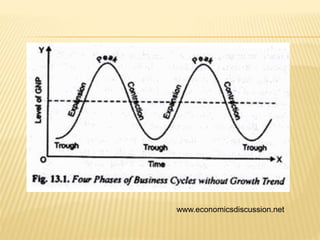
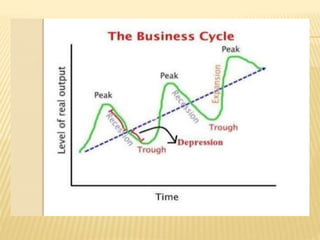
The document presents information on business cycles, including definitions, features, phases, causes, and measures to control business cycles. It defines business cycles as periodic fluctuations in economic activity measured by changes in GDP and other macroeconomic variables. The phases of a business cycle are expansion, peak, contraction, trough, and expansion again. Expansion involves recovery, boom and peak, while contraction involves recession, depression, and trough. Causes of business cycles include changes in bank lending, investments, consumption, demand and supply adjustments, and entrepreneur expectations. Fiscal and monetary policies are recommended to control business cycles.