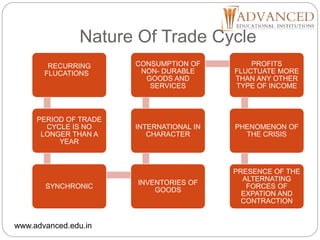
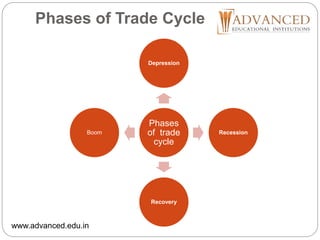
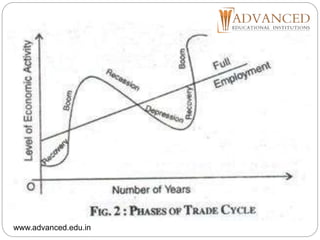
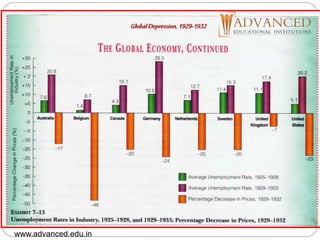
This document is a presentation by Geeta Malik on the topic of trade cycles. It defines a trade cycle as recurring periods of economic prosperity and recession that can last for several years. The document outlines the meaning, nature, causes and phases of trade cycles. It discusses fluctuations in trade cycles and lists the phases as boom, recession, depression, and recovery. Causes mentioned include banking operations, shifts between capital and consumer goods, purchasing power, and human psychology. The document also briefly discusses the global depression of 1929-1932 and preventive and corrective measures that can be used to control trade cycles.