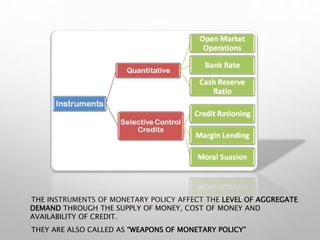
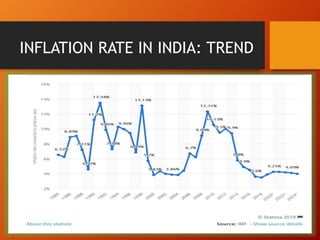
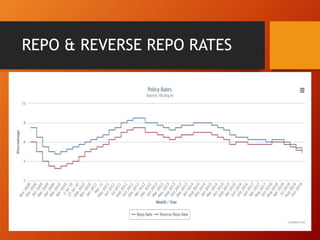
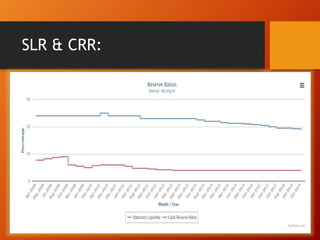
The document outlines the role of monetary policy in managing a country's economy, primarily through the actions of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as the monetary authority. It details various instruments and objectives of monetary policy, including the control of money supply and interest rates to achieve goals like inflation management and economic growth. Additionally, it discusses the framework of the Monetary Policy Committee and its process of operation and transparency in decision-making.