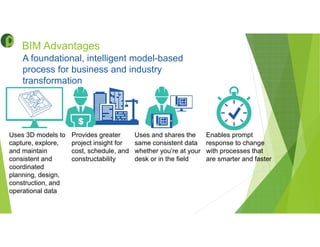
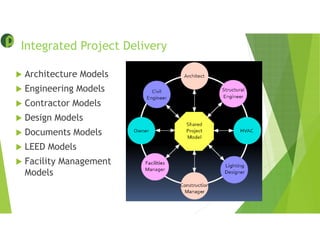
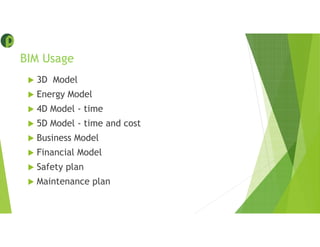
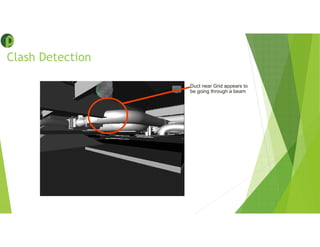
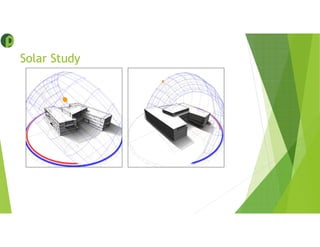
This document provides an overview of building information modeling (BIM) including its introduction, advantages, usage, examples, and future. BIM is a methodology for gathering and maintaining project information in a digital format to enable quick decision making throughout the project lifecycle. Key advantages of BIM include using consistent 3D models to capture coordinated planning and design data, providing greater project insight for cost and scheduling, and enabling prompt response to changes. BIM can be used for 3D modeling, energy analysis, 4D scheduling, 5D cost estimation, and facility management. The future of BIM is connecting digital models to physical systems for ongoing building operations and leveraging data efficiencies.