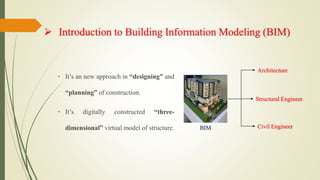
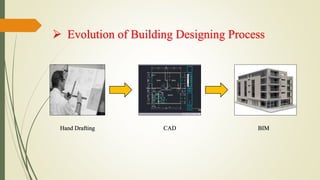
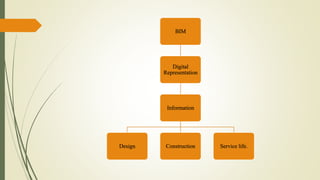
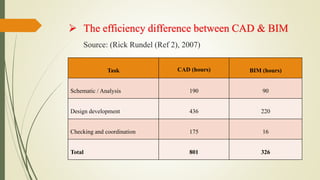
The seminar discussed Building Information Modeling (BIM) and its advantages over traditional CAD. BIM is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building and extends beyond 2D and 3D drawings to represent a building's width, height, time, cost and environmental impacts. It allows for more collaborative work and better decision making compared to CAD. Popular BIM software includes Revit, BIM 360 and Archicad. While BIM provides benefits like simulation and parametric modeling, it also faces challenges like a lack of specialists and software incompatibility. The seminar concluded that BIM is a promising new approach that saves time and improves construction quality through better communication of information.















![Reference:
1) “Scope of Building Information Modeling (BIM) in India” by J. Vinoth Kumar and Mahua
Mukherjee.
2) Rick Rundell, AIA. The Five Fallies of BIM, Part 1. cadalyst. [Online],
http://aec.cadalyst.com/aec/Column:+1-2-3+Revit/The-Five-Fallaciesof-BIM-Part-1-1-2-
3Revit-Tutor/ArticleStandard/Article/detail/470107, (November 1, 2007).
3) BIM methodology, a new approach - case study of structural elements creation by Lino
Maiaa,b*, Pedro Mêdab, João G. Freitasa.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bim-190113125532/85/Bim-20-320.jpg)
