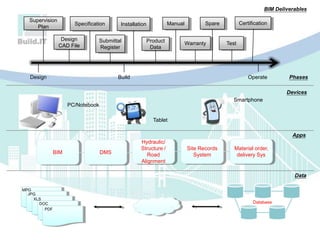
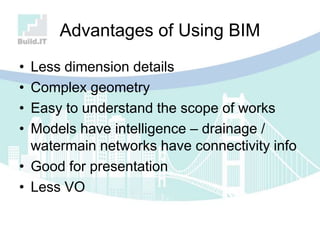
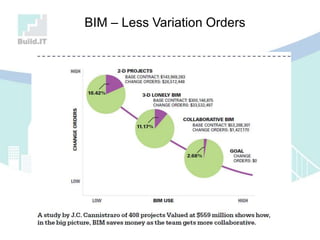
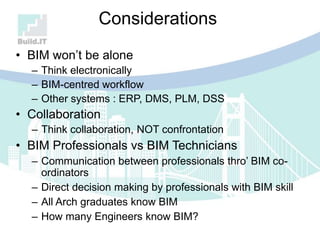
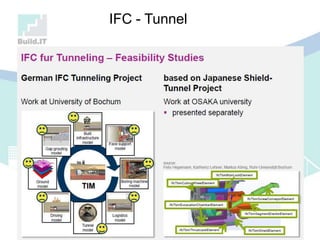
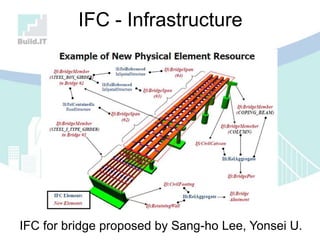
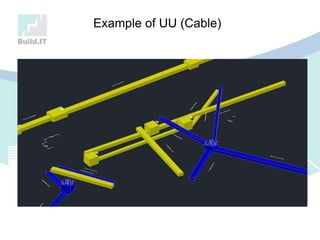
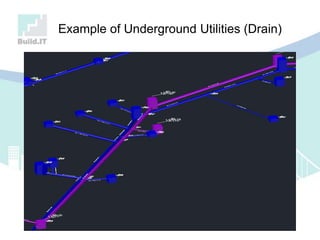
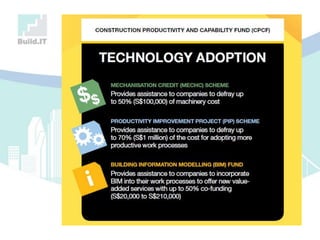
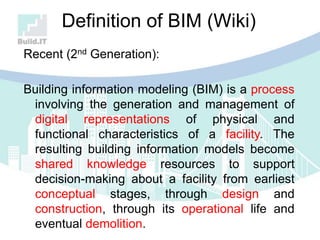
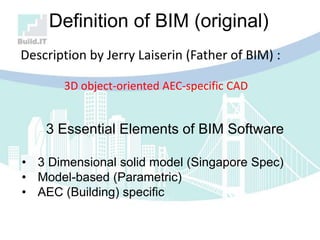
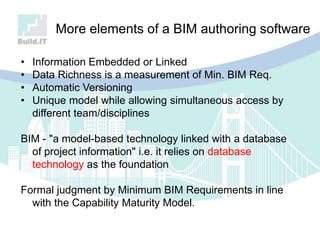
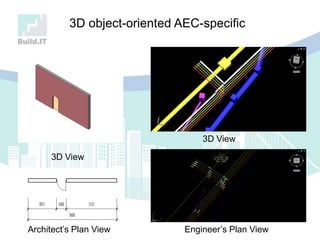
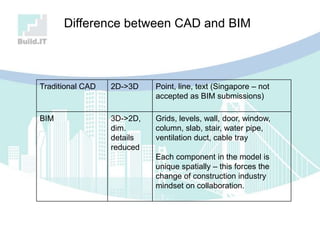
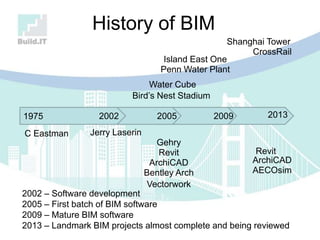
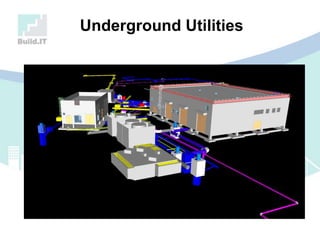
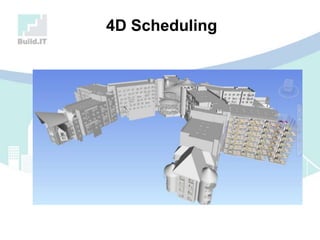
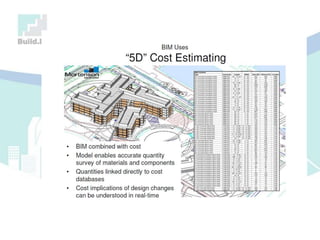
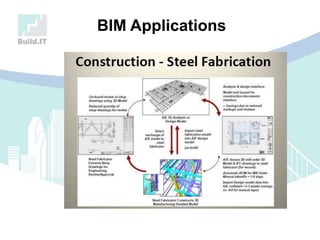
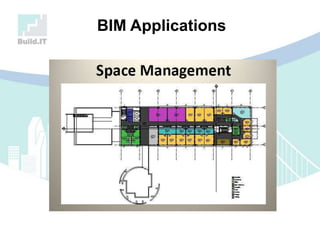
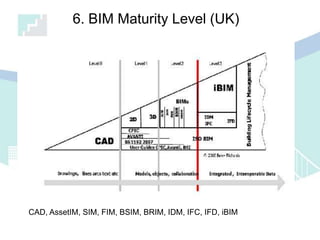
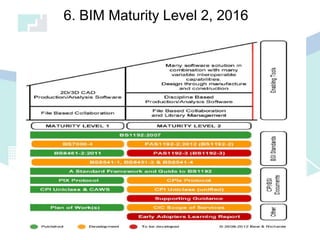
The document discusses the implications of Building Information Modeling (BIM) for civil engineers, emphasizing its importance in generating digital representations for decision-making throughout a facility's lifecycle. It outlines essential elements of BIM software, differences between traditional CAD and BIM, and the historical development and application of BIM in civil engineering. Additionally, the document highlights lessons learned, challenges, and advantages of BIM, including improved cost estimation and reduced project time.


















![2011-2015年建筑业信息化发展纲要
关于印发《2011-2015年建筑业信息化发展纲要》的通知 建质[2011]67号
各省、自治区住房和城乡建设厅,直辖市建委(建交委),新疆生产建设兵团建设局,中央管理的有关企业:
现将《2011-2015年建筑业信息化发展纲要》印发给你们,请结合实际贯彻执行。执行中有何问题和建议,请及时告我部工程
质量安全监管司。
中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部
二〇一一年五月十日
“十二五”期间,基本实现建筑企业信息系统的普及应用,加快建筑信息模型(BIM)、基于网络的协同工作等新技术在
工程中的应用,推动信息化标准建设,促进具有自主知识产权软件的产业化,形成一批信息技术应用达到国际先进水平的建
筑企业。
(2)应用系统
①设计与施工集成系统 (Integrated Design and Construction System)
。
②工程项目管理系统 (Engineering Project Management System)
。
③项目文档管理系统 (Project Document Management System)
。
④材料与采购管理系统 (Material Order Management System)
。
⑤企业运营管理系统 (Enterprise Operation Management System)
。
⑥ 综合管理系统 (Integrated Management System)
。
⑦辅助决策系统 (Decision Support System)
。
⑧知识管理系统与智能企业门户 (Knowledge Management System)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildit-ibim-iceshared-140512160905-phpapp02/85/What-does-BIM-mean-for-Civil-Engineers-53-320.jpg)