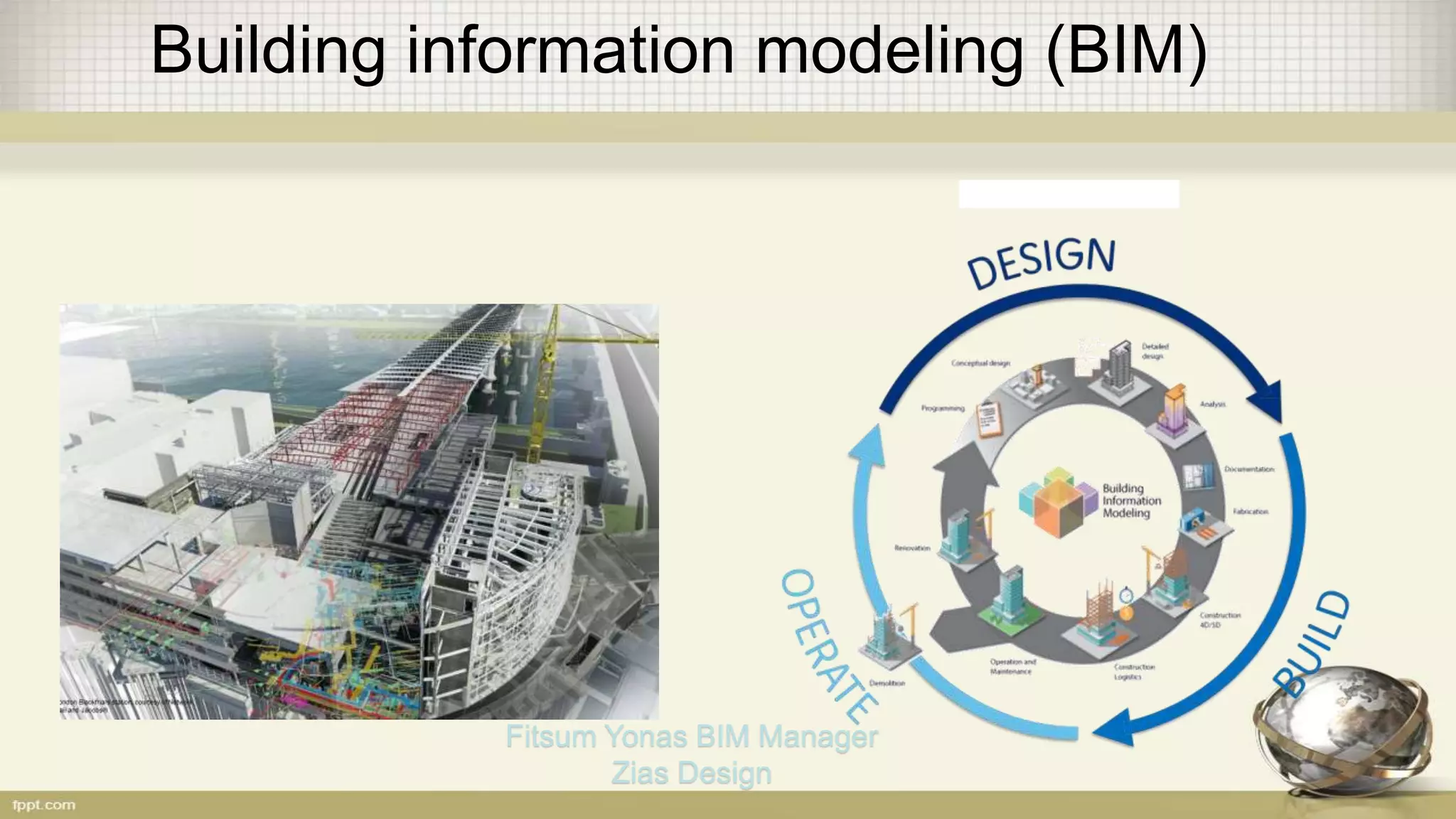
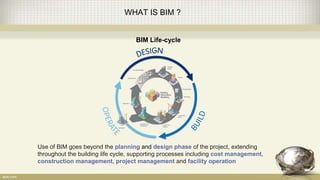
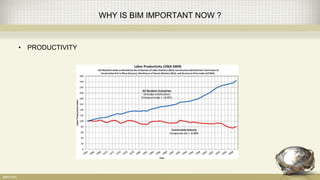
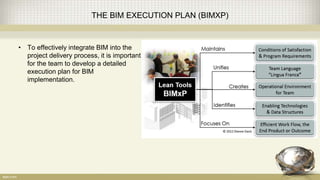
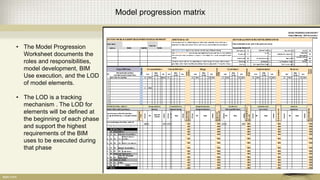
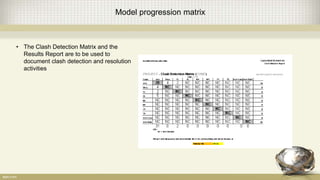
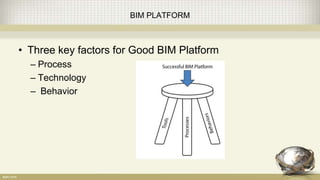
Building information modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building. A BIM is a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility from its earliest design through demolition. BIM supports various project processes throughout the building lifecycle including cost management, construction management, project management, and facility operation. The document discusses what BIM is, why it is important now in terms of productivity, interoperability, and building energy efficiency, and outlines aspects of developing an effective BIM execution plan such as defining model progression, identifying BIM uses and conditions of satisfaction, and outlining collaboration procedures.