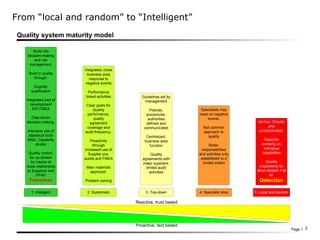
The document discusses moving quality inspections earlier in the production process to reduce costs. It presents a model showing the distribution of quality costs throughout production, from development to after sales. The goal is to shift from a reactive, trust-based quality system to a proactive, fact-based one by building quality into decision making, supplier qualifications, and development processes. A five-level quality system maturity model ranges from local and random inspections to an intelligent system that integrates quality across the business through data-driven decision making, supplier audits, and clear quality performance goals.