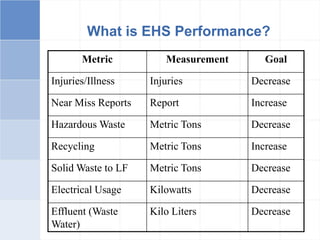
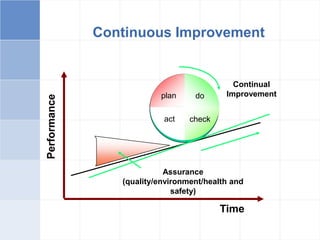
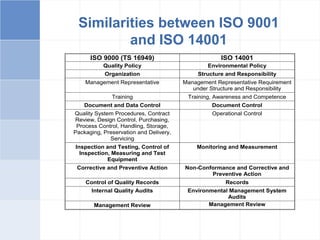
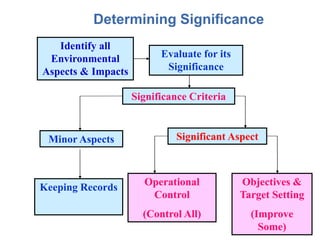
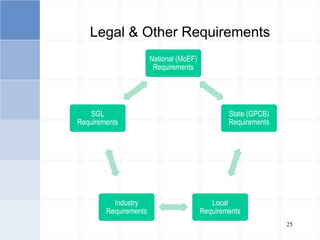
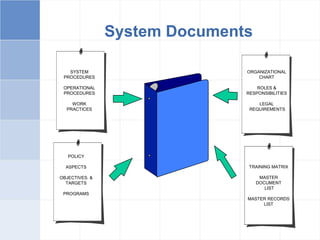
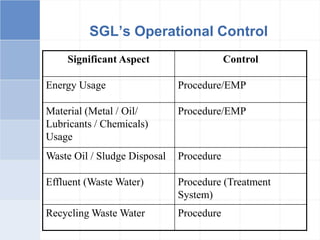
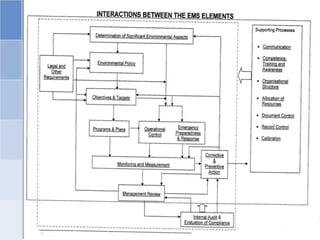
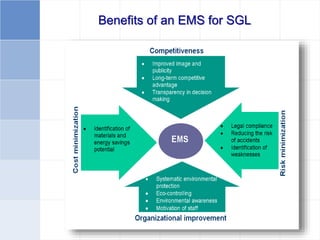
The document outlines a training program on ISO 14001 compliance for managers and supervisors at Steelco Gujarat Ltd., focusing on environmental management systems (EMS) and the responsibilities associated with its implementation. It emphasizes the importance of minimizing environmental impact, legal compliance, and continuous improvement in environmental performance. Key elements discussed include identifying significant environmental aspects, setting objectives, and ensuring employee involvement and training for effective EMS operations.