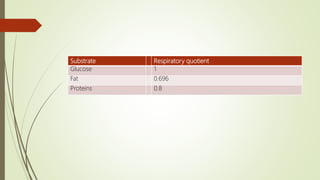
The respiratory quotient is the ratio of carbon dioxide produced to oxygen consumed during respiration over a period of time. It can be used to calculate oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production and reflects the metabolic rate of an organism. The RQ of most animals at rest is 0.8-0.9 and for humans is 0.85. The RQ varies depending on the substrate being oxidized, with glucose having an RQ of 1, fat of 0.696, and proteins of 0.8. The type of respiration, aerobic or anaerobic, can also be determined from the RQ.