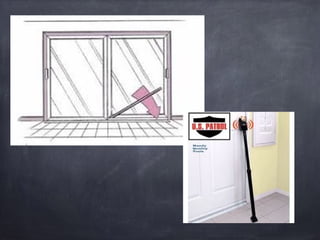
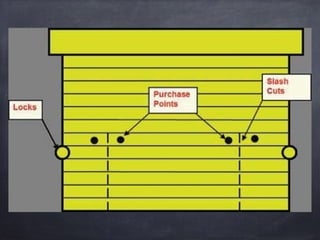
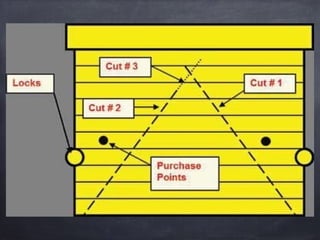
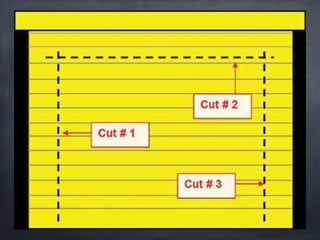
This document provides guidance on forcible entry techniques for firefighters. It discusses selecting the appropriate tools, assessing door types and constructions, and demonstrating techniques for gaining entry through various doors and barriers. The objectives are to understand tool applications, describe basic door components, achieve safe entry without damage, and control openings for ventilation and crew egress. Common door types like wood, metal, and glass are examined along with locks, hinges, security bars and high security features. Effective and controlled forcible entry methods are presented.