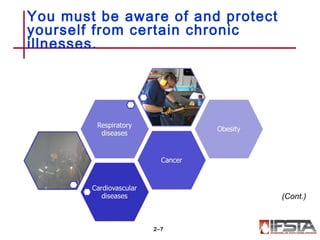
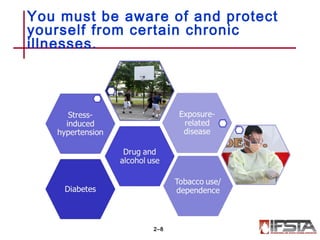
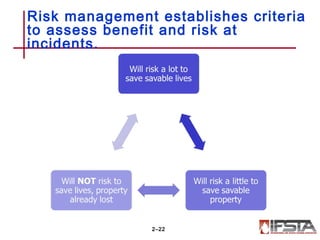
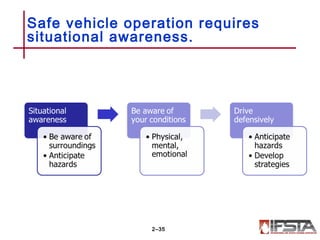
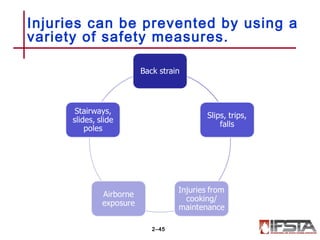
This document summarizes firefighter safety and health guidelines. It outlines 14 learning objectives covering common firefighter injuries and illnesses, NFPA safety standards, OSHA regulations, risk management principles, safety programs, health issues, safe vehicle operation, apparatus safety, injury prevention, tool safety, training safety, emergency scene safety, scene management, and personnel accountability. Safety is essential for firefighters to complete their mission safely and effectively.