This document discusses doors and windows made of aluminum. It provides details on different types of doors including exterior, interior, materials used for construction, and factors for selection like fire resistance and cost. It also describes door frames, panel doors, and swinging direction. For metal doors, it notes the most common materials used and grades available. The document also discusses door operation types, weather stripping, hardware including locks and hinges, and special doors like revolving doors. Finally, it covers window terms, materials, types, and basic locking hardware options.



![Metal Doors
Most hollow core metal doors are made of
carbon steel
Most are filled with standard fireproof, rot
proof, and sound-deadening material
Insulated doors are filled with glass fiber or
plastic foam insulation [R-values range from
8-15]
Grades range from 1: standard; 2: heavy
duty; 3: extra heavy duty [grades used
depends on type of building and locations in
building]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-150803052533-lva1-app6891/85/1-doors-and-windows-4-320.jpg)





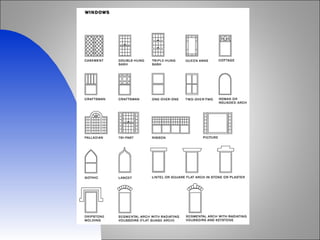
![Windows
Related terms include: rail, stile, sill, sash,
panes or lights (glass), muntin (divides the
lights), mullion
Common materials include: aluminum, steel
(including stainless), wood, or clad materials
[Styrofoam core with wood cladding]
Wide range of sizes from 2’ to 10’ – not
including custom orders](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-150803052533-lva1-app6891/85/1-doors-and-windows-10-320.jpg)