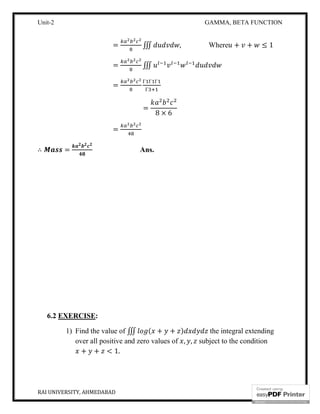
This document discusses the gamma and beta functions. It defines the gamma function and lists some of its key properties. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to evaluate integrals using gamma function properties. The beta function is then defined and its relationship to the gamma function explained. Dirichlet's integral theorem and its extension to multiple dimensions is covered. Applications to finding volumes and masses are demonstrated. References for further reading on gamma and beta functions are listed at the end.





![Unit-2 GAMMA, BETA FUNCTION
RAI UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD 8
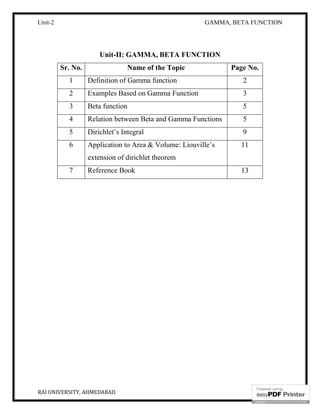
Example 2: Find the value of .
Solution: We know that,
=
Γ .
2Γ
Putting = = 0, we get ∫ =
[ ] ⁄
= Γ
= Γ
Γ =
Γ = √ _______ Ans.
Example 3: show that ∫ √ =
Solution: We know that,
∫ =
Γ .
Γ
∫ √ = ∫
⁄
⁄
= ∫ ⁄ ⁄
On applying formula (1), we have
∫ √ =
Γ Γ
Γ
=
Γ Γ
Γ( )
= Γ Γ
∴ ∫ √ = Γ Γ __________ Ans.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/690538b1-0a8e-4e6e-9bcc-bcd31cfbc843-160126121831/85/B-Tech-II_Unit-II-8-320.jpg)


![Unit-2 GAMMA, BETA FUNCTION
RAI UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD 11
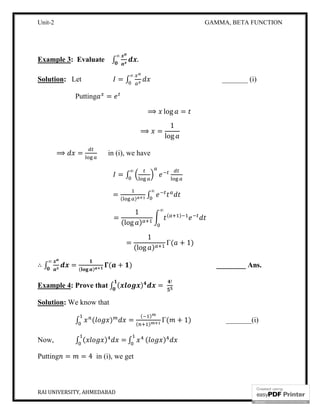
… … …
=
Γ Γ Γ … Γ
Γ(1 + + + ⋯ + )
ℎ ⋯
Example 1: Prove that ∫
( )
( )
=
∞
Solution: Let = ∫
( )
( )
∞
= ∫ ( )
∞
+ ∫ ( )
∞
= + __________ (i)
Now, put = , when = 0, = 0; when = ∞, = 1
1 + = 1 + =
=
( )
∴ =
1 −
. (1 − ) .
1
(1 − )
= ∫ (1 − )
= (5,10) _______(2)
And = ∫ . (1 − ) .
( )
= ∫ (1 − )
= (10,5) ________(3)
∴ = +
= (5,10) + (10,5) [Using(2) and (3)]
= (5,10) + (5,10) [ ( , ) = ( , )]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/690538b1-0a8e-4e6e-9bcc-bcd31cfbc843-160126121831/85/B-Tech-II_Unit-II-11-320.jpg)