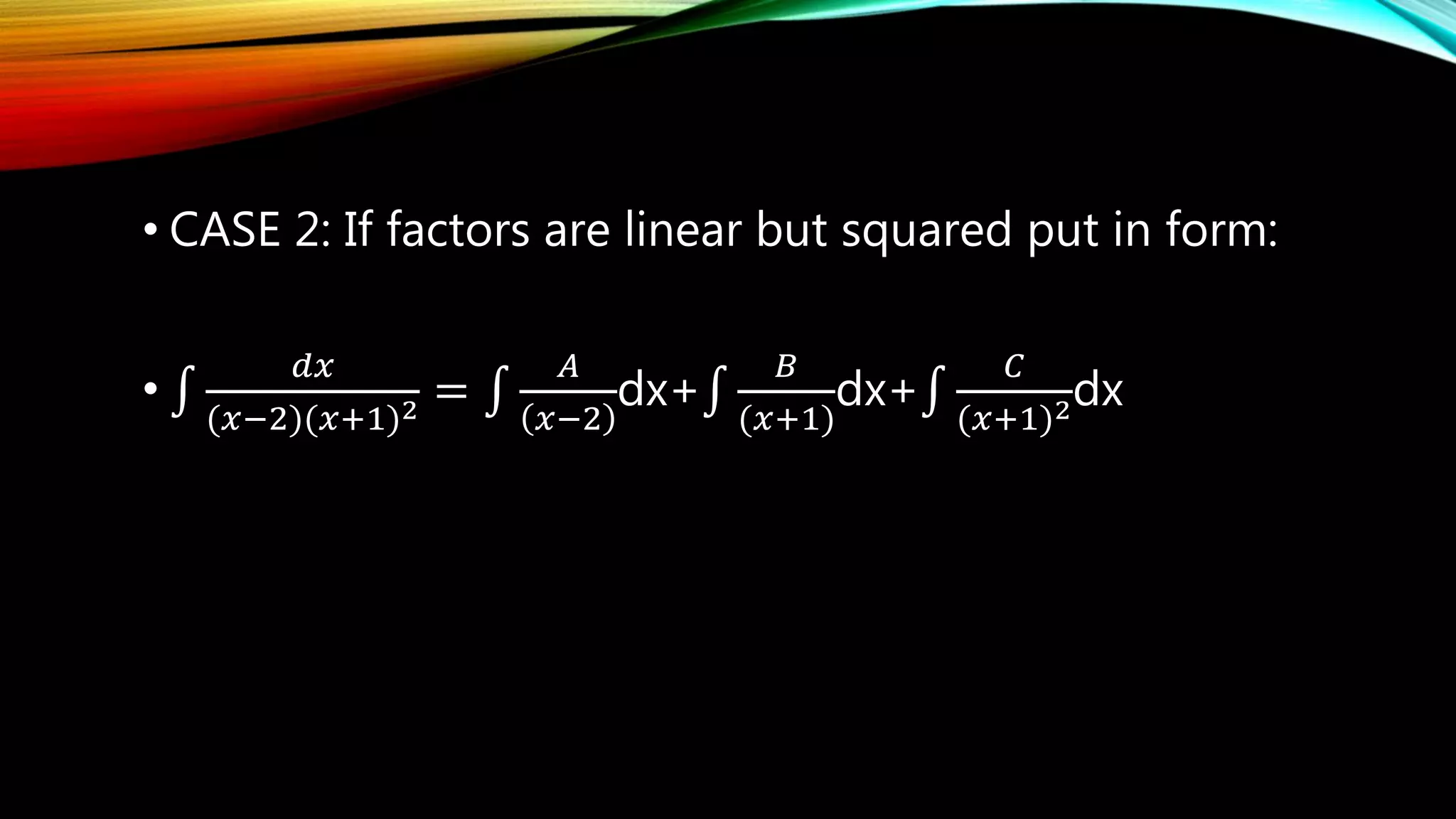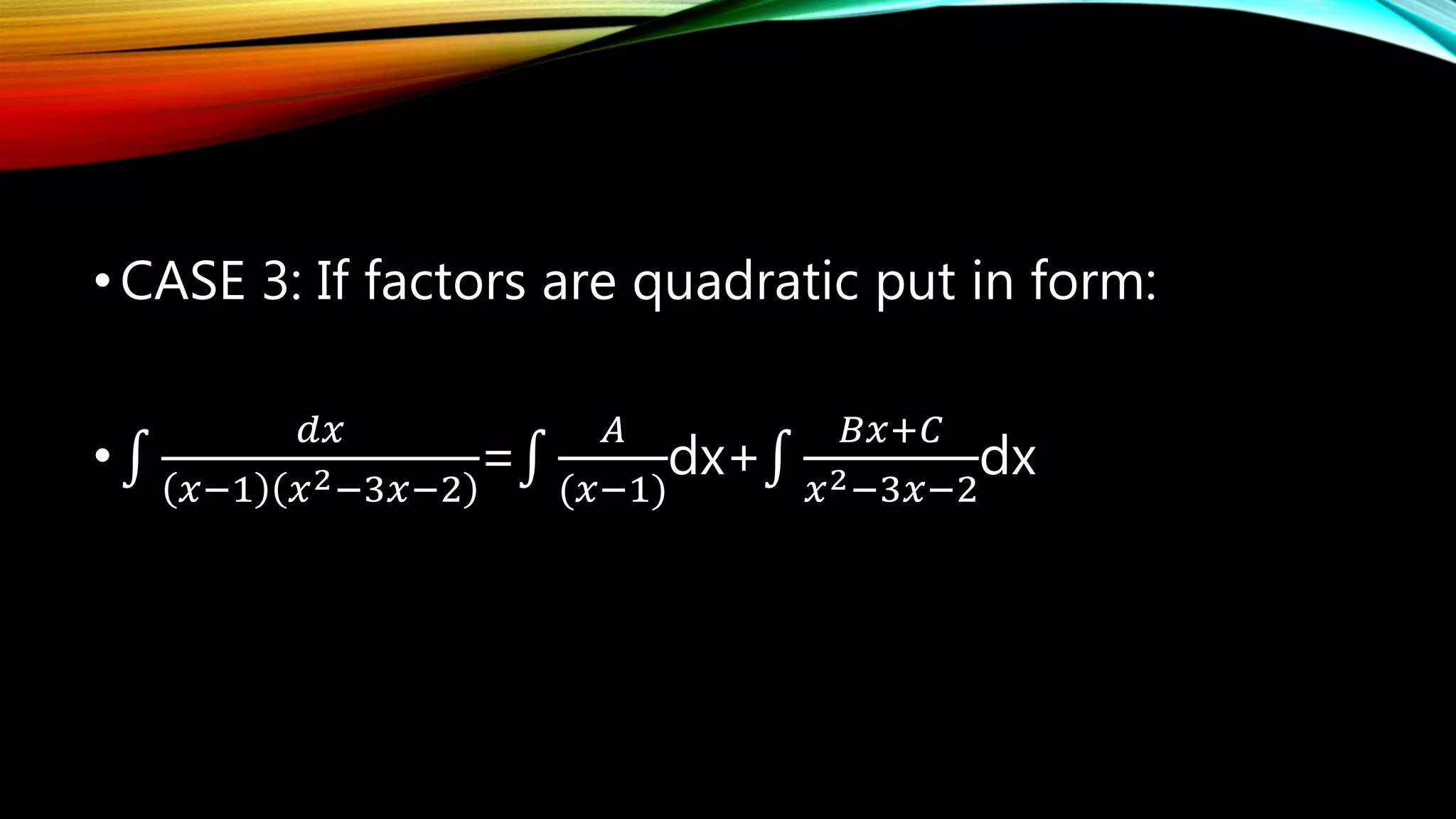Embed presentation
Downloaded 183 times




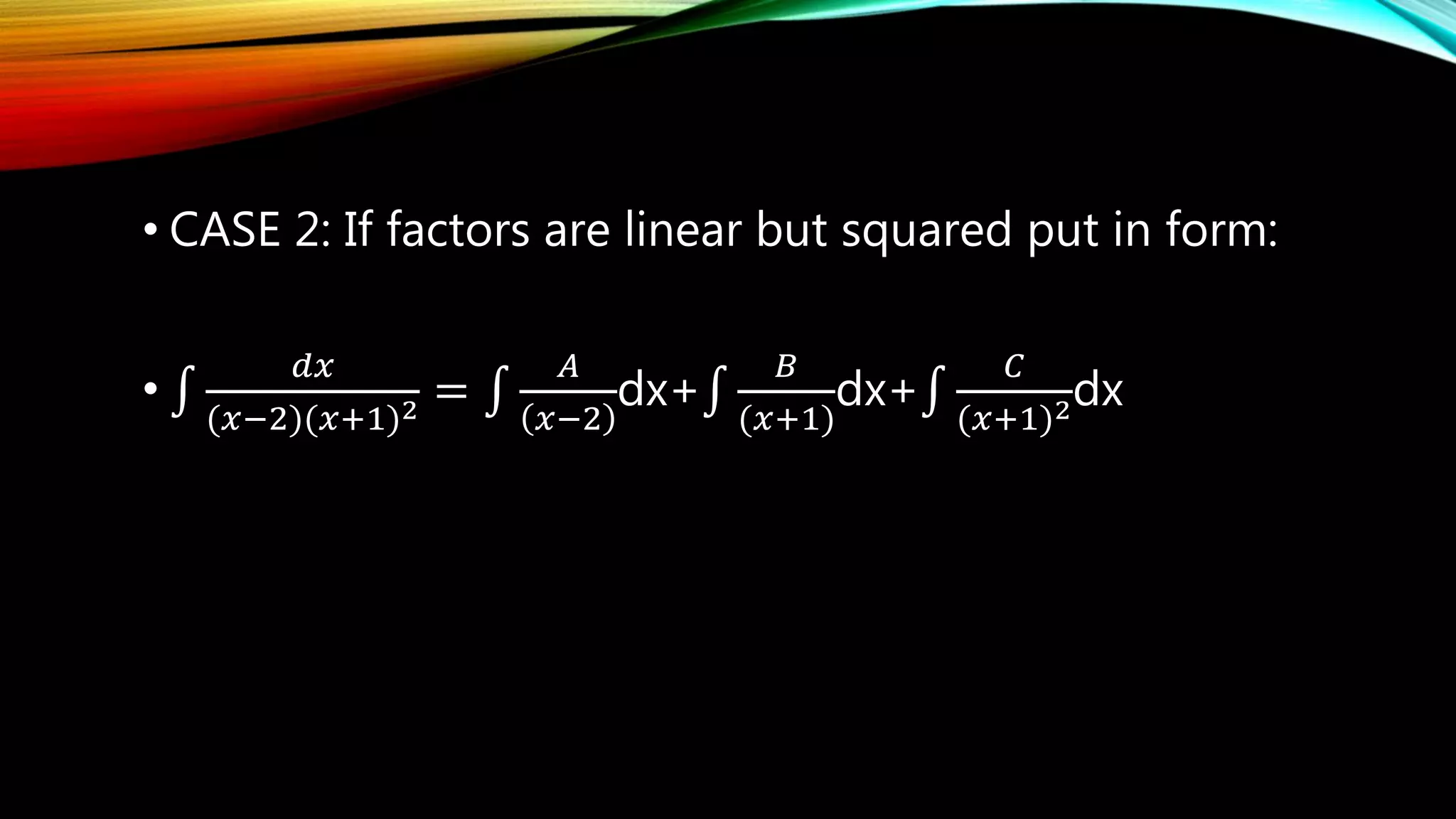
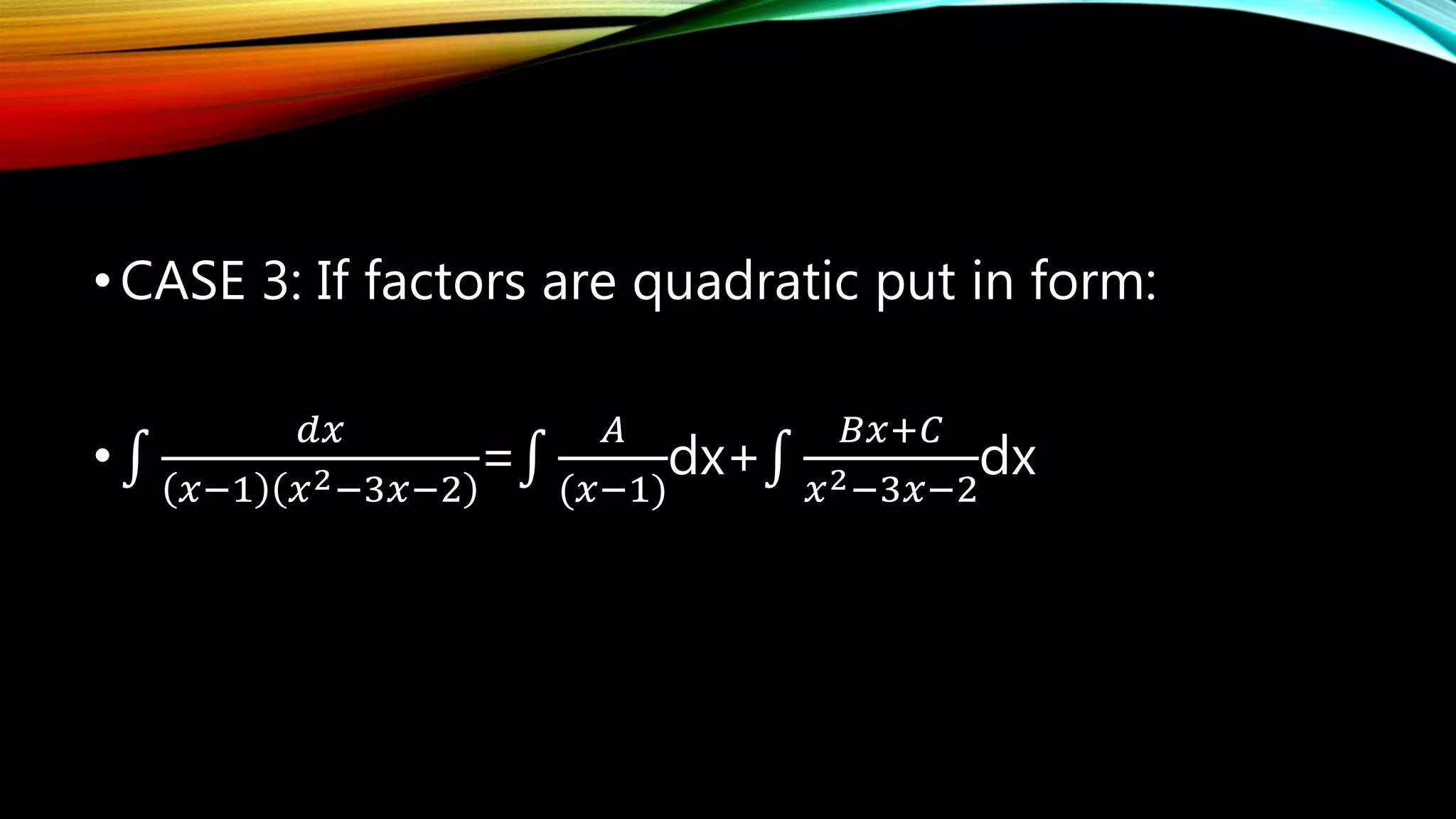

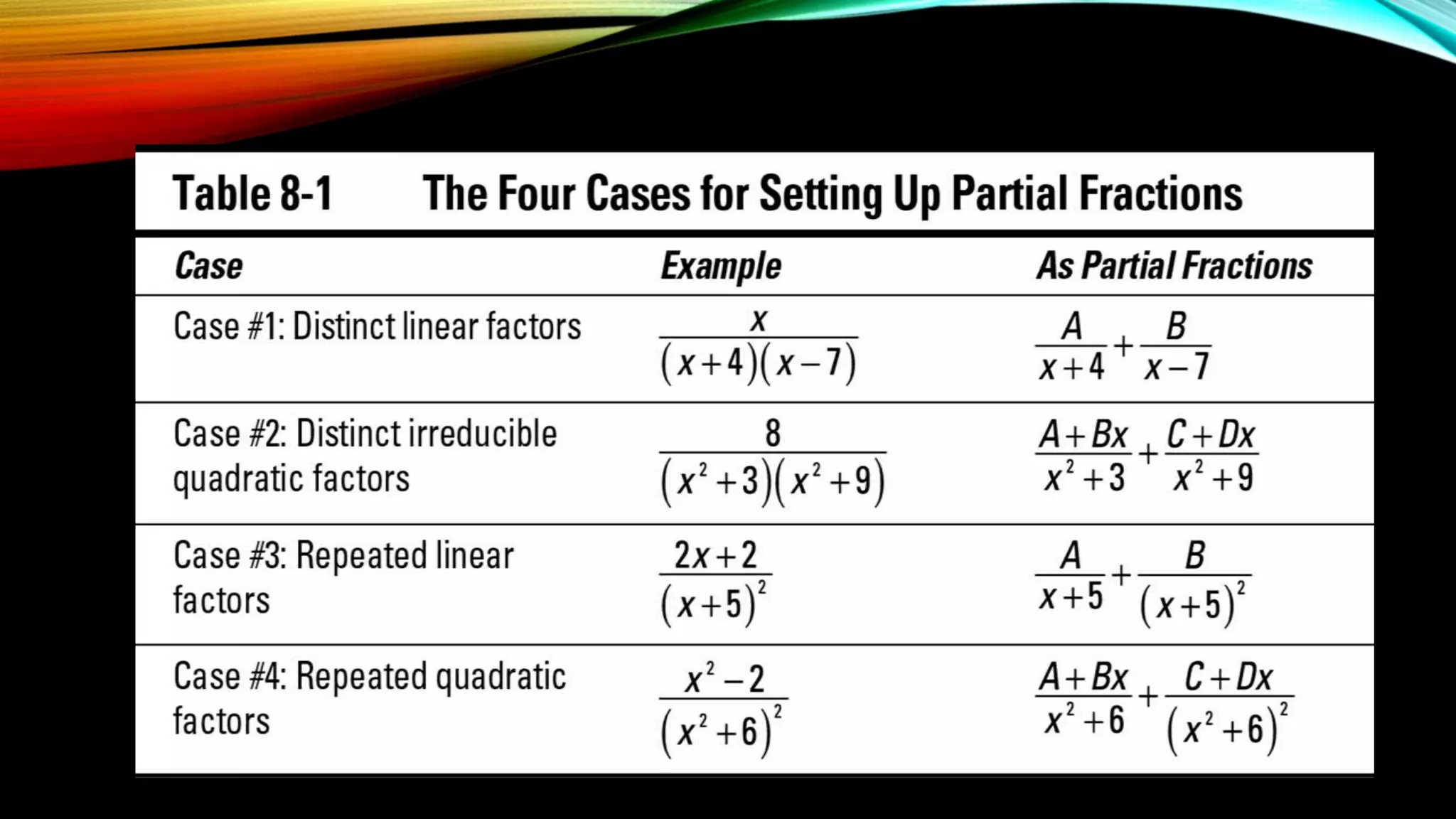
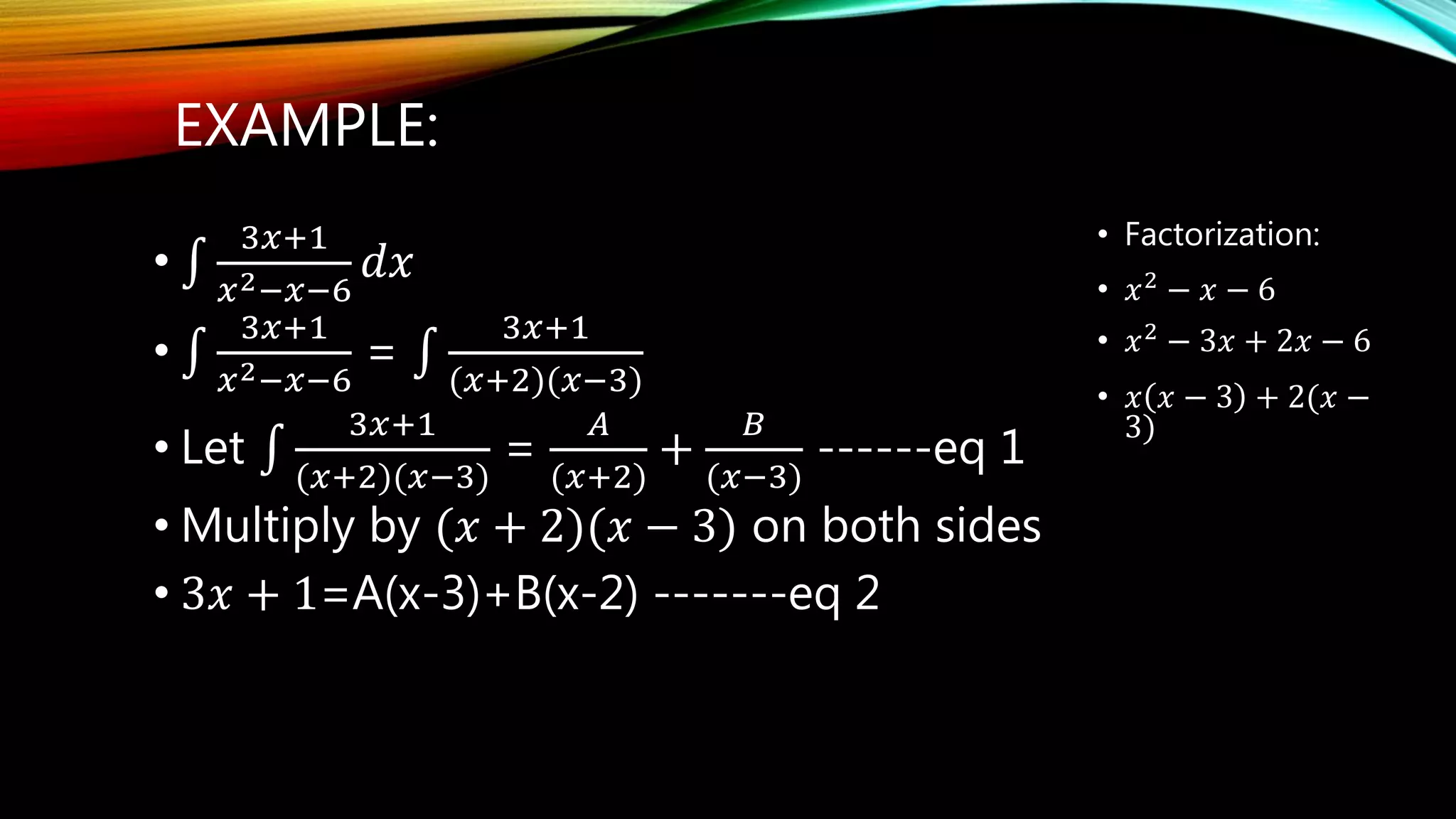

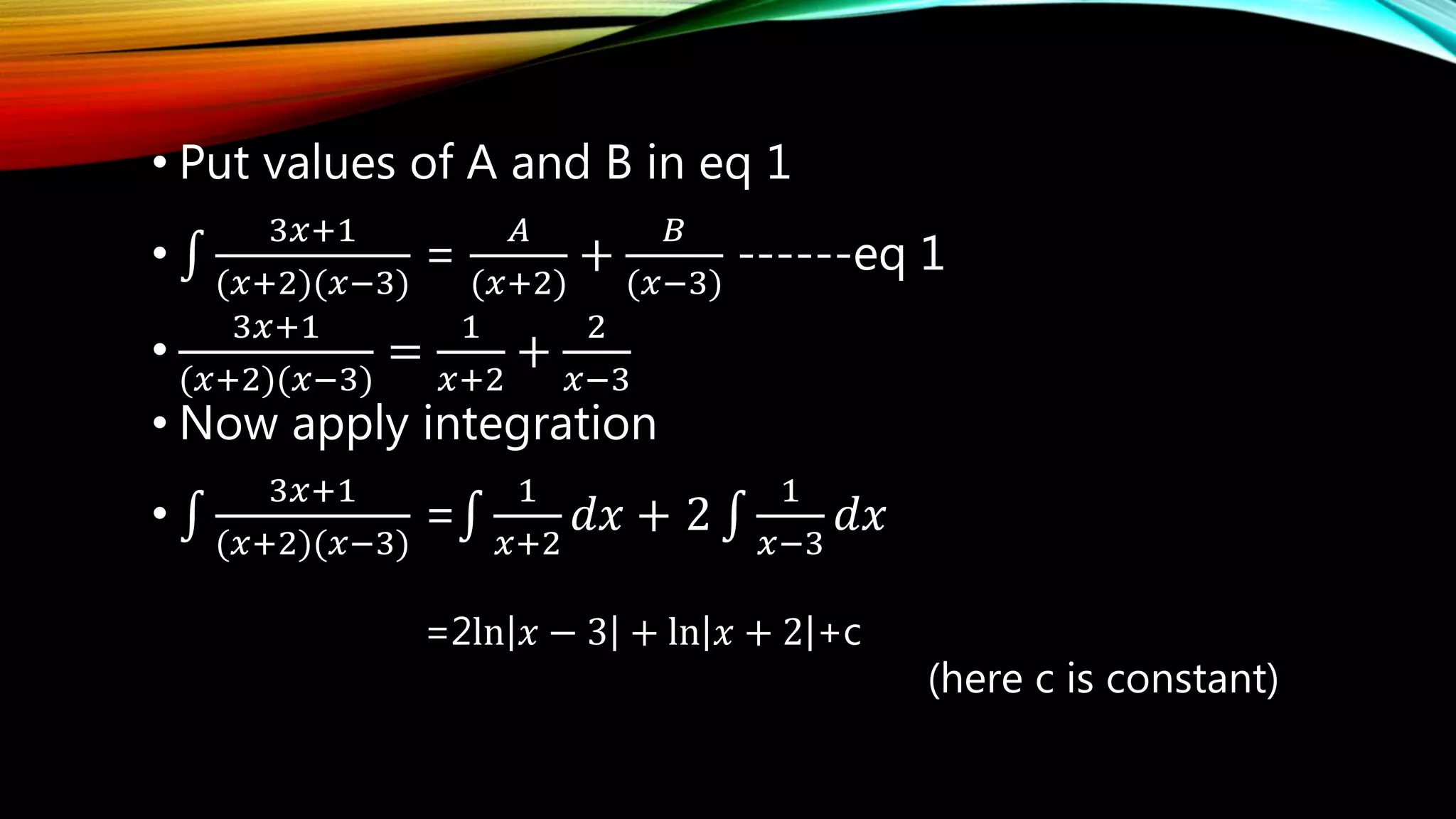

The document outlines the process of integration by partial fractions, describing various cases based on the types of factors in the denominator. It provides a series of steps to factorize denominators and solve integrals using different configurations depending on whether factors are linear or quadratic. An example is used to illustrate these steps, showing the solution for the integral of a specific rational function.