1. The document derives formulas for the nth derivative of several standard functions:
- y = xm yields Dn xm = m!/(m-n)! xm-n
- y = ax + bm yields Dn(ax + bm) = m!/(m-n)! an ax + bm-n
- y = 1/(ax + b) yields Dn 1/(ax + b) = (-1)n n! an/(ax + b)n+1
2. It also provides the nth derivatives of more complex functions like logarithmic and fractional functions by using the above formulas.
3. Several problems are worked out as examples to find the nth derivative of various fractional functions.

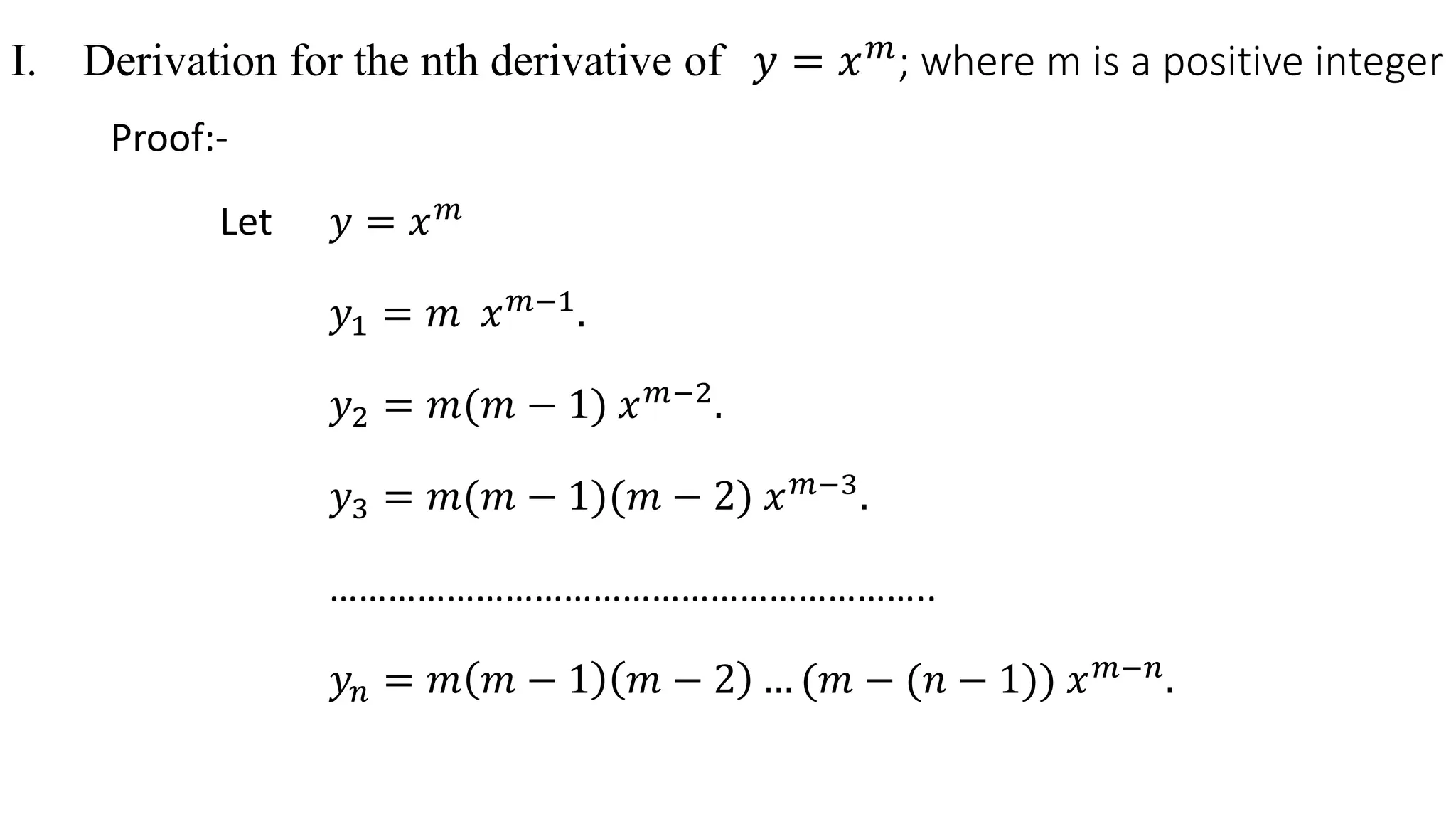



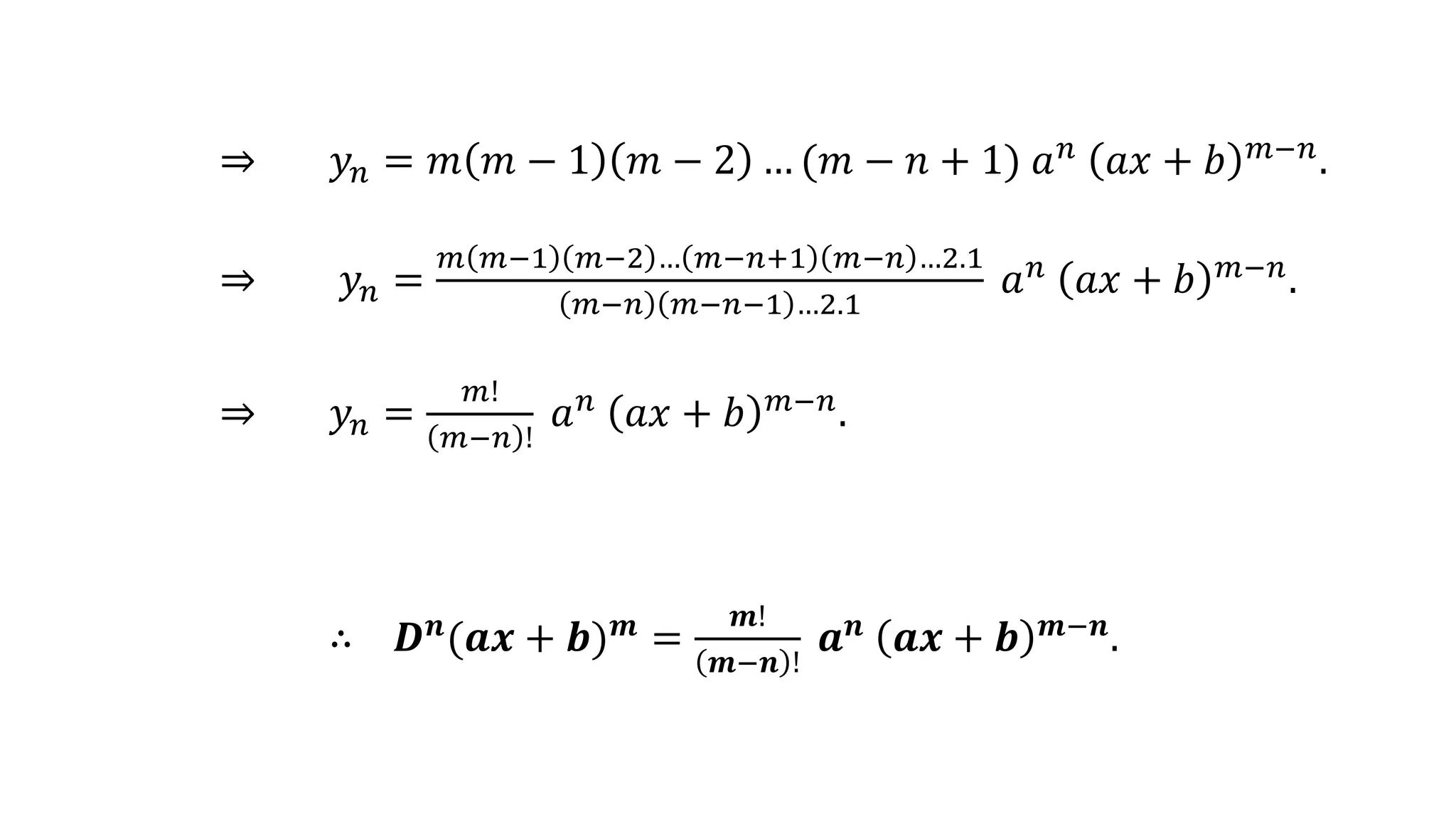
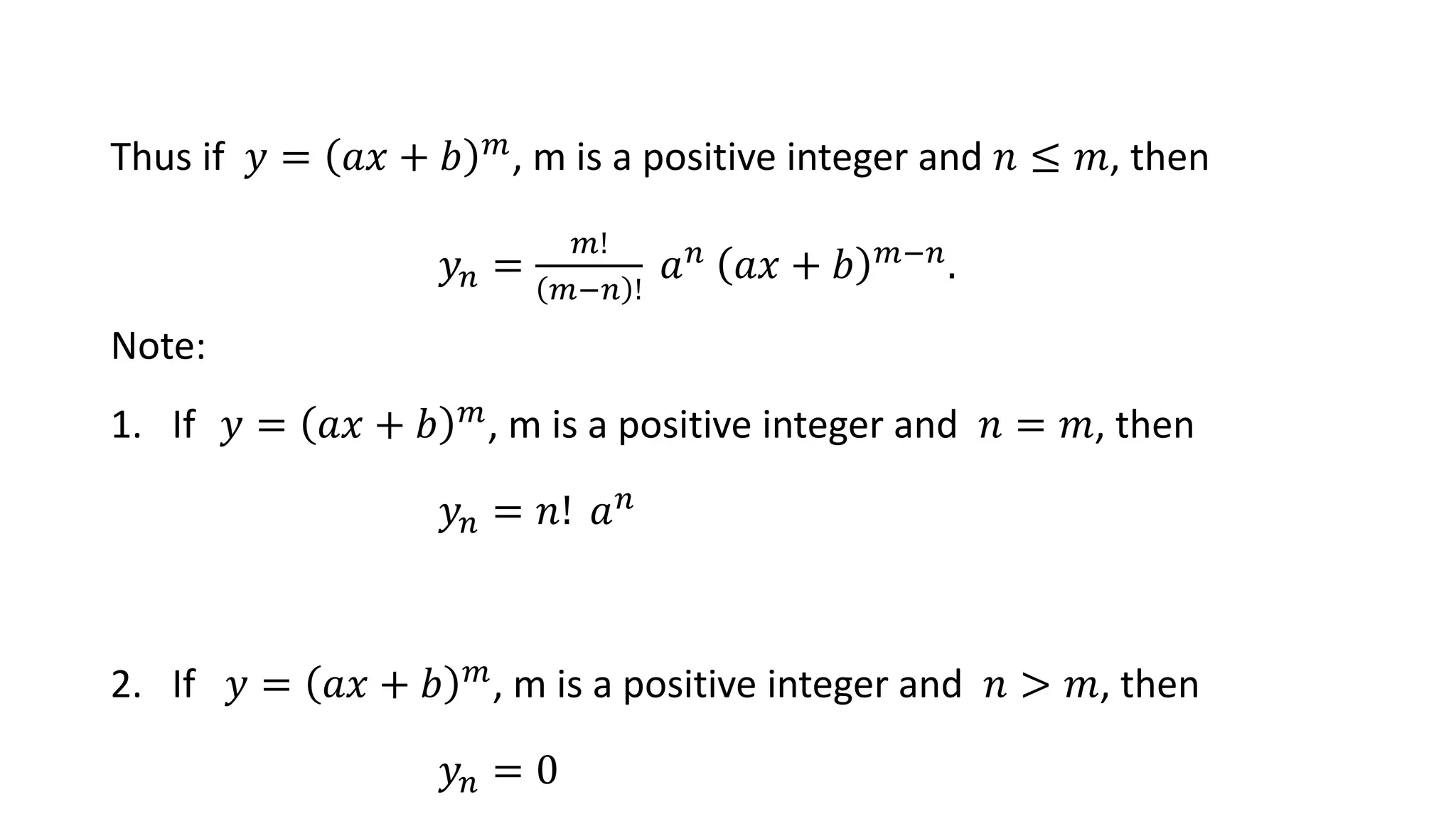
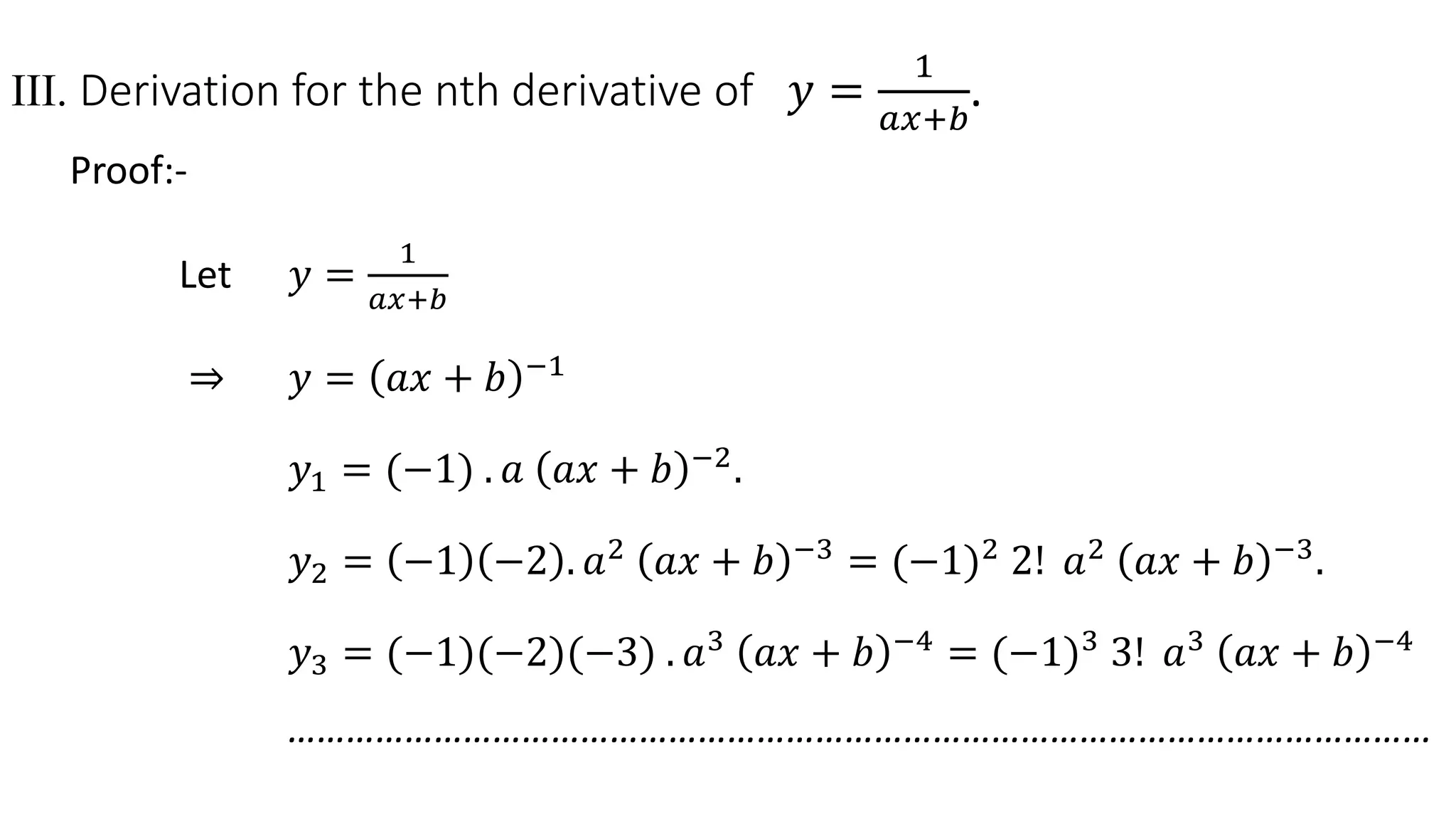
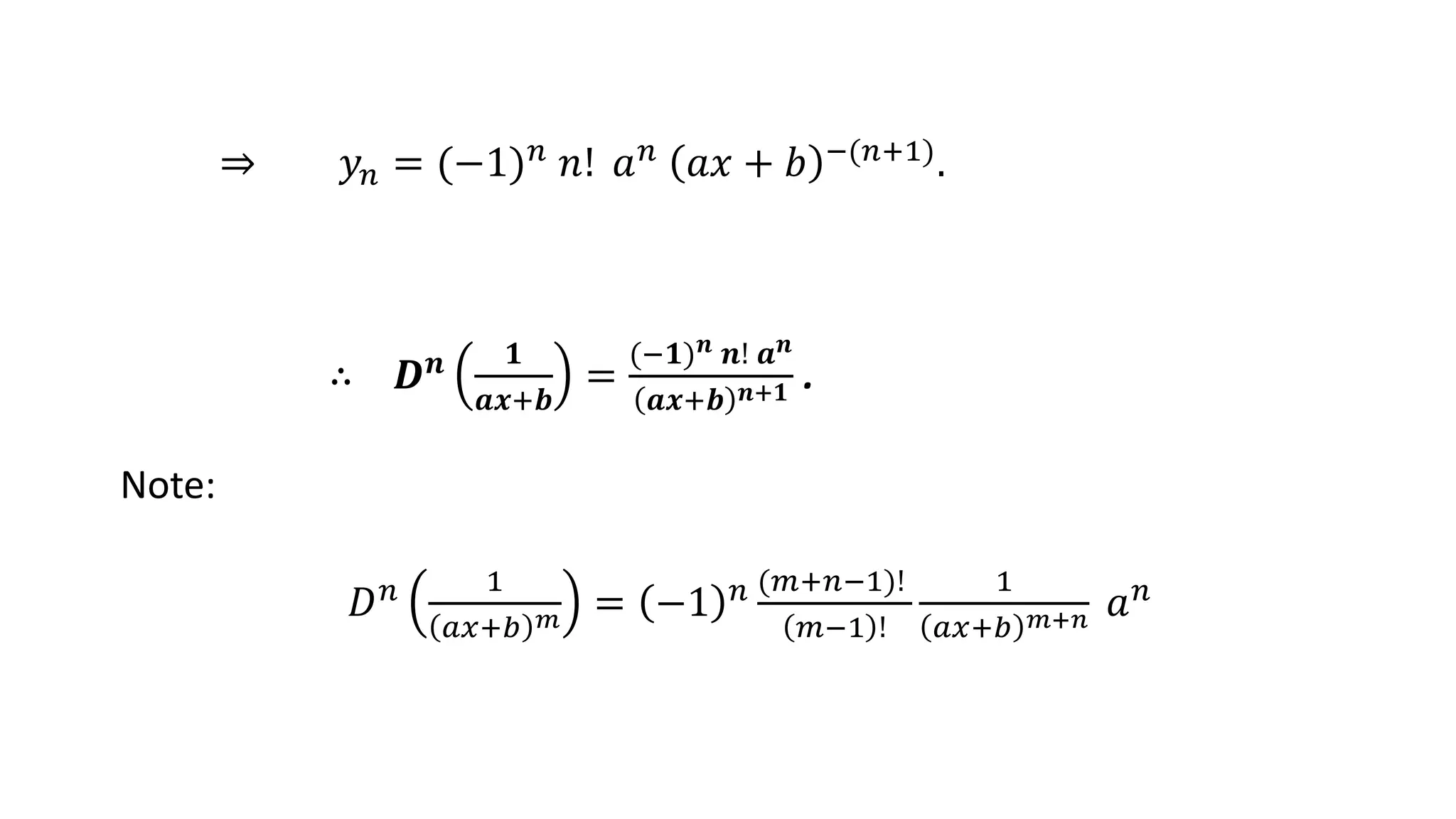

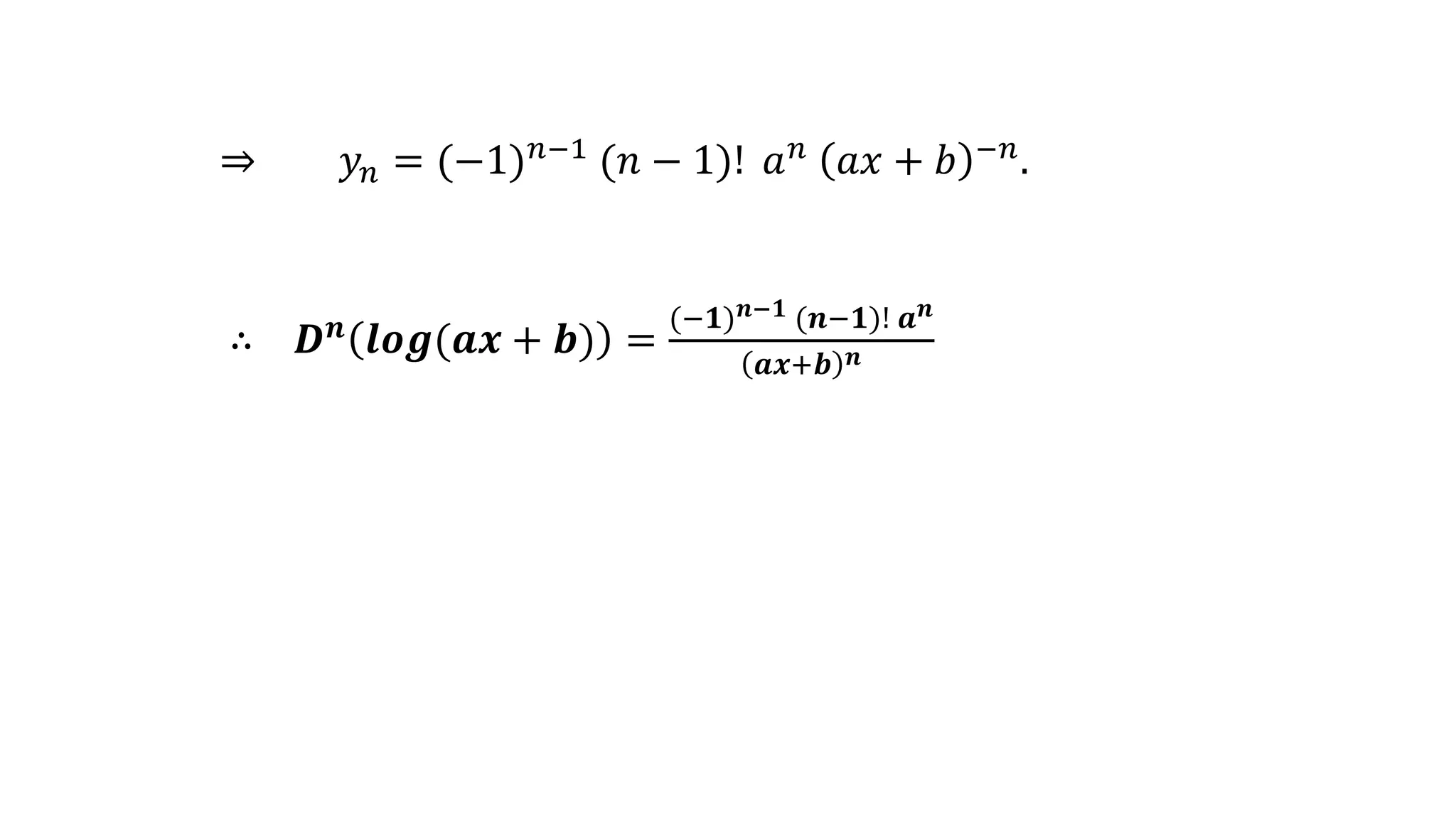



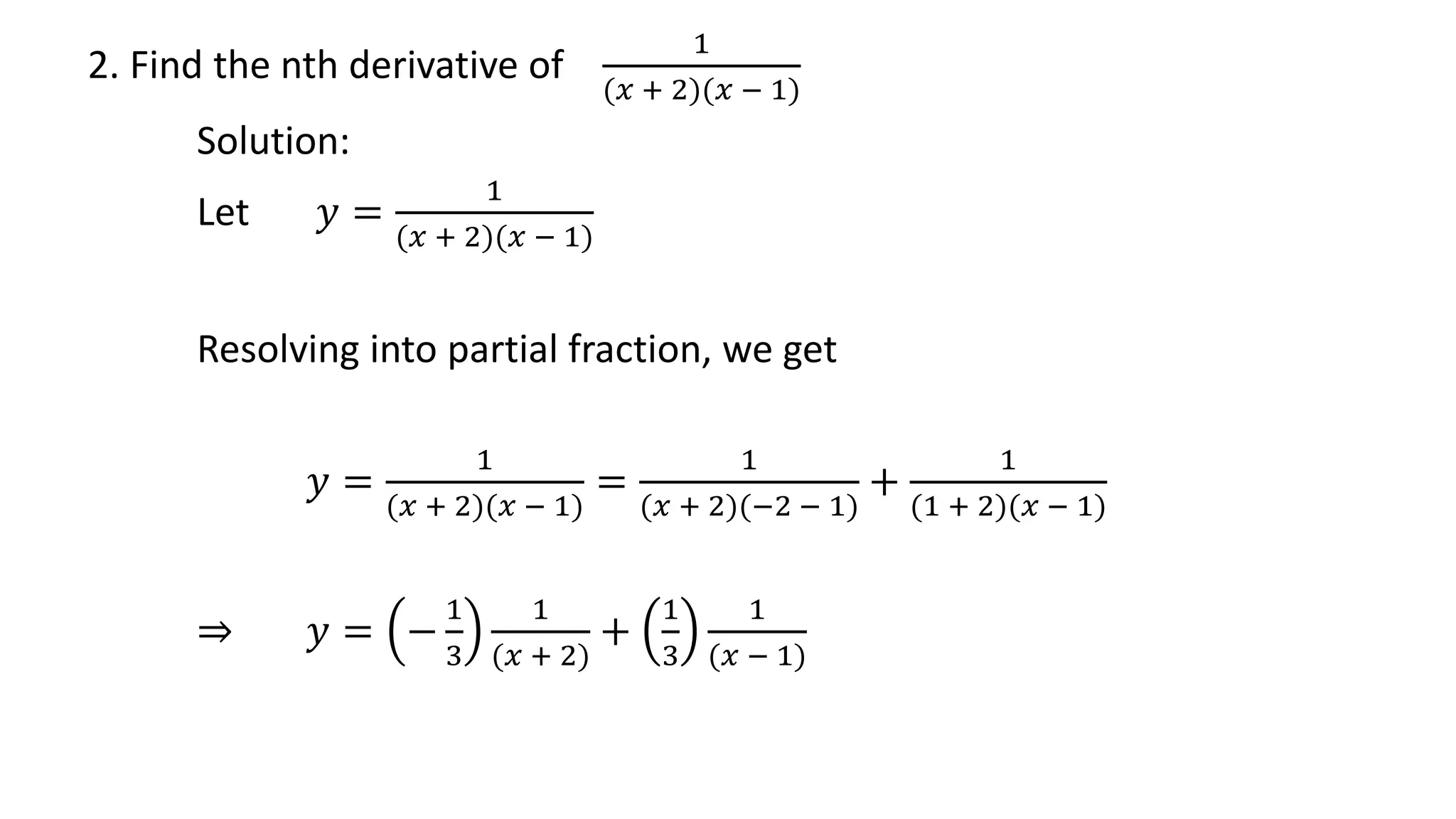
![⇒ 𝑦 =
1
3
1
(𝑥 − 1)
−
1
(𝑥 + 2)
∴ 𝑦𝑛 =
1
3
𝐷𝑛 1
𝑥 − 1
− 𝐷𝑛 1
𝑥 + 2
⇒ 𝑦𝑛 =
1
3
[
−1 𝑛 𝑛!
𝑥 − 1 𝑛+1 −
−1 𝑛 𝑛!
𝑥 + 2 𝑛+1]
⇒ 𝑦𝑛 =
−1 𝑛 𝑛!
3
[
1
𝑥 − 1 𝑛+1 −
1
𝑥 + 2 𝑛+1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-nthderivatives-231122082402-c4240e5e/75/nth-Derivatives-pptx-16-2048.jpg)


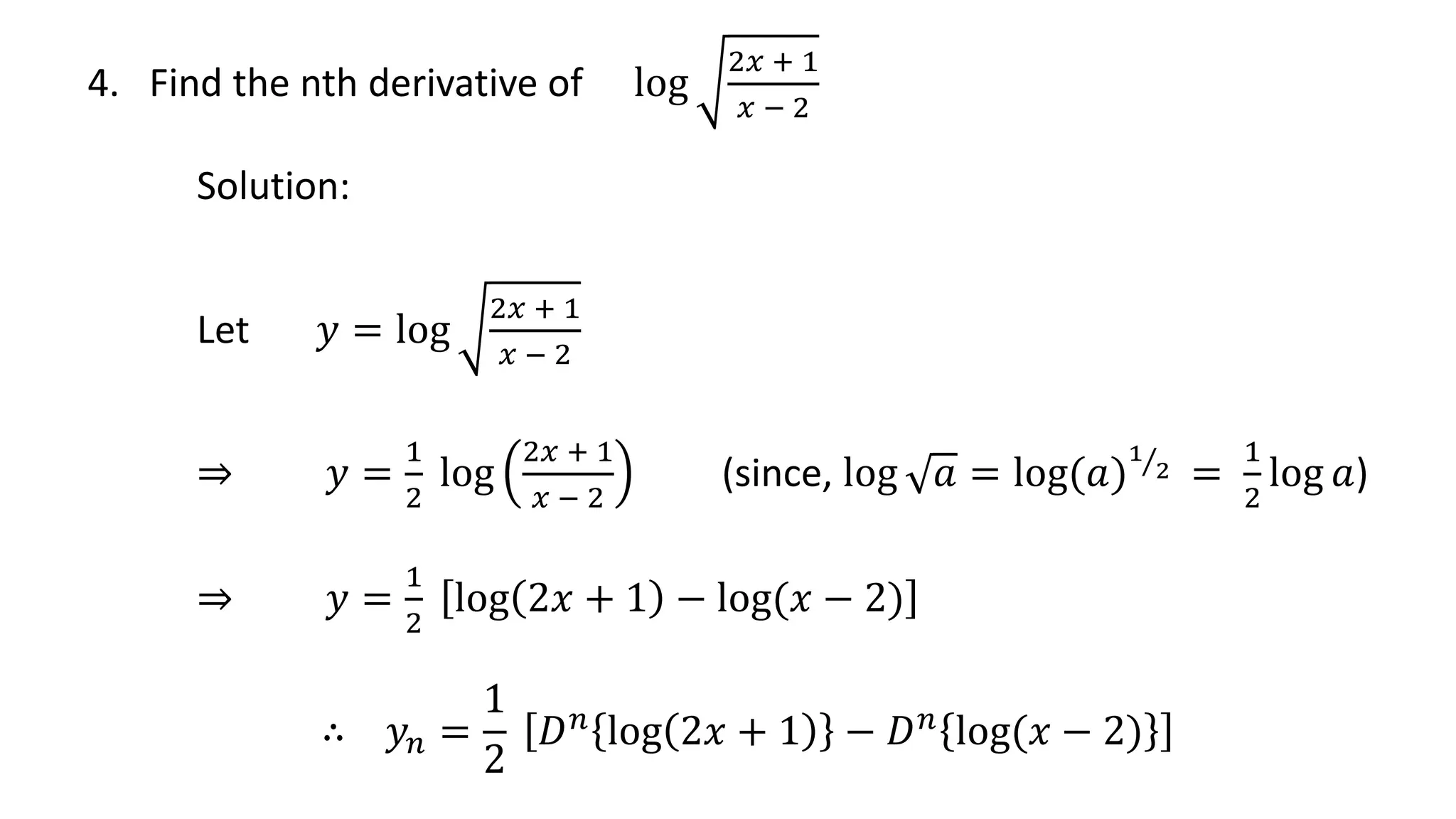
![⇒ 𝑦𝑛 =
1
2
[
−1 𝑛−1(𝑛−1)! 2𝑛
2𝑥 + 1 𝑛 −
−1 𝑛−1(𝑛−1)!
𝑥 − 2 𝑛 ]
⇒ 𝑦𝑛 =
−1 𝑛−1(𝑛−1)!
2
[
2𝑛
2𝑥 + 1 𝑛 −
1
𝑥 − 2 𝑛]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-nthderivatives-231122082402-c4240e5e/75/nth-Derivatives-pptx-20-2048.jpg)
![5. Find the nth derivative of 𝑦 = log (𝑎𝑥 + 𝑥2)
Solution:
Let 𝑦 = log [𝑥 𝑎 + 𝑥 ]
⇒ 𝑦 = log 𝑥 + log(𝑎 + 𝑥) (since, log 𝑎𝑏 = log 𝑎 + log 𝑏)
∴ 𝑦𝑛 = 𝐷𝑛
log 𝑥 + 𝐷𝑛
log 𝑎 + 𝑥
⇒ 𝑦𝑛 =
−1 𝑛−1(𝑛−1)!
𝑥 𝑛 +
−1 𝑛−1(𝑛−1)!
𝑎 + 𝑥 𝑛
⇒ 𝑦𝑛 = −1 𝑛−1(𝑛 − 1)!
1
𝑥𝑛 +
1
𝑎 + 𝑥 𝑛](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-nthderivatives-231122082402-c4240e5e/75/nth-Derivatives-pptx-21-2048.jpg)

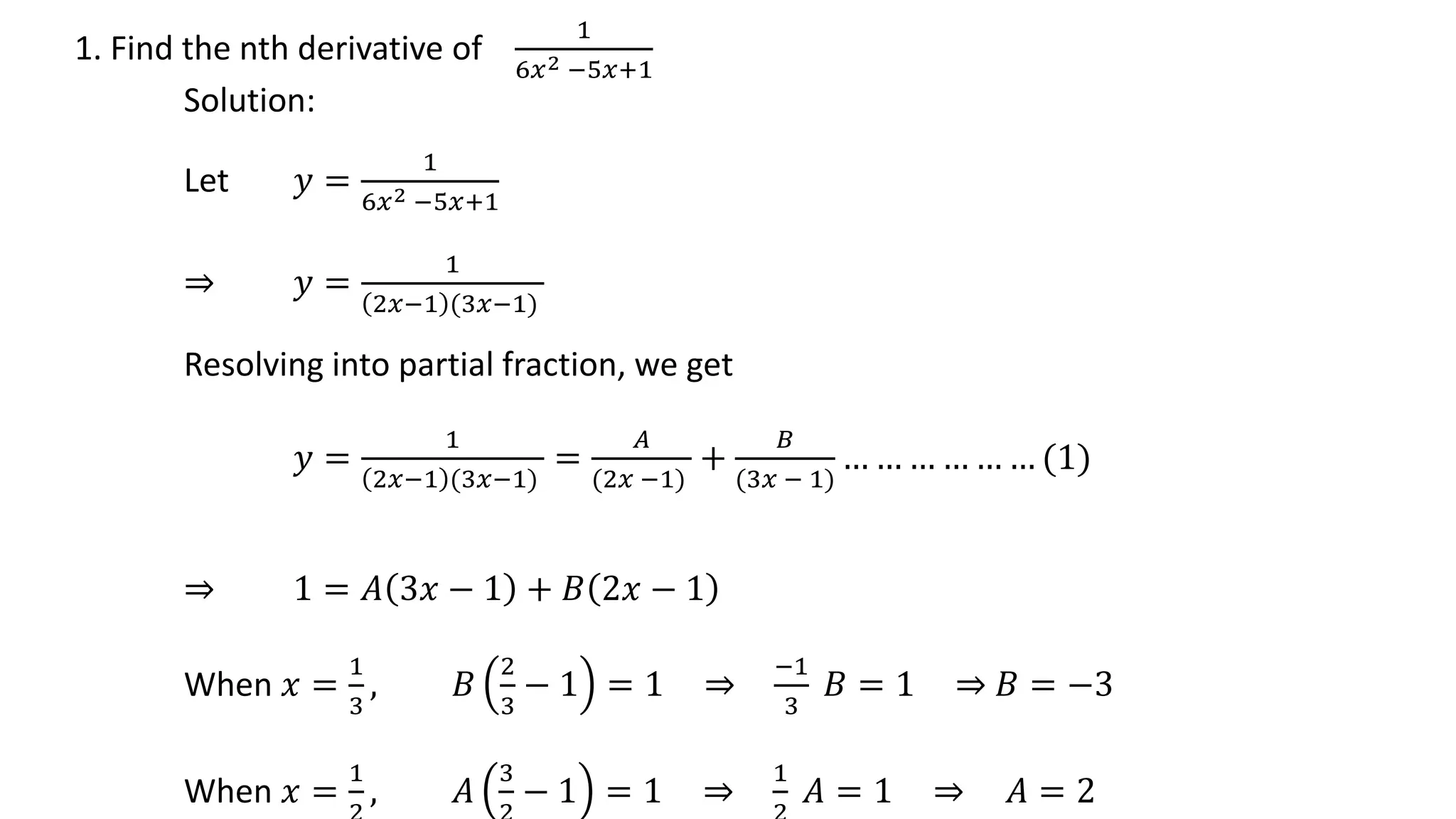



![3. Find the nth derivative of 𝑦 = log(𝑥2
− 𝑎2
)
Solution:
Let 𝑦 = log(𝑥2 − 𝑎2)
⇒ 𝑦 = log [(𝑥 + 𝑎) (𝑥 − 𝑎)]
⇒ 𝑦 = log (𝑥 + 𝑎) + log (𝑥 − 𝑎)
∴ 𝑦𝑛 = 𝐷𝑛 log(𝑥 + 𝑎) + 𝐷𝑛 log 𝑥 − 𝑎
⇒ 𝑦𝑛 =
−1 𝑛−1(𝑛−1)!
𝑥 + 𝑎 𝑛 +
−1 𝑛−1(𝑛−1)!
𝑥 − 𝑎 𝑛
⇒ 𝑦𝑛 = −1 𝑛−1
(𝑛 − 1)!
1
(𝑥+𝑎)𝑛 +
1
𝑥 − 𝑎 𝑛](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-nthderivatives-231122082402-c4240e5e/75/nth-Derivatives-pptx-27-2048.jpg)
![4. Find the nth derivative of 𝑦 = log(𝑎𝑥 − 𝑥2
)
Solution:
Let y = log(𝑎𝑥 − 𝑥2)
⇒ 𝑦 = log [𝑥 𝑎 − 𝑥 ]
⇒ 𝑦 = log 𝑥 + log(𝑎 − 𝑥)
∴ 𝑦𝑛 = 𝐷𝑛 log 𝑥 + 𝐷𝑛 log 𝑎 − 𝑥
⇒ 𝑦𝑛 =
−1 𝑛−1(𝑛−1)!
𝑥 𝑛 +
−1 𝑛−1 𝑛−1 ! −1 𝑛
𝑎 − 𝑥 𝑛
⇒ 𝑦𝑛 = −1 𝑛−1(𝑛 − 1)!
1
𝑥𝑛 +
−1 𝑛
𝑎 − 𝑥 𝑛](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-nthderivatives-231122082402-c4240e5e/75/nth-Derivatives-pptx-28-2048.jpg)
