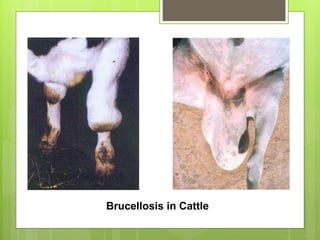
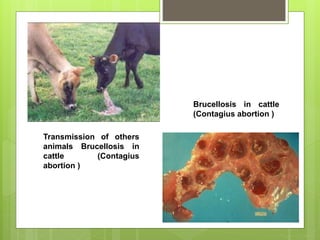
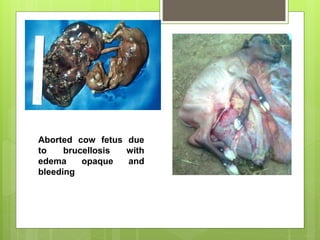
Brucellosis, also known as Bang's disease, is a contagious disease in animals caused by the bacterium Brucella abortus. It is transmitted between animals through ingestion or inhalation of contaminated materials from aborted fetuses or birthing discharges. Symptoms include abortion in late pregnancy as well as retained placentas and weak newborn calves. Diagnosis involves isolating the bacterium from aborted fetal tissues or testing milk and blood samples. While antibiotics can treat infected animals, vaccination of young cattle is the most effective control method for preventing transmission and economic losses to livestock operations.