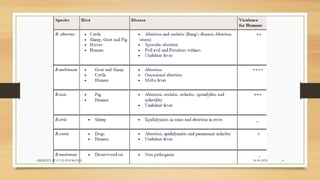
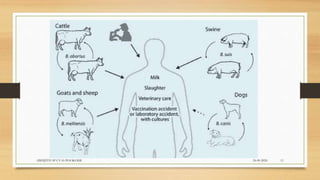
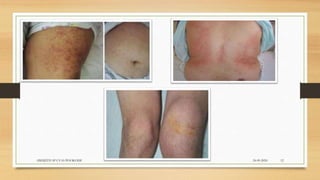
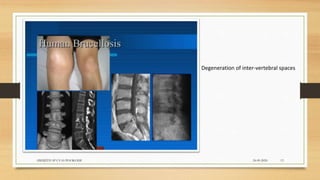
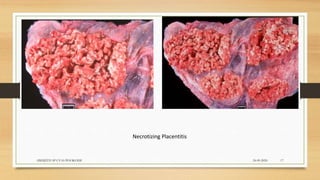
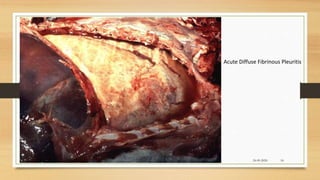
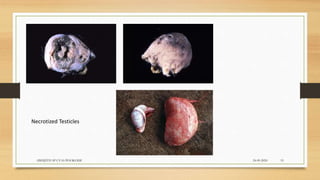
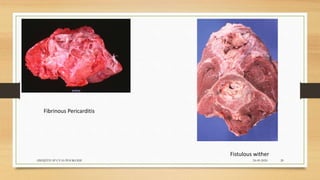
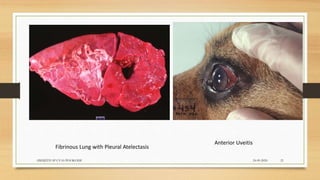
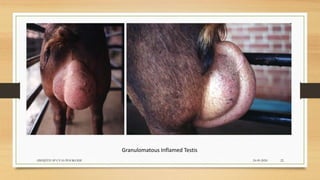
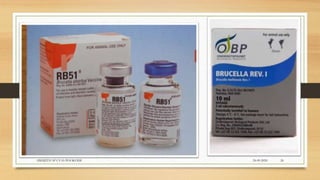
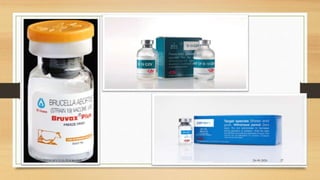
Brucellosis is caused by bacteria of the genus Brucella which localize in the reproductive organs of animals. It causes abortions and sterility in hosts. The disease was first diagnosed in 1897 and different species of Brucella were identified in subsequent years that affect various animals. Brucella bacteria are small, Gram-negative, intracellular parasites that preferentially infect the reticuloendothelial system and reproductive tract. The most common routes of transmission are ingestion, contact with mucous membranes or broken skin. Symptoms in humans are similar to flu with fever, joint pain and fatigue.