This document provides information about Marek's Disease, including:
1) It is a lymphoproliferative disease of chickens caused by the Marek's Disease Virus (MDV), a herpesvirus. MDV has three serotypes, with Serotype 1 including the oncogenic strains responsible for Marek's Disease.
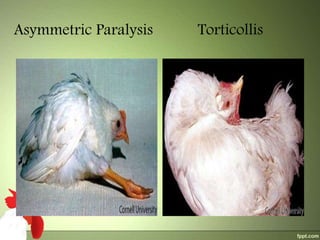
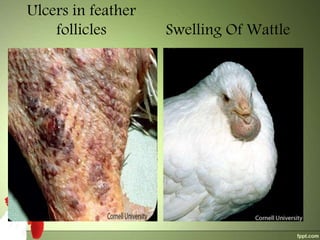
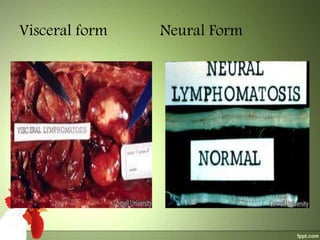
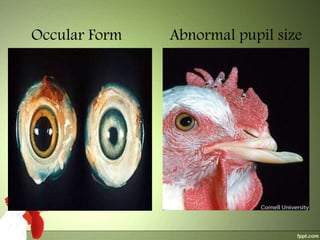
2) The virus spreads via dander from infected feather follicles through the air. It causes proliferation of lymphocytes which can deposit in various tissues, leading to neural, visceral, cutaneous or ocular forms of the disease.
3) Clinical signs include paralysis, enlarged organs, skin nodules or eye protrusion. Diagnosis involves post-mortem