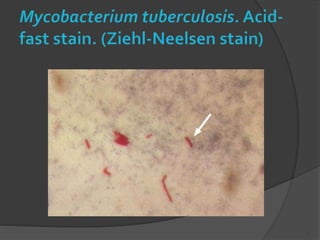
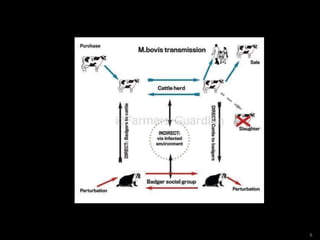
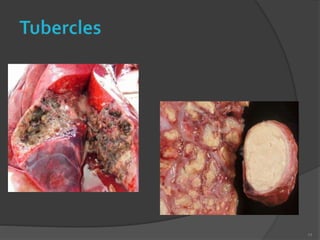
Bovine tuberculosis is a chronic bacterial disease of cattle caused by Mycobacterium bovis that can occasionally infect other mammals. It is a zoonotic disease that can be transmitted to humans through the inhalation of aerosols or ingestion of unpasteurized milk. The disease spreads between animals through close contact and shedding of bacteria in excretions or lesions, and from animals to humans occupationally through farming or slaughterhouse work. Clinical signs in animals include coughing, weight loss, and enlarged lymph nodes that can rupture and drain.