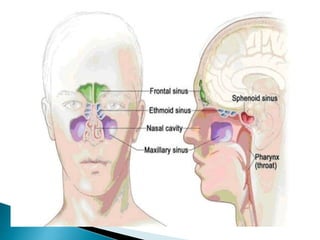
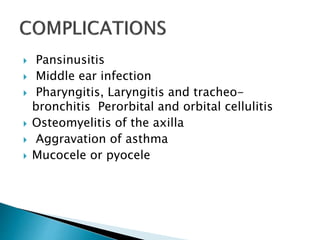
The document discusses paranasal sinuses and sinusitis. It defines paranasal sinuses as four paired air-filled spaces surrounding the nasal cavity. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane in the sinuses. Sinusitis can be classified based on location of the affected sinus or duration of symptoms. Acute sinusitis lasts less than 4 weeks while chronic sinusitis persists for over 12 weeks. Common causes include viral and bacterial infections, allergies, and structural issues impairing drainage. Symptoms vary depending on the affected sinus. Diagnosis involves medical history, exam, and imaging tests. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms for acute cases but may involve antibiotics for persistent infections.