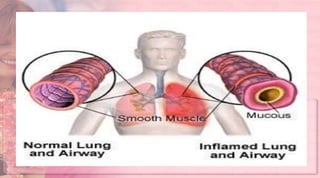
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi. It can be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis often occurs with a cold or flu and is characterized by cough with mucus. Chronic bronchitis lasts more than 3 months per year for over 2 years and is usually caused by smoking or air pollution. Symptoms include productive cough. Treatment involves antibiotics for bacterial infections, bronchodilators to open airways, mucolytics to thin mucus, steroids to reduce inflammation, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Nursing care focuses on breathing treatments, pulmonary hygiene, comfort measures, and health education. Preventing bronchitis involves avoiding tobacco smoke, managing diet, hand washing, and using a humidifier.