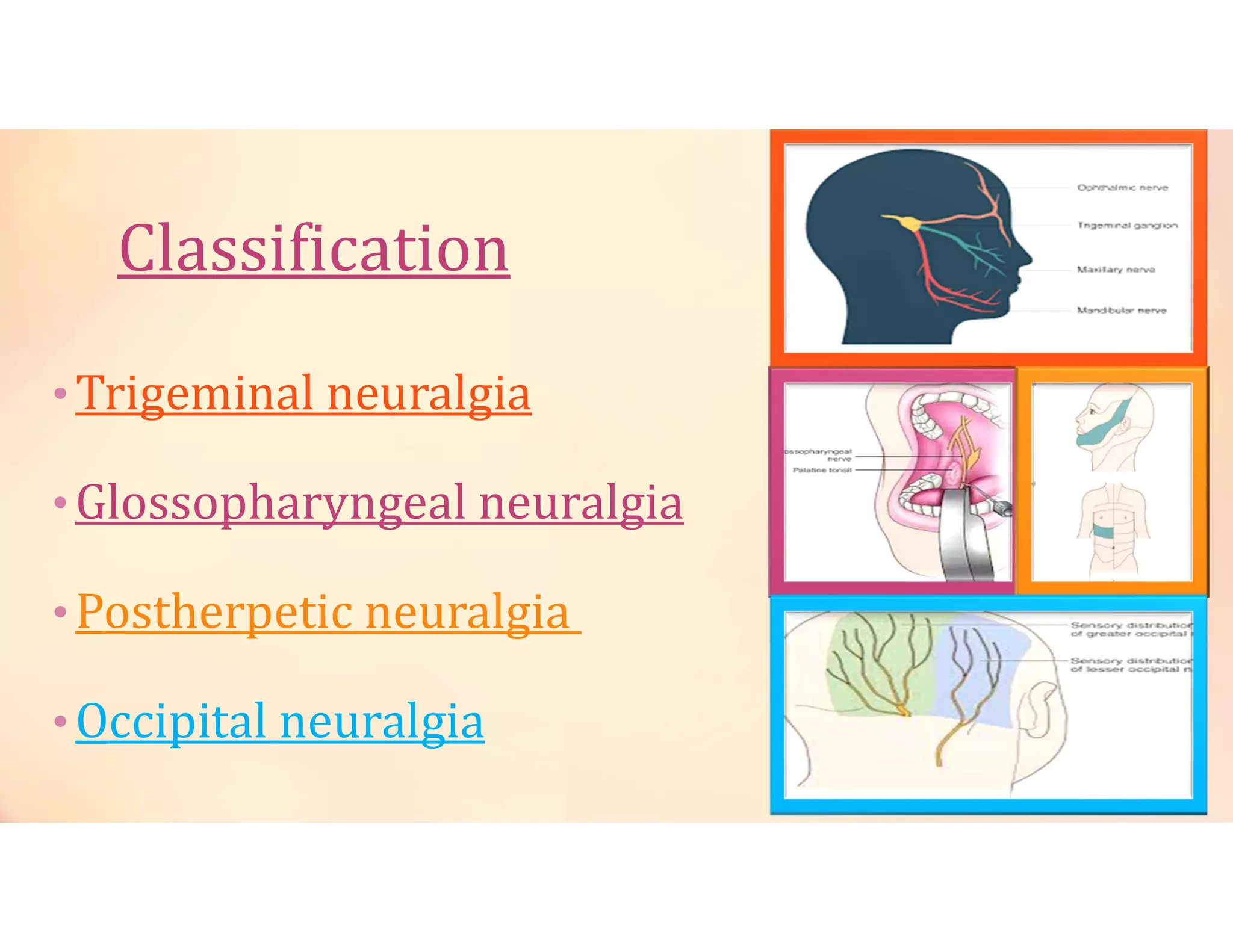
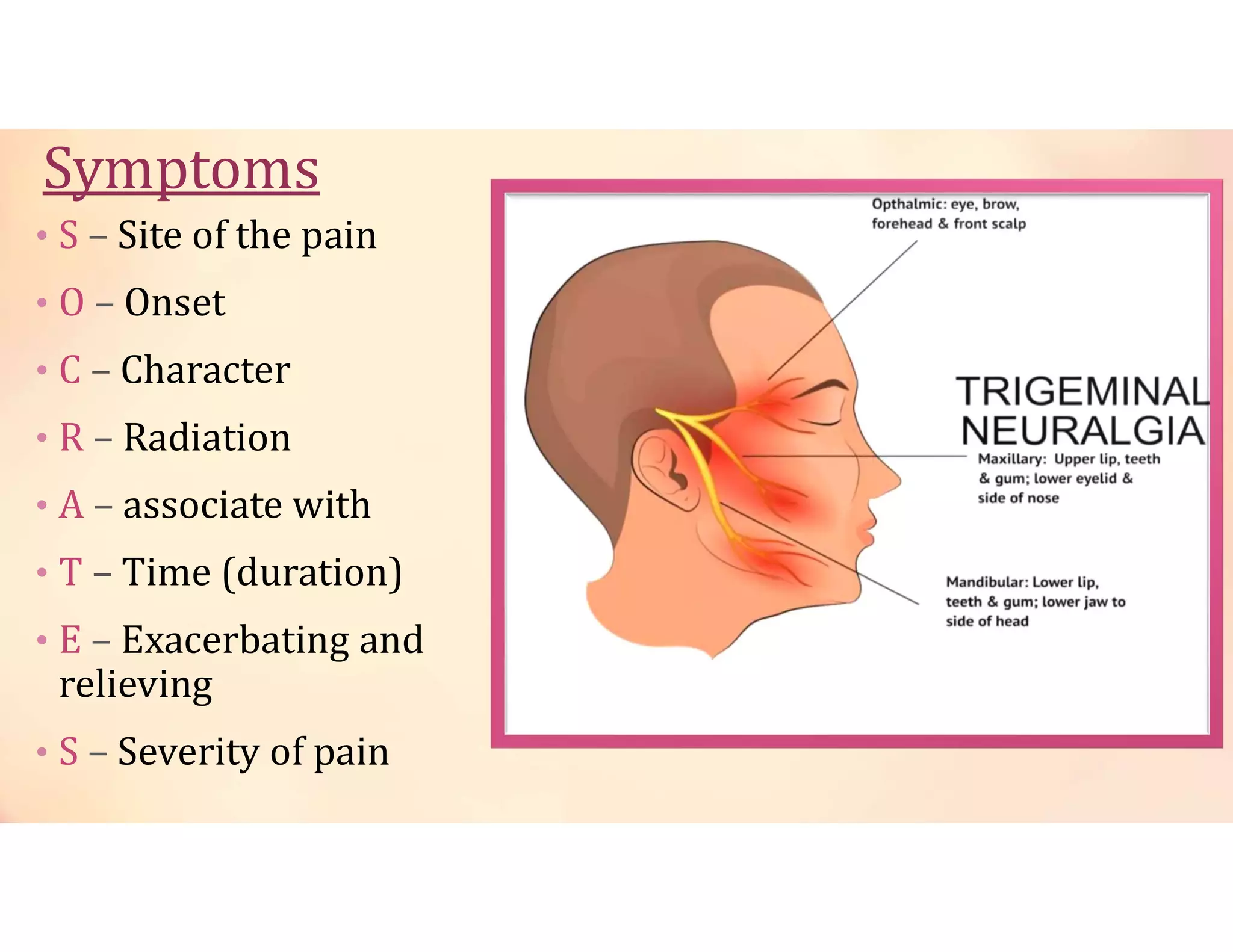
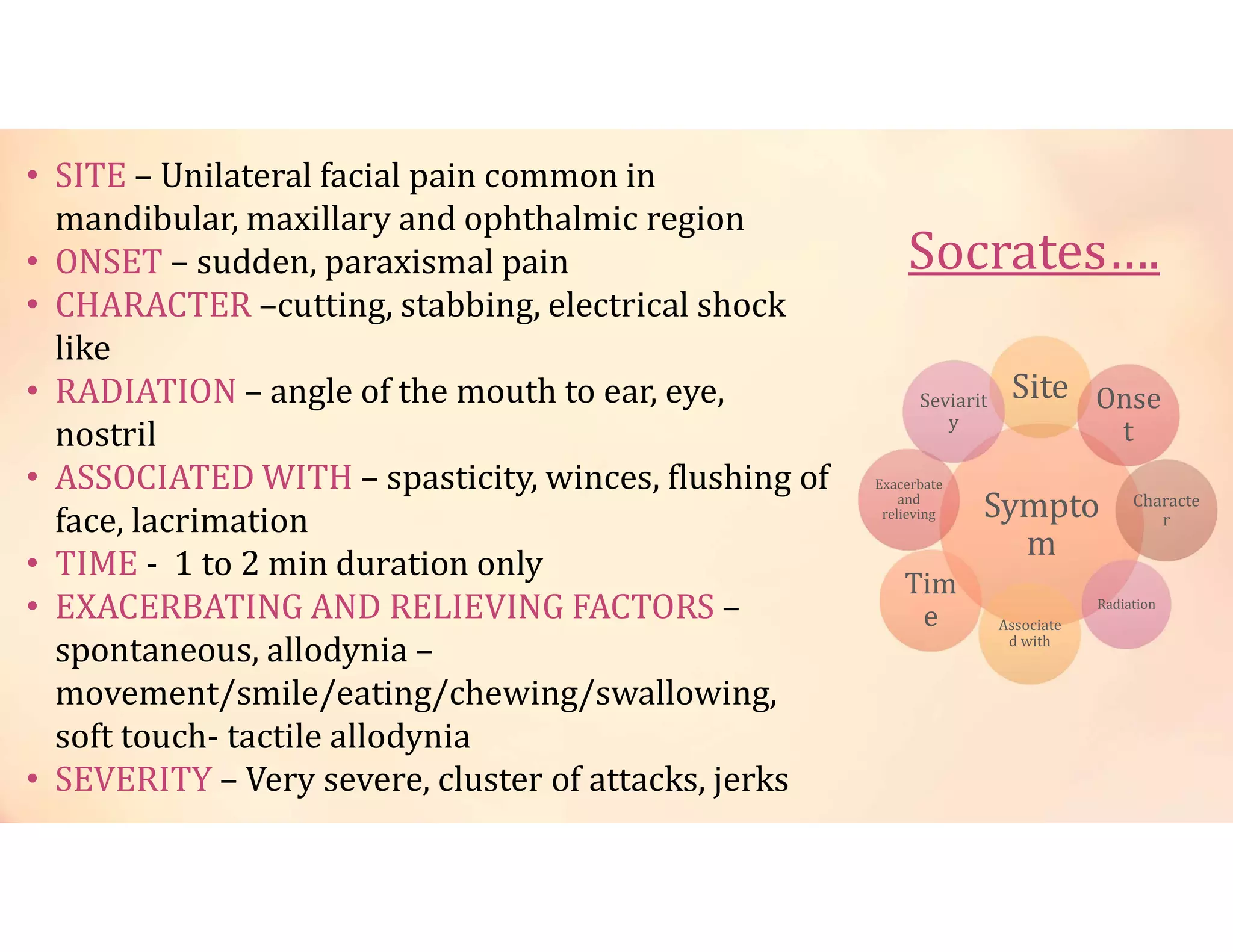
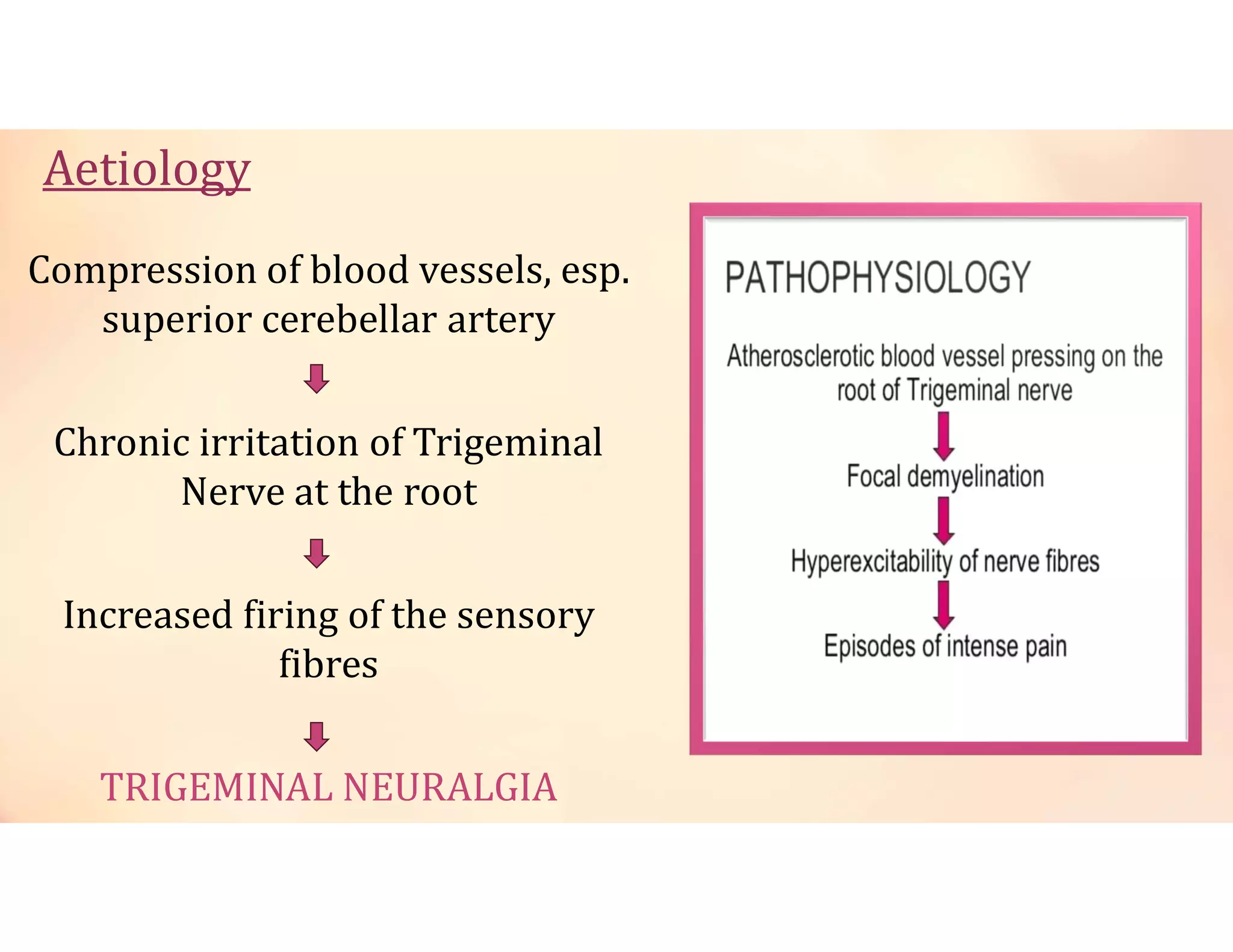
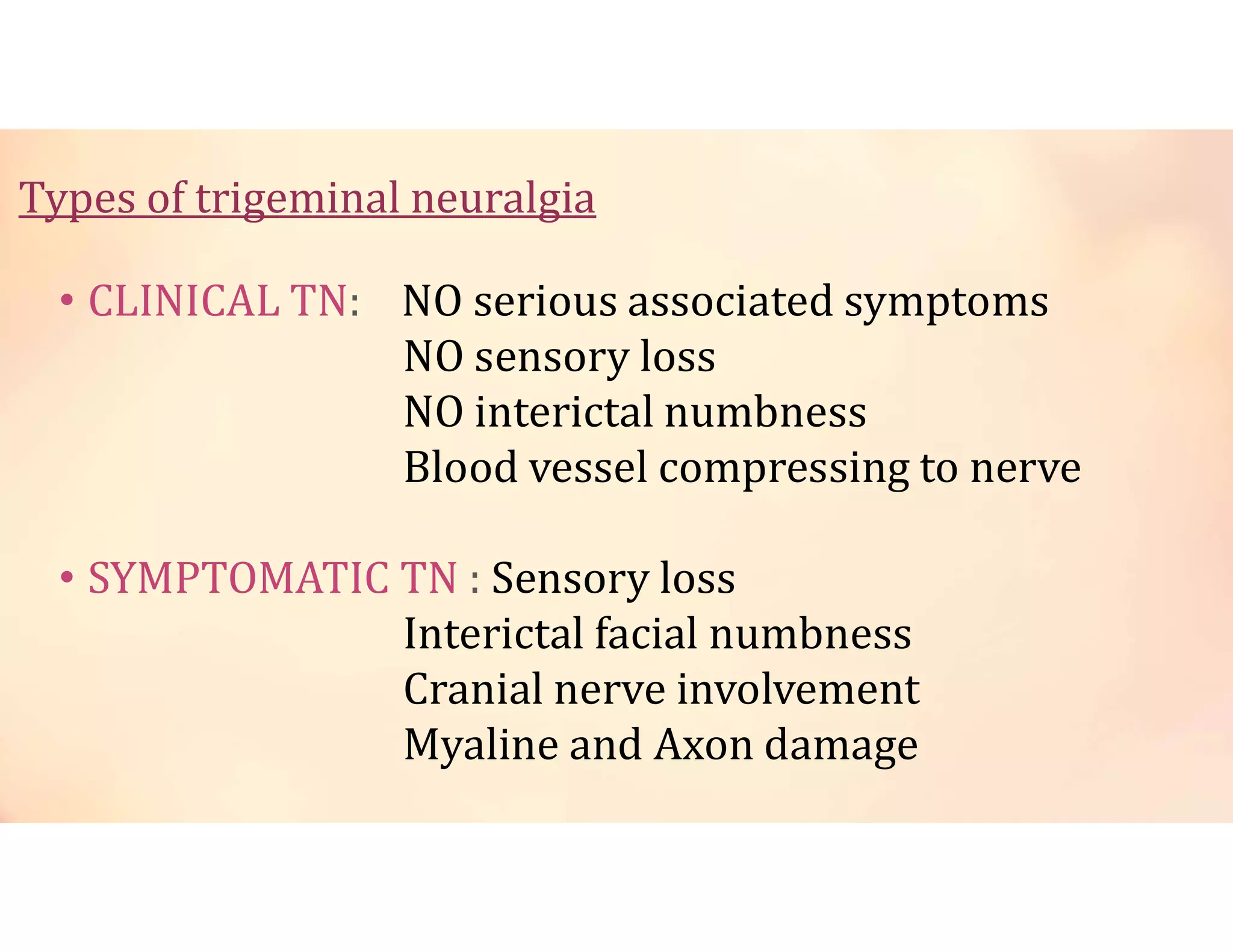
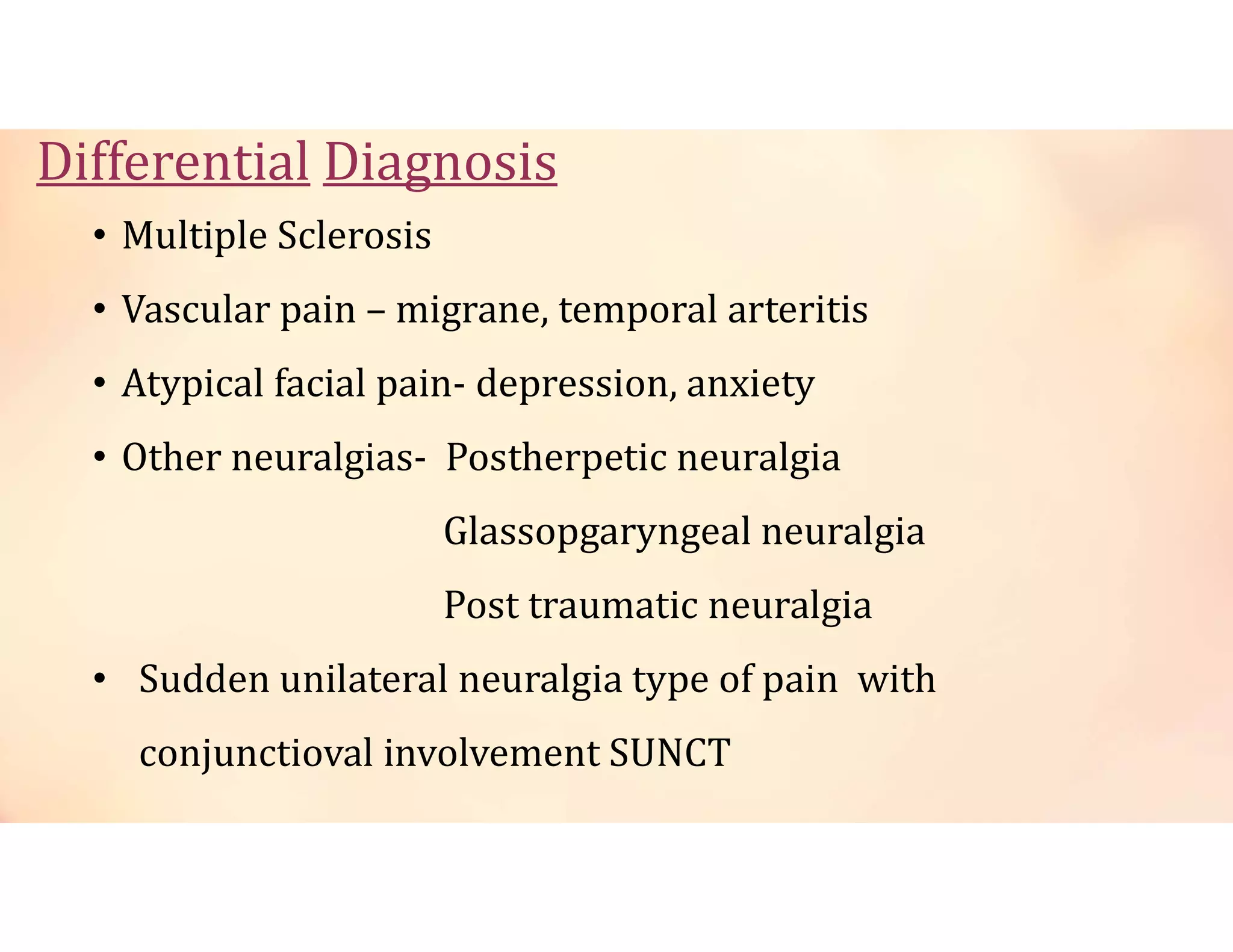
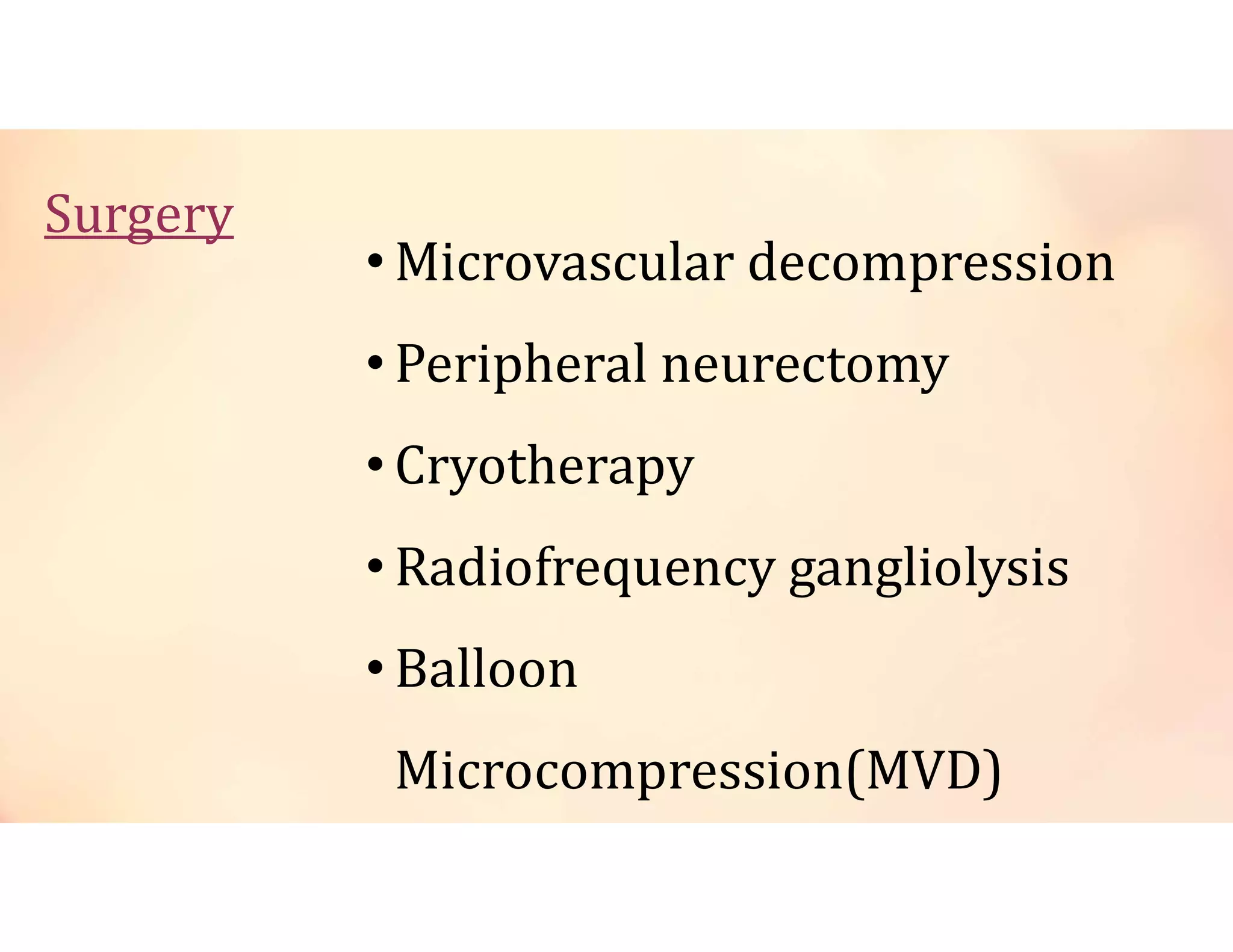
Neuralgia is a neuropathic pain condition affecting one or more nerves. It can be caused by damage to the peripheral or central nervous system. The document discusses several types of neuralgia - trigeminal, glossopharyngeal, postherpetic, and occipital neuralgia. It provides details on symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and management of trigeminal neuralgia, which involves sudden, severe facial pain that may be treated initially with carbamazepine or phenytoin medication or potentially through microvascular decompression surgery.