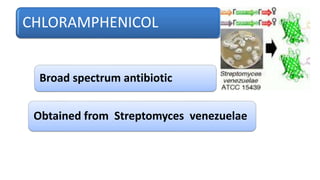
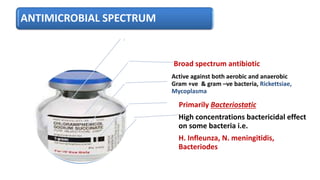
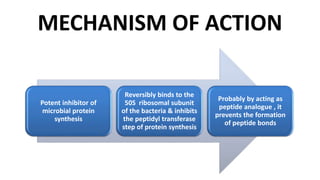
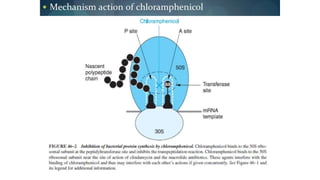
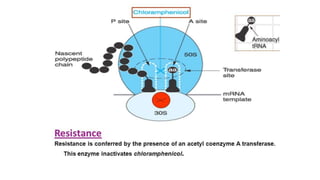
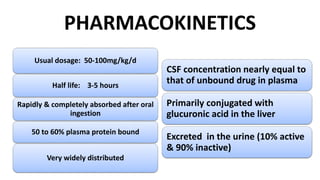
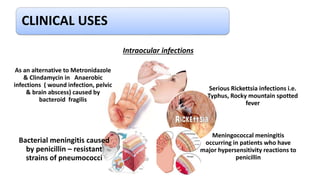
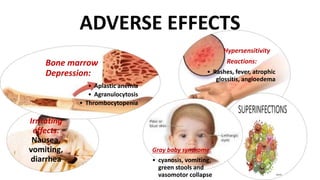
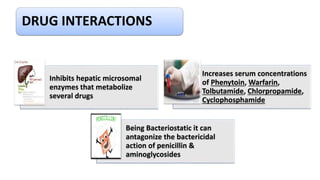
Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic obtained from Streptomyces venezuelae that is active against both aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It works by reversibly binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit of bacteria and inhibiting protein synthesis. Resistance can develop through production of an acetyltransferase enzyme, decreased permeability, or lower bacterial ribosome affinity. Chloramphenicol has various clinical uses including treatment of serious rickettsial infections, meningococcal meningitis, and anaerobic infections. Adverse effects include bone marrow depression, hypersensitivity reactions, and gray baby syndrome in neonates.