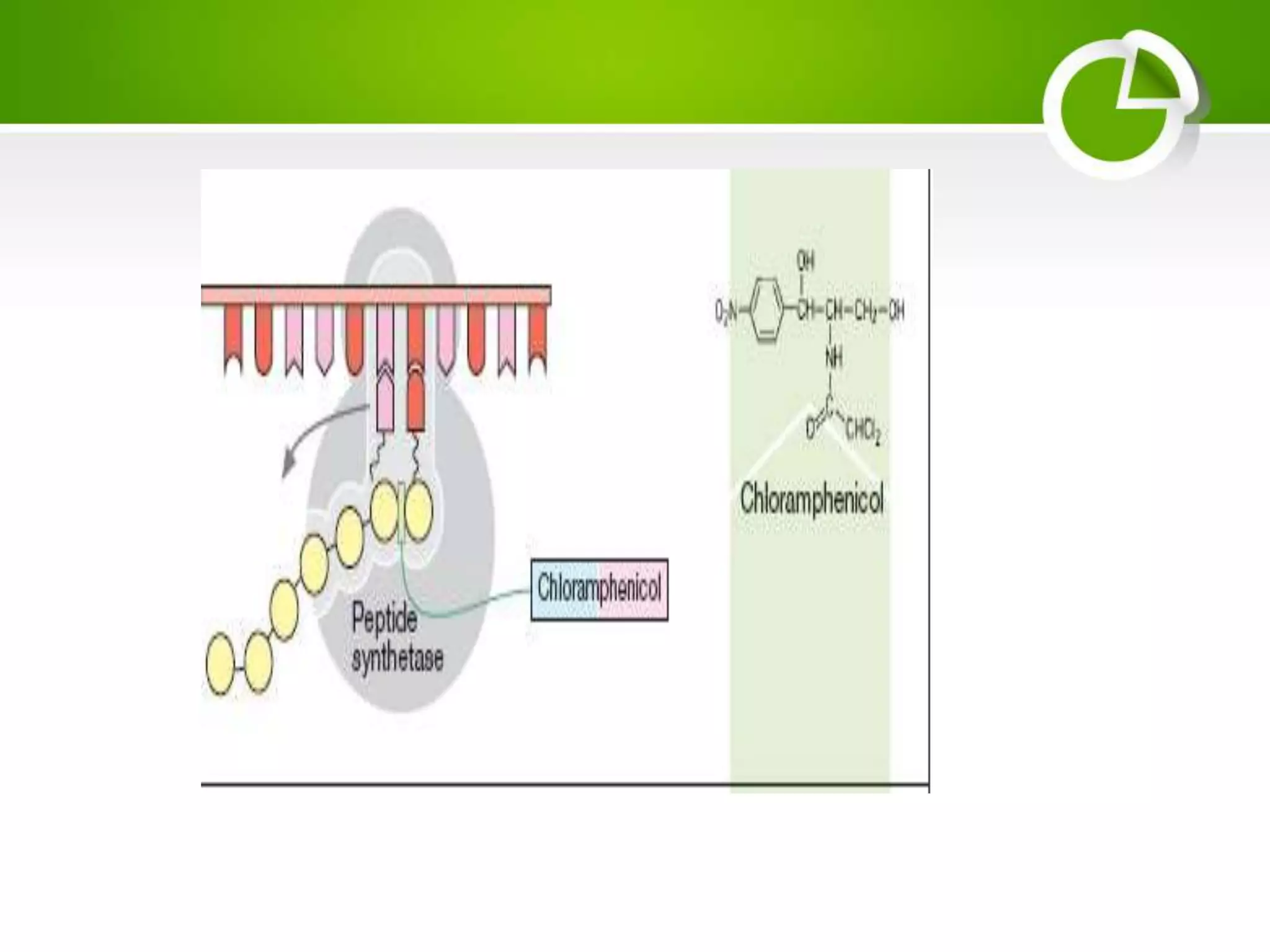
Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that was first introduced in 1949. It inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and blocking peptide bond formation. While effective against many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, its use has limitations due to potential bone marrow toxicity. Common adverse effects include reversible anemia, bone marrow suppression, and gastrointestinal disturbances. It remains an important treatment option for certain life-threatening infections.