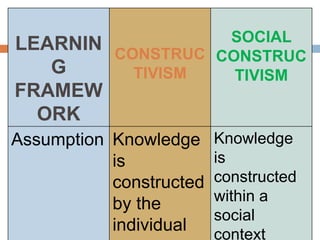
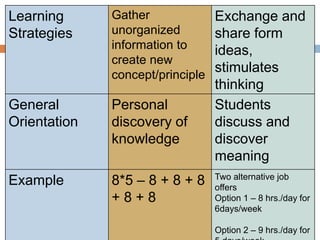
The document discusses the role of technology in developing student-centered learning and higher-order thinking skills. It explains that technology can support constructivist and social constructivist learning frameworks by allowing students to discover and construct knowledge both individually and collaboratively. Examples of how technology facilitates student-centered learning include word processing, creating presentations, conducting online research, and enabling individualized and interactive instruction.