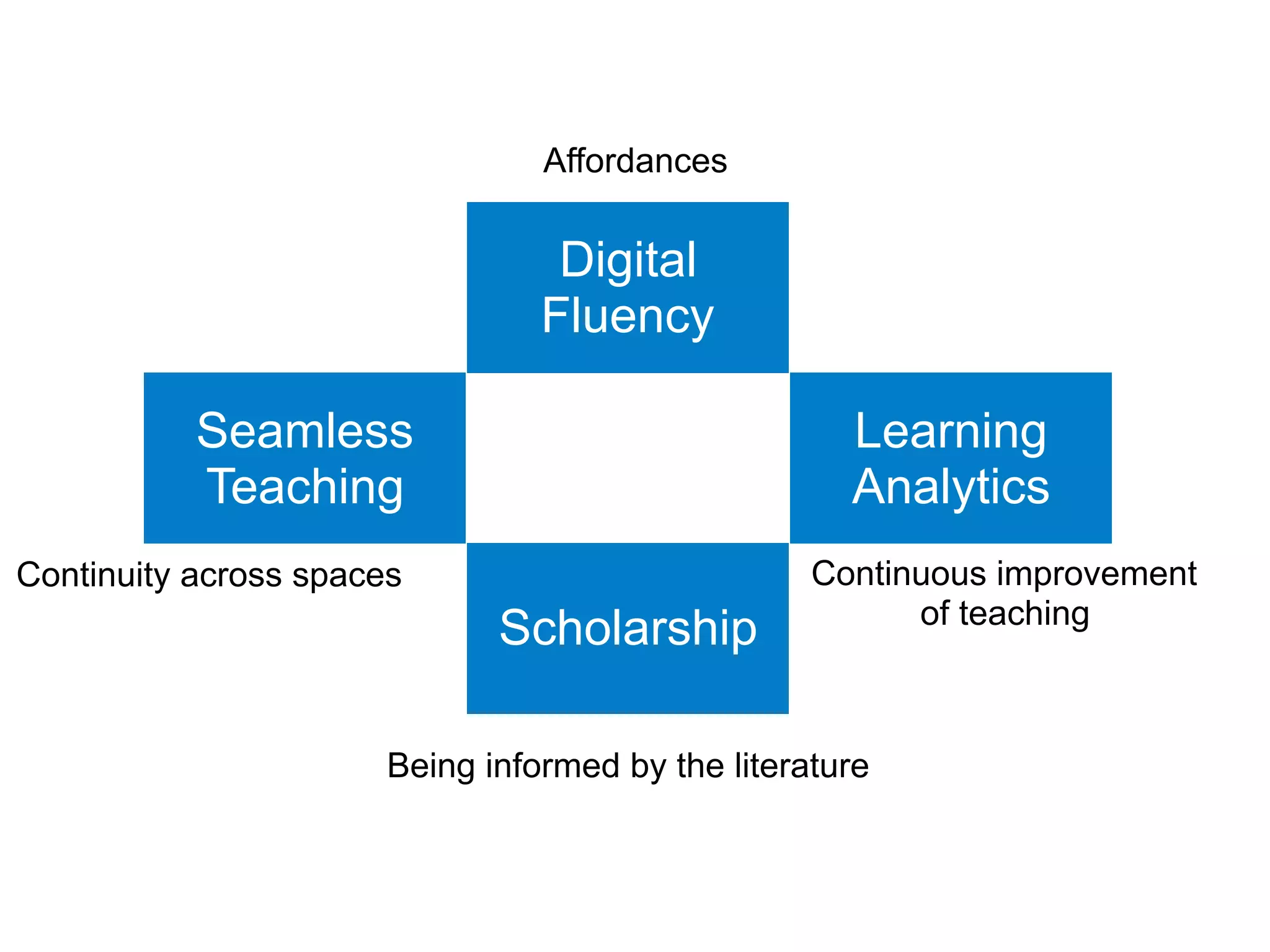
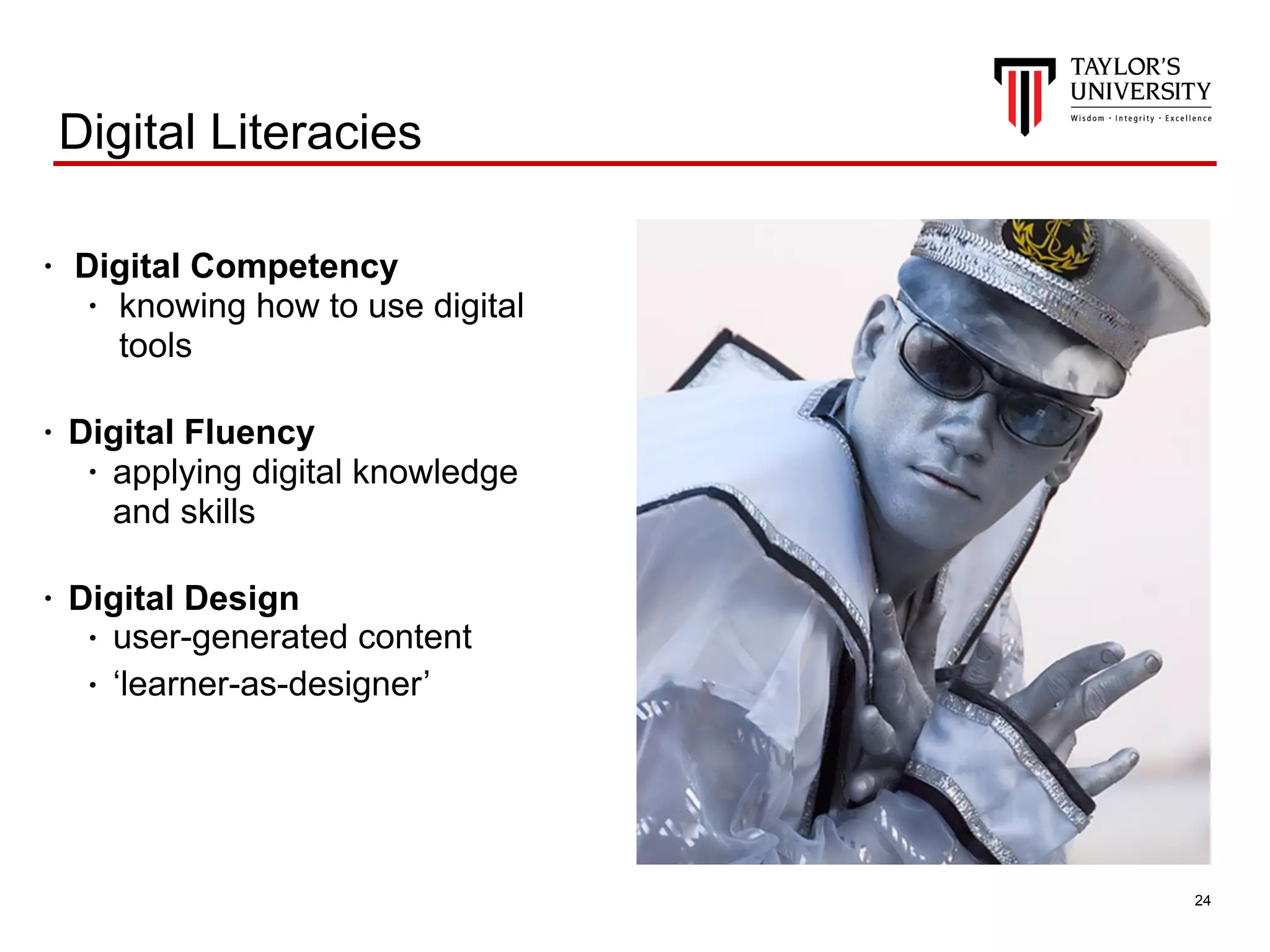
The document discusses the integration of blended learning and innovative teaching practices in educational institutions to better prepare students for future challenges. It emphasizes the importance of active and personalized learning spaces, digital fluency, and lifelong learning, alongside principles for effective learning space design. Additionally, it highlights a focus on authentic assessments and the need for continuous improvement in teaching methodologies to enhance student learning experiences.