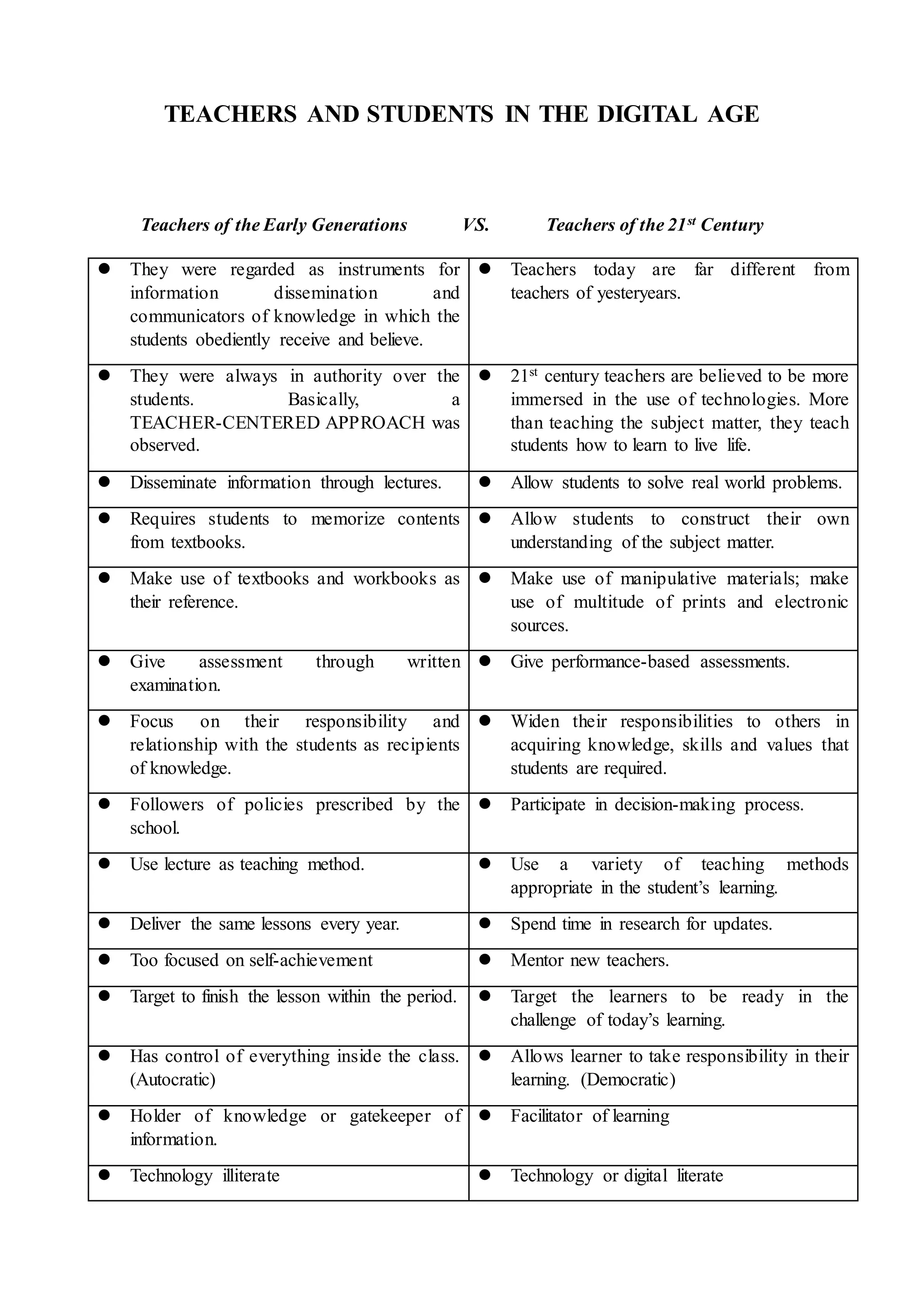
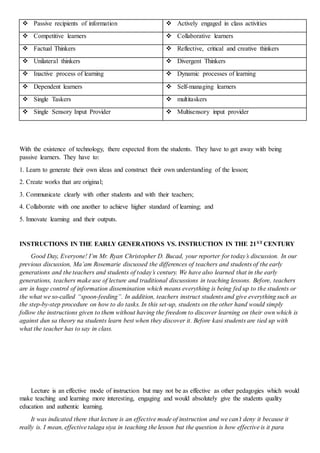
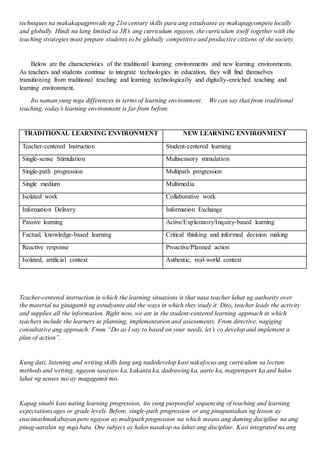
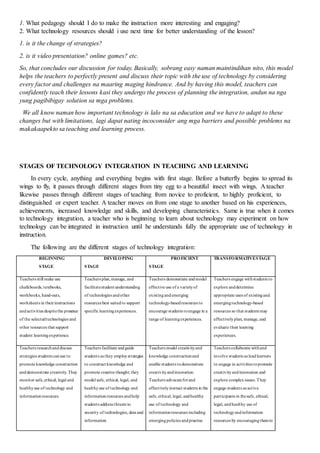
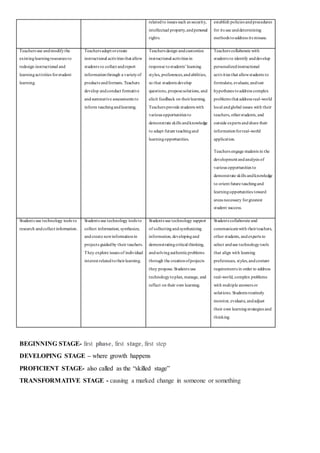
The document compares teachers and instruction methods of the early generations to those of the 21st century. In the early generations, teachers disseminated information through lectures and students memorized content passively. Now, teachers facilitate active, student-centered learning through varied methods like interactive lectures, case-based learning, and problem-based learning. Students construct their own understanding and solve real-world problems collaboratively using technology to access information. The challenges for 21st century teachers are to utilize technology to enhance authentic, quality learning opportunities for students.