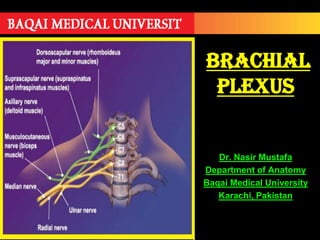
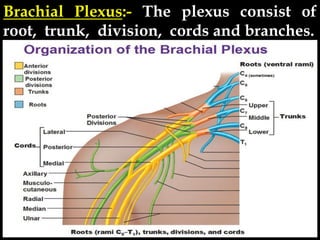
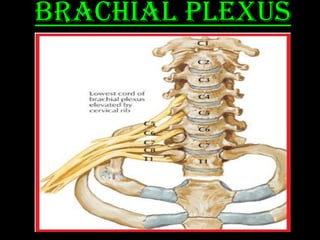
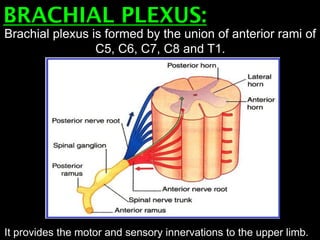
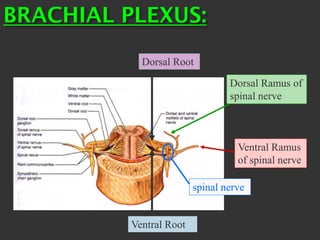
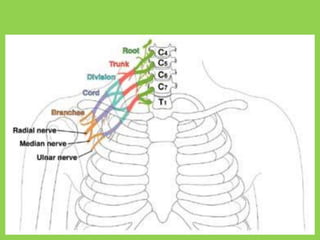
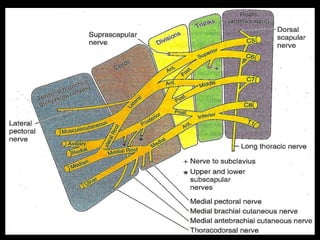
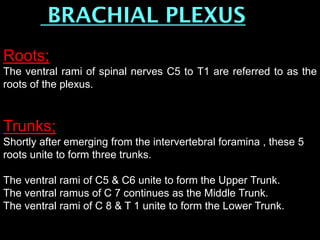
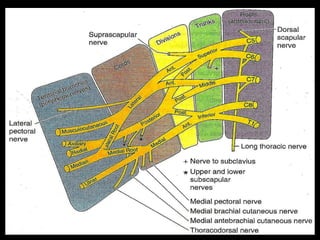
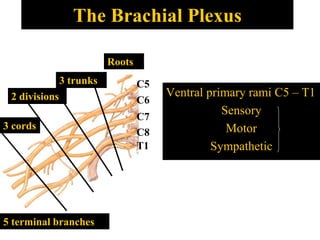
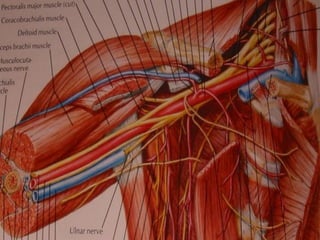
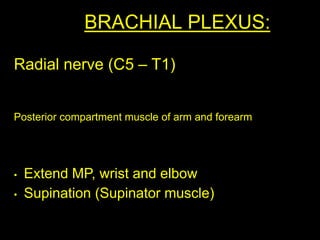
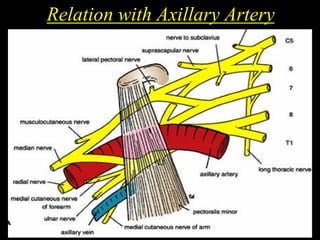
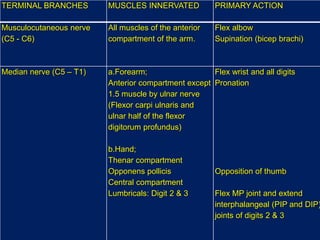
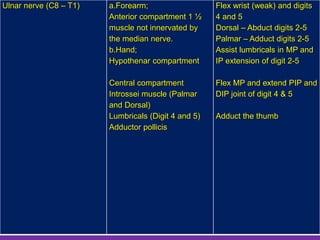
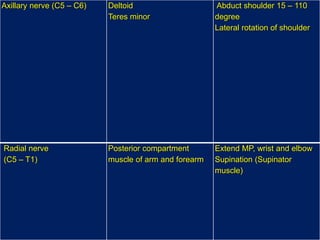
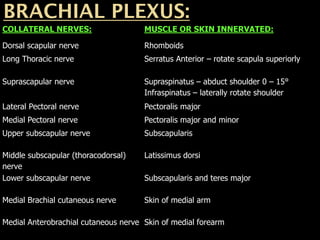
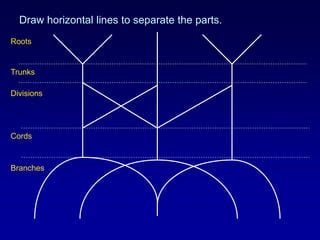
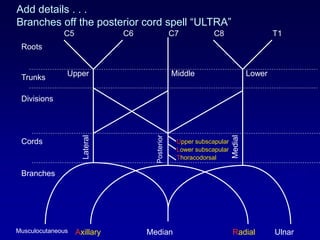
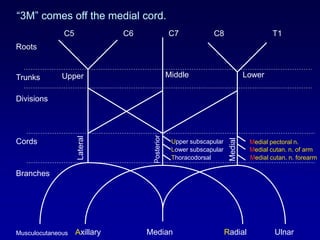
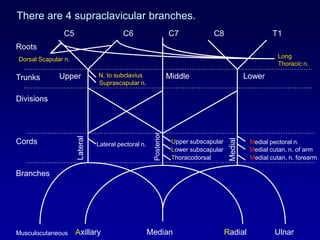
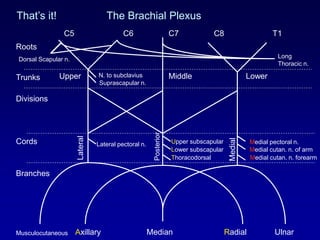
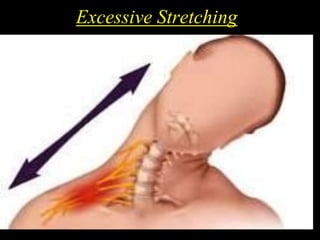
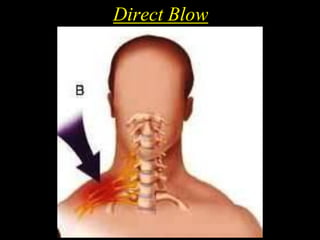
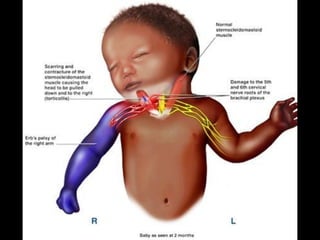
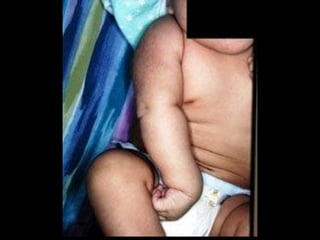
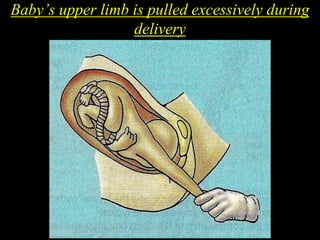
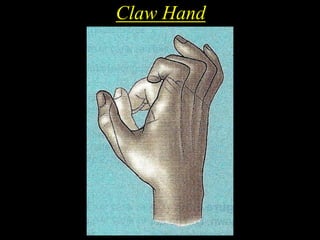
The document discusses the brachial plexus, which is formed by the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5 to T1. It has roots, trunks, divisions, cords, and terminal branches. The roots unite to form three trunks, which each divide into anterior and posterior divisions. The anterior divisions form the lateral and medial cords, and all three posterior divisions form the posterior cord. The terminal branches are the musculocutaneous, median, ulnar, radial, and axillary nerves. The document also discusses the muscles innervated and clinical correlations of injuries to different parts of the brachial plexus.