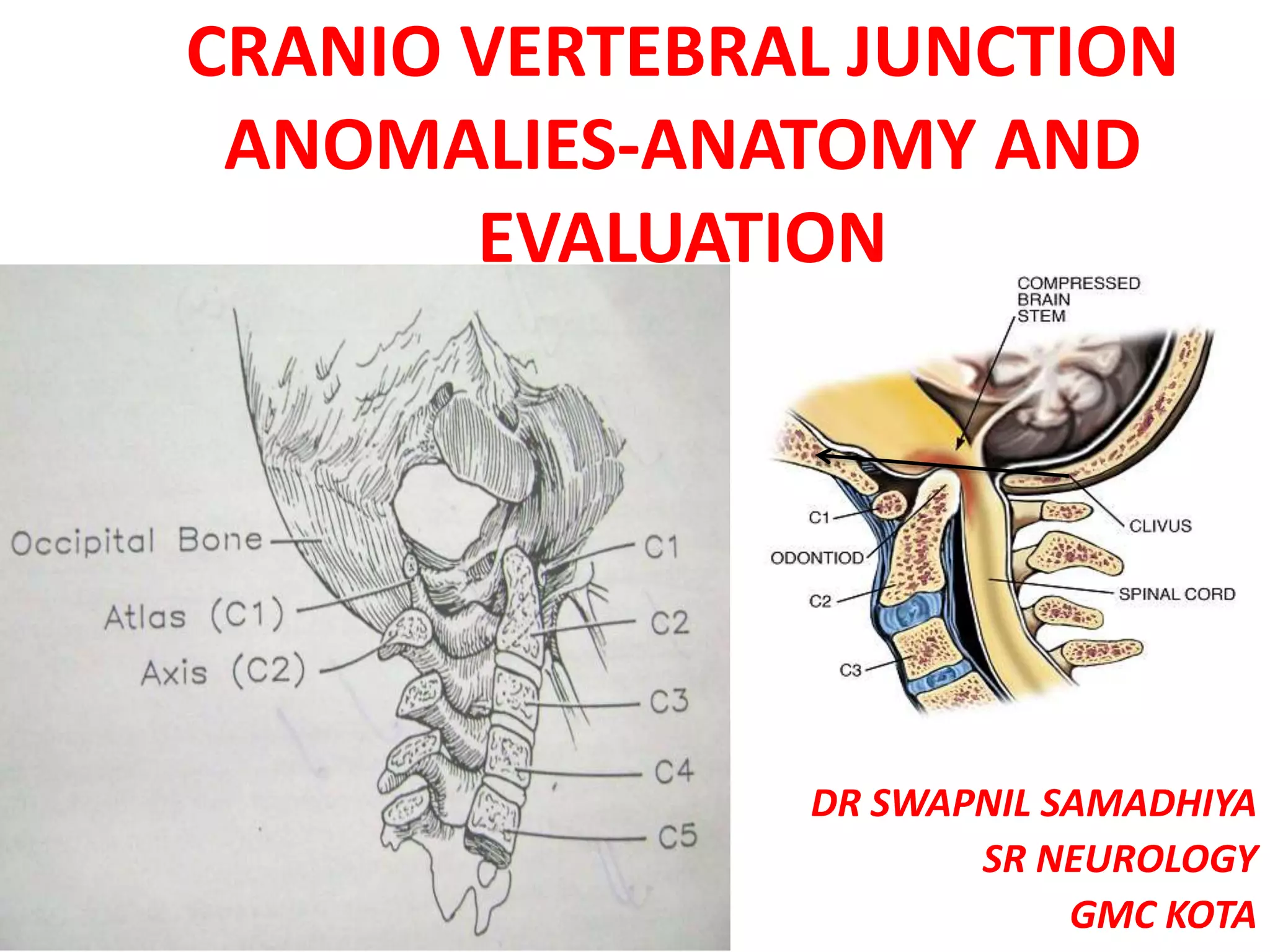
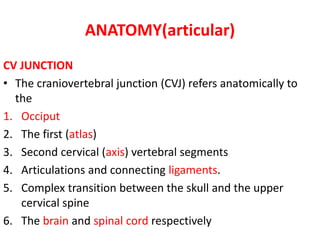
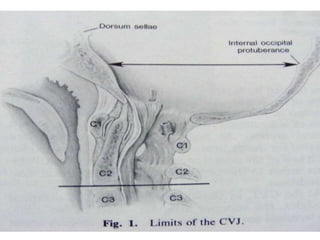
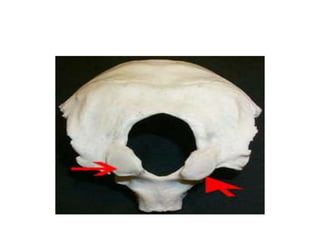
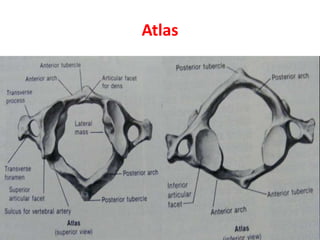
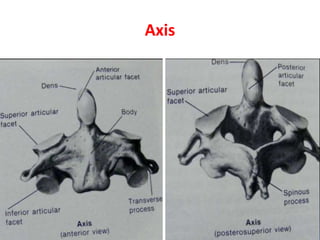
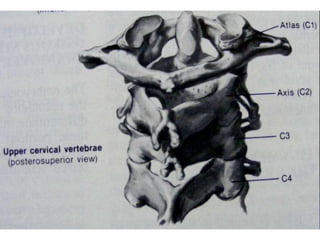
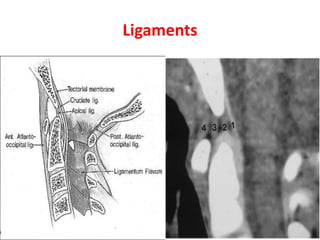
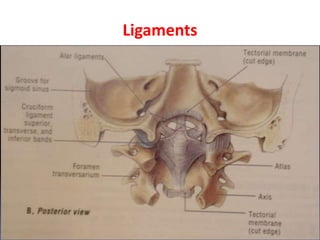
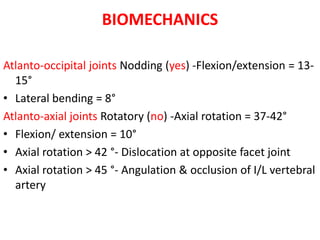
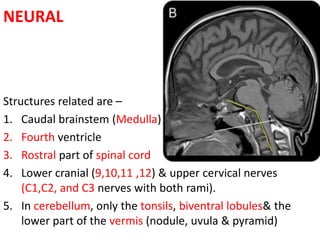
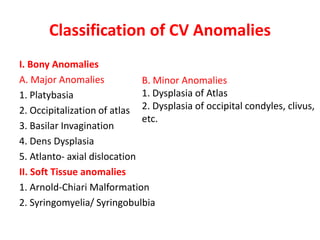
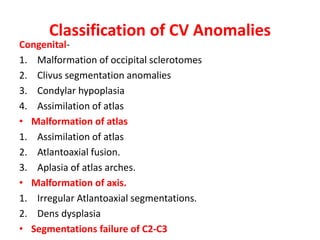
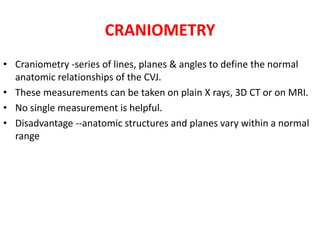
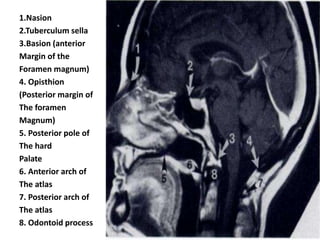
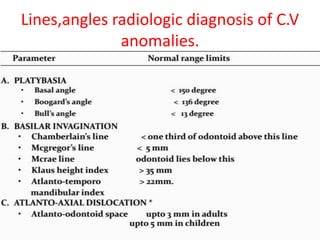
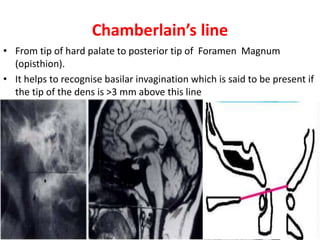
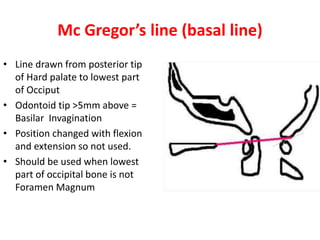
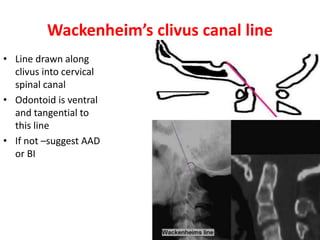
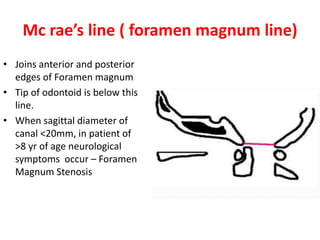
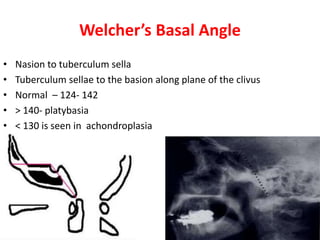
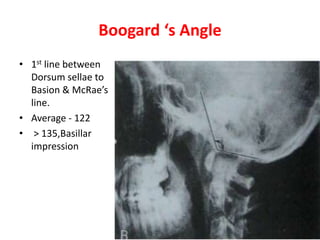
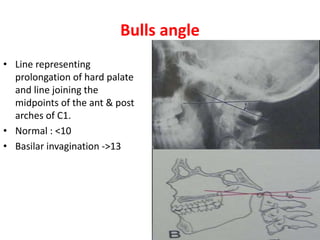
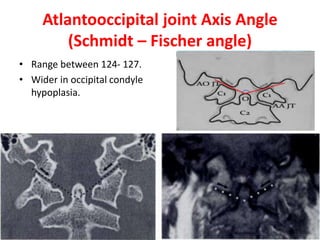
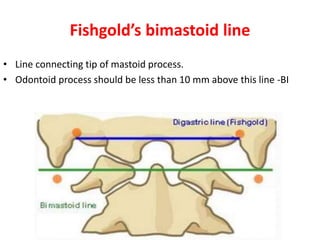
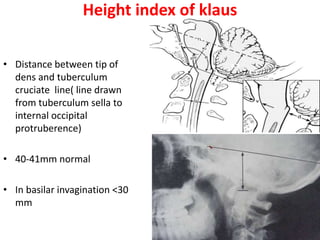
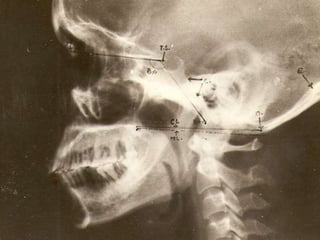
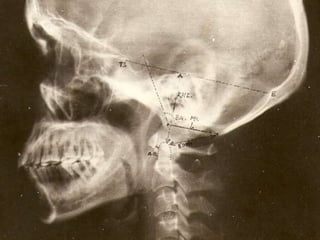
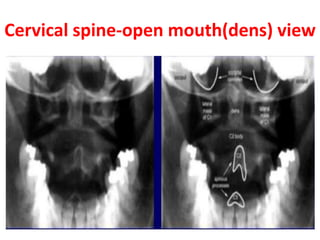
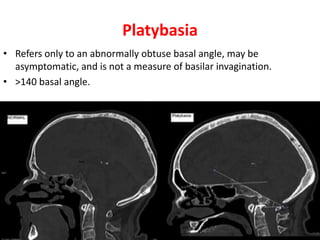
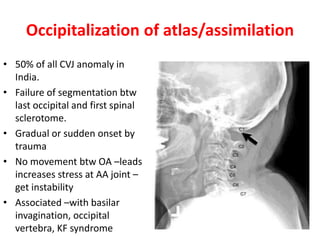
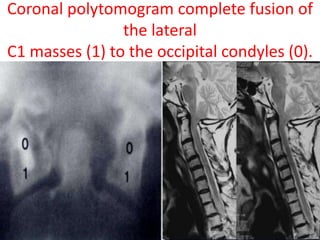
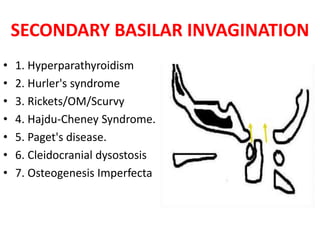
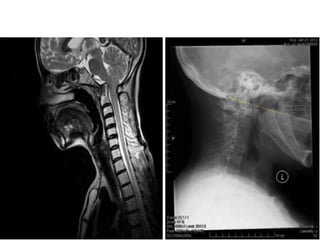
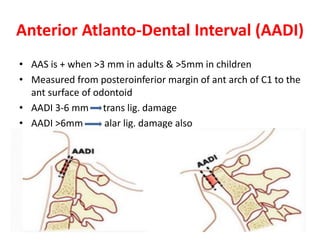
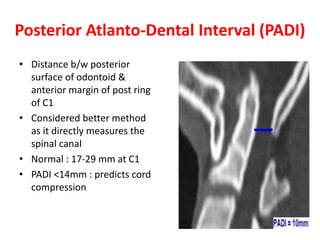
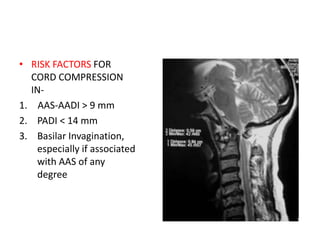
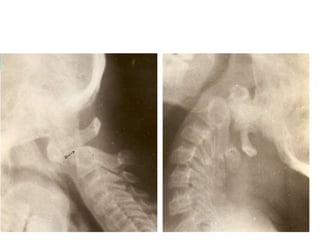
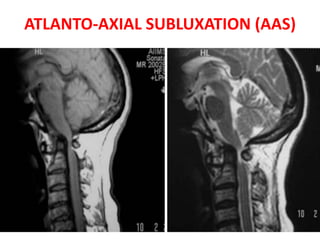
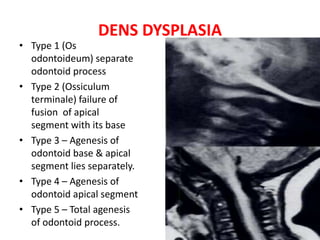
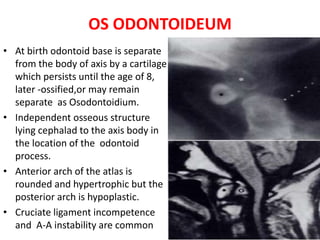
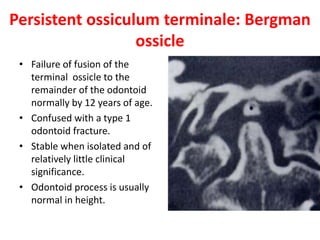
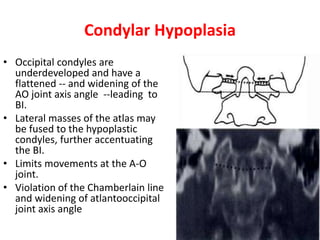
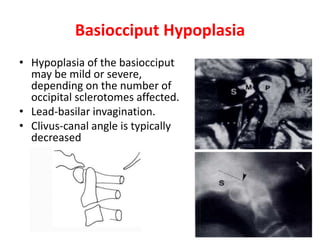
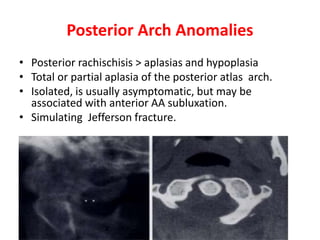
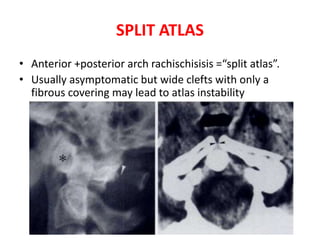
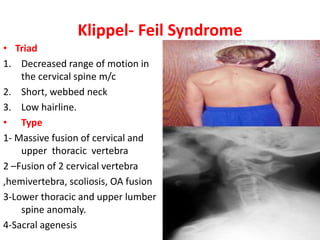
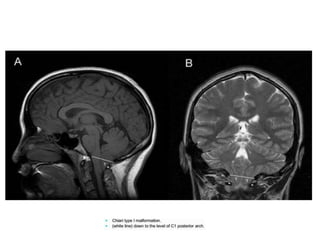
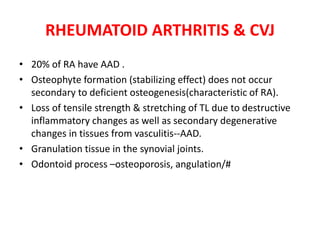
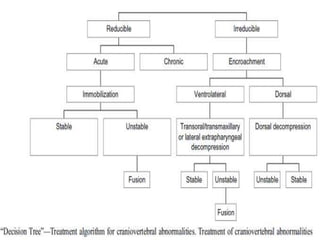
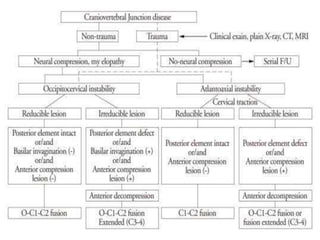
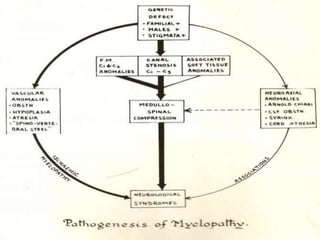
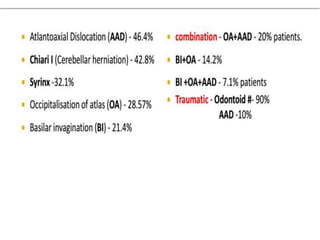
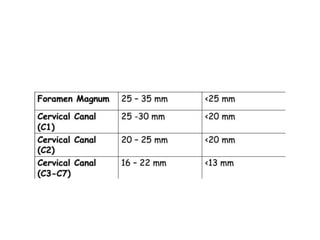
The craniovertebral junction refers to the occiput, atlas, and axis vertebrae and their articulations and ligaments. It is a complex anatomical region forming the transition between the skull and cervical spine. Common craniovertebral junction anomalies include occipitalization of the atlas, basilar invagination, atlantoaxial dislocation, and dens dysplasia. These anomalies can be developmental, post-traumatic, or acquired. Imaging studies including X-rays, CT, MRI are used to classify and evaluate the anomalies. Treatment may involve surgery such as fusion if the anomaly causes spinal cord compression.